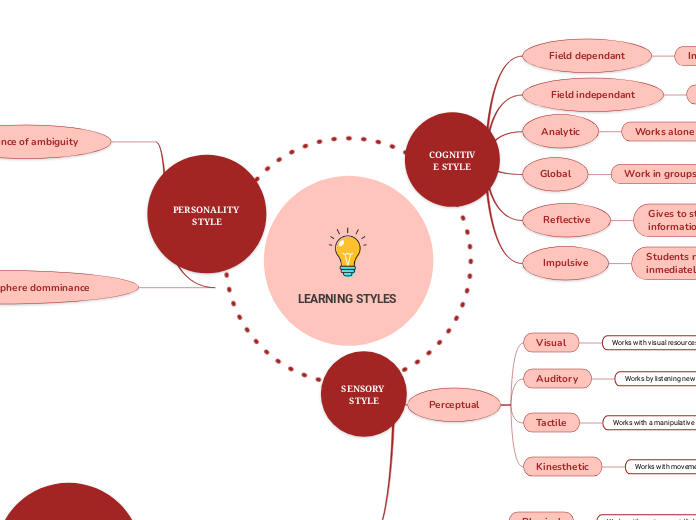
LEARNING STYLES
Bibliographic References:
Nunan, D. (2011). Teaching English to young learners. Anaheim, CA:
Anaheim University Press.
Witkin, H. A., Moore, C. A., Goodenough, D. R., & Cox, P. W. (1977). Field-dependent and field-independent cognitive styles and their educational implications. Review of educational research, 47(1), 1-64.
COGNITIVE STYLE
Field dependant
Information is presented in context.
Example: Students receive the information about Global warming, then, they discuss with other students avbout the topic.
Field independant
Information is teaching step-by-step.
Example: Students solve a puzzle after being explained about a certain topic with new vocabulary and reading a paragraph.
Analytic
Works alone and at their pace.
Example: Students are able to create a simple mindmap about Ecuadorian cultures.
Global
Work in groups.
Example: Students have to listen a short podcast about values. They habe to take notes with the information they heard, then, they join in groups and organize a presentation about the most important value they consider.
Reflective
Gives to students time to process the information.
Example: Students have to make a simple survey in the class, then, analyze the information and make a conclusion.
Impulsive
Students respond to new information inmediately.
Example: Students have to participate in a brainstorm about animlas.
SENSORY STYLE
Perceptual
Visual
Works with visual resources.
Example: Students watch a short video about prepositions.
Auditory
Works by listening new information.
Example: Students listen a song about farm animals.
Tactile
Works with a manipulative resources.
Example: Students have to practice prepositions with objects like a box and a ball.
Kinesthetic
Works with movements related with learning.
Example: Students have to sing a song about directions and move according to the song. (Above, below, right, left.)
Environmental
Physical
Works with environment (light, temperature, furniture)
Example: Students have to make a picture about their favorite hour of the day. It would be about morning, afternoon or night.
Sociological
Refers to relationships.
Example: Stuents try to exchange personal information of their classmates trough short conversations.
PERSONALITY STYLE
Tolerance of ambiguity
Works with many possible correct answers.
Example: Students sollve an test about selecting the incorrect answer .
Right and left hemisphere domminance
Left-brain
visual, analytical, relfective, self-reliant
Example: Write a paragraph about their favorite signature.
Right-brain
Auditory, global, impulsive, interactive
Example: Students have to talk about their favorite instrument.