Eukaryotic Cells
Animal Cells
Lysosomes
membrane bound packed with enzymes,Acid pH(acid hydrolases),H+ pumps/membrane proteins
hydrolyze(break covalent bonds) molecules
Phagocytosis=cell membrane extends & engulfs foreign cell/food particle,forms vacuole(food) & is digested
Autophagy=membrane surrounds damaged organelle(forms vesicle) outer membrane of vesicle and lysosome fuse and lysosome enzyme digests inner membrane to reuse
Lamin A
MAJOR structure protein that lines the inner surface of the nuclear envelope , affects shape & function of nuclear envelope
Extracellular Matrix
Subtopic
Subtopic
Plant Cells
Cell Wall
multiple layer
Primary=thin & flexible
Middle Lamella:thin layer between primary walls of adjacent cells
Secondary=in SOME cells,added between plasma membrane and primary cell wall
maintains cell shape & protects cell from mechanical damage
Chloroplast
double membrane and membrane sacs(thylakoids)
Granum(thylakoids stacked)
Stroma(internal fluid)
Photosynthesis(converts sunlight/energy--->chemical energy stored in sugar molecules)
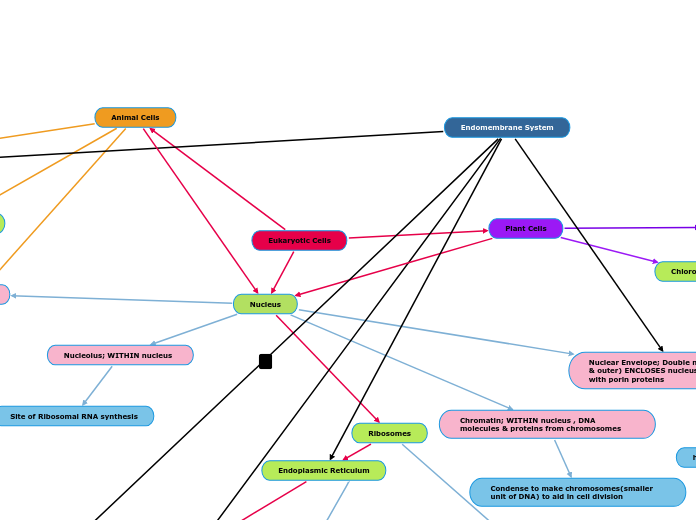
Nucleus
Nuclear Envelope; Double membrane (Inner & outer) ENCLOSES nucleus, & has pores with porin proteins
help transport things in & out of nucleus
Chromatin; WITHIN nucleus , DNA molecules & proteins from chromosomes
Condense to make chromosomes(smaller unit of DNA) to aid in cell division
Ribosomes
Made of ribosomal RNA and protein
Make proteins in 2 places :
In Cytosol= Free ribosomes
Bound to Rough ER or Nuclear Envelope= Bound ribosomes
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Apparatus
Vacoules
Mitochondria
Plasma Membrane
Peroxisomes
Cytoplasm
Specialized metabolic compartment single membrane packed with enzymes
Chemical reaction converts molecules to hydrogen peroxide which is further converted into H2O
Subtopic
Subtopic
Double membrane(inner mem. folds into cristae) , space in the mitochondria called matrix DNA & free ribosomes present in matrix
Matrix=site of reactions involved in cell respiration to make ATP(which makes it the powerhouse)
Large vesicle from ER and golgi, 3 diff types
1.Food 2.Contractile(in freshwater protists) 3.Central(in mature plant cells)
Food vac=formed when cell engulfs food/other particles
Contractile=pump excess water OUT of cell
Central=Serve as storage for inorganic ions like K and Cl
2 Sides
Cis side=Receives vesicles from ER
Trans side=Ships out changed vesicle
Synthesizes,modifies,sorts,and secretes/ship out cell products
more than half of membrane
Smooth=no attached ribosomes
Rough=surface of bound ribosomes
Smooth=makes lipids,metabolizes carbs,detoxifies, & stores calcium ions
Rough=Secretes glycoproteins,distributes transport vesicles,membrane factory
Nucleolus; WITHIN nucleus
Site of Ribosomal RNA synthesis