Neuro OSCE
- Will teabag the shit out of you
- That's why God made brains
and scrotums similar in
appearance
- Hx = establishing chronology
+ Site of symptom Psn
- PE = Determining site of lesion
Grouping of signs/symptoms
Cerebellar signs
UMN/LMN
UMN = Pyramidal weakness!!!
- Affects extensors > flexors
- CLONUS IS ALSO AN UMN SIGN
NMJ Probelms (i.e. MG):
- Fatiguability
- Reflexes normal; Tone normal
- Power normal w/ rapid weakening
- Ptosis at the end of the day
- +/- speech dysarthria at the end of the day
Peripheral neuropathy
NB Romberg's = tests sensory ataxia; NOT cerebellar.
Higher function
Neuro hx taking (Ask 1, Think 2)
1. Is a bitch
2. 1 thing to ALWAYS ask:
i. Hand dominance!!!
3. 2 things to ALWAYS think of:
i. Temporal course of illness.
ii. Location of SYMPTOM.
Temporal course (brief overview)
1. Triggers/warnings
i. Triggers: exercise, flashing lights, etc.
ii. Warnings: hallucinations (auditory/visual);
Changes in smell; sensory/motor dysfn, etc
2. Acute onset (mins-hrs):
i. Cerebrovascular: TIA/Isch stroke/Haemorrhage
ii. Seizures
iii. Migraines
3. Subacute (hrs - days):
i. Inflammation (e.g. meningitis, Guillian Barre)
4. Chronic
i. Wks - mths = Tumour
ii. Months - years = Degenerative disorders
5. Disseminated through space and time = MS!!!
6. Don't forget to ask about previous infections
Cardinal symptoms
1. Headache (HA), facial pain, Neck/back pain
2. Cerebrovascular accidents
3. Faints, fits, or funny turns
4. Dizziness/vertigo
5. Vision/hearing/smell
6. Gait
7. Sensory/motor
8. Incontinence
9. Tremor
10. Speech and swallowing
11. Altered cognition
'Neuro Hx overview' in hyperlink
Headaches, neck pain
SOCRATES
CBVA
General temporal course:
Acute (minutes)
Gross localization:
Posterior headache = posterior circulation
Anterior headache = anterior circulation
Broca's = Frontal lobe = Expressive dysphasia
Wernicke's = Temporal = Receptive dysphasia
Haemorrhage
Ischaemia
TIA
- Stroke like syndromes
- Spontaneous resolution w/in 24h
- Amaurosis fugax (transient U/L blindness)
Strokes:
- FOCAL LESIONS
Lacunar
MCA
ACA
Brainstem
Faints, Fits, Funny turns
Don't need to open this shit for OSCE.
Just look at questions in hyperlink.
Dizziness/Vertigo:
Does it come on with HEAD MOVEMENTS?
Is there HEARING LOSS?
Persistent or intermittent?
Vision
- Diploplia
- Blurred vision
- Photophobia
- Visual loss
Which eye?
Which field?
Acute? Gradual?
Preceding event?
Deafness
Acute? Gradual?
U/L, B/L?
+ Pain? + Dizziness?
Changes in facial expression (CN 7)?
Changes in taste?
Preceding ear infection?
Hx trauma?
Gait
- Occurs in the dark (sensory ataxia)?
- Occurs with eyes open (cerebellar)?
- Disappears when running (Pakinsonism)?
- Trouble initiating gait (Parkinsonism)?
- Dance-like movements superimposed on gait (Chorea)?
- Unable to lift toe while walking (Foot drop)?
- Always obtain fall hx
TO LEARN GAIT, SWALLOW WHATEVER MORALS YOU THINK YOU MAY HAVE, & PRACTICE WALKING THEM IN FRONT OF THE MIRROR. LAUGH AT YOUR ABSURDITY.
Motor:
- Pure motor?
- Mixed?
- Other associations?
- Location of symptoms?
- Severity?
- Timing, onset?
- Worsening progression?
- Recurring bouts w/ remission? (i.e. MS)
- What is the biggest problem with movement?
- MG = Fatiguability with repeated movement
- McArdle's = Improves w/ continued movement
- Parkinson =Difficulty initiating movement (rigidity)
- UMN/LMN = Decreased strength = UMN/LMN
- Cerebellar = Clumsy hand dysarthria
- Frontal = X complex sequence of actions
Sensory:
- Pure sensory?
- Mixed?
- Fine touch (DCML)?
- Pain/Temperature (ST)?
- Neuropathic pain
Dyskinesia:
- At rest? Or with movement?
- Description of tremor
- Resting = Parkinson's
- Intentional = Cerebellar
- At rest & on movement = Benign essential tremor
N.B Intentional tremor = deviation from intended trajectory of motion in a HORIZONTAL PLANE.
N.B BET is relieved by alcohol. Pts @ risk of becoming alcoholic.
Speech:
Dysarthria = X Articulation
Dysphasia = Receptive/Expressive
Dysphonia = Damage to vocal cords
Hyperlink not relevant to exam prep
Random bits and bobs for MS
- Disseminated through space and time
- Optic neuritis (pain on moving eye; loss of (color) vision)
- INO
- Acute bouts (wks) interspersed w. remission (mths-yrs)
- Permanent loss in function with each attack
- Urthoff's phenomenon (heat intolerance w exercise)
- Lhemitte's sign (electrical tingling on back of neck when neck is bent)
- MS = loads of positive on motor ex.
Lower limb
Is almost identical to UL.
Only key differences will be listed.
1. WIPE
Place, time, person, handedness
2. General observation
PT TO BE SUPINE
Expose the pt if wearing long pants
3. Motor
LL specific
- Tone
- Babinski reflex
- Coordination.
- Gait
Tone
Motor
Coordination/Gait
4. Sensory
Thank the patient.
Wash hands.
Summarize findings
Further investigations
Cranial Nerves
CN 1
General observation
- Nasal polyps?
Examination
Smell alcohol wipes
CN 2
General observation
- Glasses on bedside?
- Mydriasis (dilation of pupils)?
- Miosis (constriction)?
- Aniscora (unequal pupillary size)?
- Lacrimation of eyes?
ALWAYS BE EYE-TO-EYE WITH THE PT.
Cover opposite eye as pt.
Visual acuity:
- Mention that you'd use a Snellen chart
Visual fields
Position: Arm length away from pt; 'eye-to-eye' level.
Pt. covers R eye, you cover L. Swap.
Don't apply pressure on your eye.
Keep your eyes on the bridge of my nose
i. Test each eye separately for:
a. Peripheral vision (white pin)
b. Central vision (red pin)
ii. Test both eyes for inattention
Mention that you'd do a fundoscopy
CN 2, 3 (Pupillary reflexes)
To be done in these OSCE's:
i. CN 2 test
ii. CN 3, 4, 6 test
Afferent limb = CN 2
Efferent limb = CN 3
Don't forget to DIM THE LIGHTS
Direct response:
Illuminated pupil constricts
Consensual response:
Non-illuminated pupil constricts synchronously.
Swinging light test (afferent pupillary defect
Normal = Both eyes constrict when one is illuminated
Both eyes relax a little while light is being swung
RAPD = B/L dilatatn when light is swung to AFFECTED eye
+ Direct response
+ IN PT'S W/ MS & OPTIC NEURITIS!!!!!
CAPD = NO direct response on affected eye
Site of lesion = OPTIC NERVE (N --> Chiasm --> Tract)
Test accomodation
Basically get pt to go 'cross-eyed'
Normal = Convergence + Constriction (miosis)
Site of lesion = OCCIPITAL LOBE (visual cx)
CN 3, 4, 6
General observation
- Same as CN2
- 1 Eye looking down and out (CN 3 lesion)?
Examination
- Pursuit
- Saccades
NB For pursuit and saccades, do horizontal movements first, then vertical
- Eye movements (H)
'Do not move your head, just your eyes.'
Pursuit:
- B/L = Age, alcohol, antipsychotics
- U/L = ALWAYS pathological
Lesion ~ Frontal lobe/Pons
Saccades (PD):
- Look@myfinger, look@mythumb
- This is basically finger-nose test for the eyes.
Lesion ~ Occipital lobe
Eye movements
- 'Tell me if you notice any visual abnormalities.'
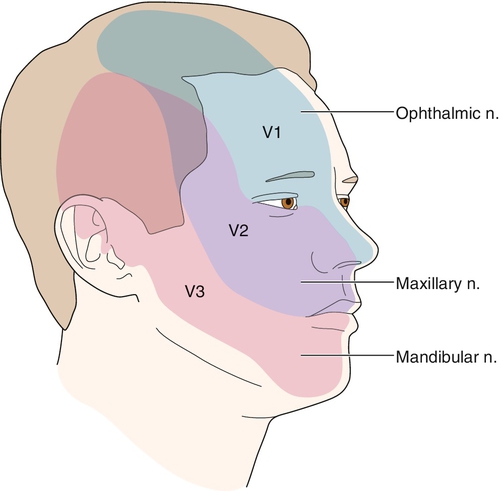
CN 5 - V1, V2, V3
Sensory - Cotton wool
Pain - Pin
Temp - Tuning fork
NB. Always establish
a base of reference for
the pt by 1st applying
stimuli to be tested
on the pt's sternum.
CN 5 - V3 motor
- Clench teeth: Masseter
Temporalis
- Open mouth: Deviates to
side of lesion
- OFFER TO DO JAW JERK
CN 5, 7 (Corneal reflex)
OFFER to do in:
i. CN 5 test
ii. CN 7 test
Afferent limb: V1
Efferent limb: VII
CN 7
General observation:
- Widening of the opening b/w eyelids?
- Flattening of nasolabial fold?
- Asymmetry?
- Involuntary movements?
- Drooling?
- Dry eyes?
- Ask about dysphasia/dysphagia
- Ask about taste
- Ask about hyperacusis
OFFER TO TEST TASTE
Then test motor:
- Wrinkle forehead
- Squeeze eyes
- Puff out cheeks
- Bare your teeth
- Squeeze lips together
- Whistle
CN 8
Ask about tinnitus/vertigo
i.e. make sure pt is comfortable
Hearing:
- Mask & whisper
- Rhinne's (mastoid --> air)
- Weber's (Teletubby)
Balance:
- Per testing of cerebellar signs (i.e. nystagmus)
- Gait/Truncal ataxia
- Offer to do Hallpike
Rinne/Weber interpretation
CN 9, 10
- Highly unlikely to be tested.
- Palate elevation:
If + U/L weakness, deviates TO normal side
- Gag reflex
- 'KA KA KA' - palatal sounds
- 'GO GO GO' - guttural
- 'AAAAHHHHHH'
CN 11
General observation
Asymmetry?
Atrophy?
Shoulders on same level?
Examination
- SCM (U/L) - 'Turn your head to the left/right.'
Passive, then active
Always palpate musc belly
- SCM (B/L) - 'Flex your neck down against my palm'
- #shrugs - Passive; then active
CN 12
General observation
Patient to open mouth
Fasciculations? Atrophy?
i. Stick tongue out - deviates TO weak side
ii. Push tongue against cheek and feel
Hodgepodge of relevant information for the motor/sensory examination
Power/Reflex scoring
Types of tone
Sensory Dermatomes
UL
LL
Motor innervation

Upper limb
1. WIPE
Be sure to check time, place, person.
And FFS, ALWAYS ASK ABOUT HANDEDNESS
2. General observation:
- Surroundings
- Patient (general)
- Patient (neuro specific)
- Pronator drift
PT TO BE SEATED!
3. Motor
- Fasciculations (pt to relax limb)
- Tone (see note)
- Power (Brotip: Get pt. to hold pose in link. That way you
can test all muscles above hand in one go.)
- Reflexes
- Co-ordination
i. Finger/nose
Cerebellar = intentional tremor, dysmetria
ii. Dysdiadochokinesia (cerebellar, PD)
iii. Rebound ("Please lift your arm up quickly from your
sides." cerebellar HYPOtonia = overshoot)
Move from arm to arm for each of the above.
4. Sensory
Thank the Patient.
Wash your nasty hands.
Summarize findings
Further investigations:
- Full neurological exam
- CT/MRI if indicated