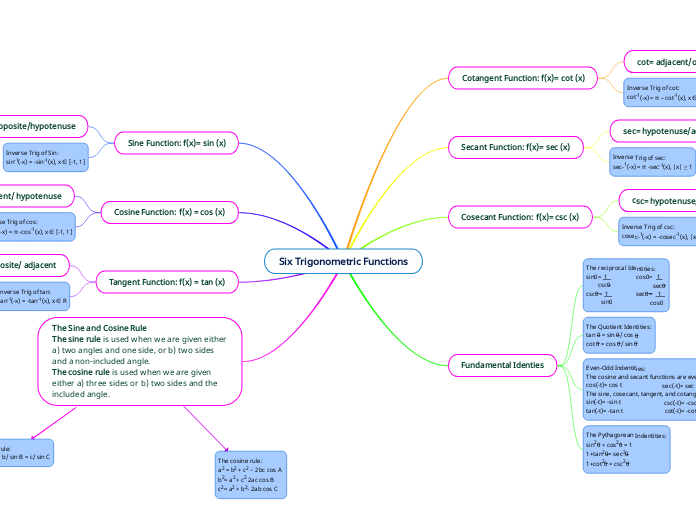
cot= adjacent/opposite
Inverse Trig of cot:
cot-1(-x) = π – cot-1(x), x ∈ R
sec= hypotenuse/adjacent
Inverse Trig of sec:
sec-1(-x) = π -sec-1(x), |x| ≥ 1
csc= hypotenuse/opposite
Inverse Trig of csc:
cosec-1(-x) = -cosec-1(x), |x| ≥ 1
The reciprocal Identities:
sin0= 1 cos0= 1
csc0 sec0
csc0= 1 sec0= 1
sin0 cos0
The Quotient Identities:
tan 0 = sin 0/ cos 0
cot 0 = cos 0/ sin 0
Even-Odd Indentities:
The cosine and secant functions are even.
cos(-t)= cos t sec(-t)= sec t
The sine, cosecant, tangent, and cotangent functions are odd.
sin(-t)= -sin t csc(-t)= -csc t
tan(-t)= -tan t cot(-t)= -cot t
The Pythagorean Indentities:
sin20 + cos20 = 1
1+tan20= sec20
1+cot20 = csc20
sin= opposite/hypotenuse
Inverse Trig of Sin:
sin-1(-x) = -sin-1(x), x ∈ [-1, 1]
cos= adjacent/ hypotenuse
Inverse Trig of cos:
cos-1(-x) = π -cos-1(x), x ∈ [-1, 1]
tan= opposite/ adjacent
Inverse Trig of tan:
tan-1(-x) = -tan-1(x), x ∈ R
The sine rule:
a/ sin A = b/ sin B = c/ sin C