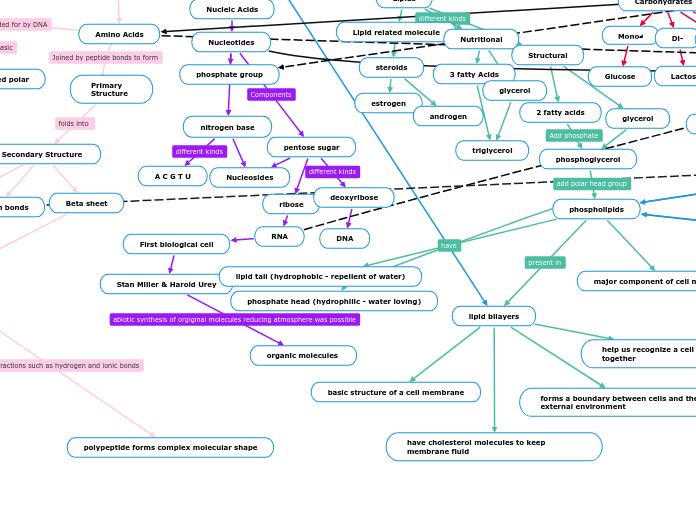
Amino Acids
Primary Structure
Secondary Structure
Beta sheet
Alpha Helix
Tertiary Structure
Domains
Quartenary Structure
non-covalent bonds
one or more polypeptide is present, form 3D shape
polypeptide forms complex molecular shape
motifs
hydrogen bonds
R groups
non-polar
uncharged polar
charged polar
Nucleotides
phosphate group
nitrogen base
Nucleosides
A C G T U
pentose sugar
ribose
RNA
First biological cell
Stan Miller & Harold Urey
organic molecules
deoxyribose
DNA
Lipid related molecule
steroids
estrogen
androgen
Nutritional
3 fatty Acids
triglycerol
glycerol
Structural
2 fatty acids
phosphoglycerol
phospholipids
lipid bilayers
have cholesterol molecules to keep membrane fluid
help us recognize a cell and holds cells together
basic structure of a cell membrane
forms a boundary between cells and their external environment
major component of cell membrane
phosphate head (hydrophilic - water loving)
lipid tail (hydrophobic - repellent of water)
glycerol
Mono-^
Glucose
Di-
Lactose
Oligo-
Poly-
Starches
amylose
amylopectin
Cellulose
Glycosaminoglycans
Chitin
low to high concentration
polar
nonpolar
interactes with vesicles
phospholipid bilayer
intraceulllar
extracellular
bilayer v hydro
head hydrophobic
tail hydrophilic
high water potential
low solute
equal water potential
equal solute
low water potential
high solute
receptor proteins ^
signal transduction
glycoprotein
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
cell recognition
Concentration gradients
no
attributes
Body
shape
basic
coccus; spherical
basilius; rod shaped
spiral
additional
pleomorphic
unusual
no fixed shape (chaotic)
size
diameter
length
Inner structure
ribosomes
cytoplasm
resources
nuclear area(nucleoid)
double strand DNA
cell wall- surrounding and protecting the cell
inner wall
outer wall
phili
flagella- helps bacteria move
peptidoglycan- provides support
gram-positive
gram-negative
inclusions
lipid inclusion
sulfur granules
metachromatic granules
polysacchaide
carboxysomes
magnetosomes
gas vacuoles
endospore
produces copy of its chromosome
survives in rough conditions
extremophiles
halophiles
live in high saline enviroments
thermophiles
thrive in hot enviroments
nuclear envelope
membrane organelles
a small molecule of DNA that can reproduce independently
cell wall
structure &. strength for cell
chloroplast
plastid
photosynthesis
central vaculoes
a respiratory for inorganic ions (potassium &' chloride)
nucleus
chromosomes
DNA
carry genetic information
cytoplasm
nutrients
shape of cell
cell movement
nuclear envelope (double mem.)
nuclear pores
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
smooth ER
lacks ribosomes attached to it
rough ER
surface is filled with ribosomes
powerhouse of the cell
food vacuoles
when cells engulf food or other particles
contractile vacuoles
many freshwater protists
pumps excess water of cells
packed with enzymes
target cells that receive the signal molecule
membrane receptor
polar
large
can't diffuse through plasma membrane
embedded in membrane
signal molecule
needs help of other molecule inside cells
G-protein
signal molecule binds to g-protein coupled receptor (GPCR)
when binded the shape of GPCR changes
allows g-protein to bind to altered shape
GDP is then replaced by GTP on g-protein
g-protein is now activated
can activate enzyme nearby
able to remove a phosphate group
once it activates an enzyme it removes phosphate group from GTP and goes back to GDP
inactive
active
tyrosine kinase receptor
made of 2 polypeptides
dimerize when signal molecule is bound to each polypeptide
polypeptide has ability to function as a kinase
is an enzyme that adds phosphate groups
each polypeptide takes phosphate groups from ATP &' adds it to other polypeptides
now activated, it can now intercact with other proteins to get a response from the cell
ATP
Cellular Respiration
Electron Carriers
NAD+
Electron Transport Chain
Sythnesis ATP
Glycolysis
Pyruvate
occurs in the cytoplasm, outside mitochondria
breaks down glucose into 2 molecules of pyruvate
Hexokinase transfers phosphate group from ATP to glucose.
Phosphfructokinase transfers a phospahte group from ATP to opposite end of sugar investing 2nd molecule of ATP.
FADH2
Citric Cycle
Oxaloacetate
combining the two-carbon acetyl group with a four-carbon oxaloacetate molecule to form a six-carbon molecule of citrate
Citrate
citrate is converted into its isomer
Isocitrate
regulates the speed at which the citrate isomer isocitrate loses a carbon to form the five-carbon molecule α-ketoglutarate.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
ETC
pump H+ against concentration gradient in the intermembrane space
forms water
Chemiosmosis
H+ gradient is used to add an inorganic phosphate (Pi) to ADP to form ATP.
Photosynthesis
H2O splits to provide electrons and protons, O2 is released, NADP+ reduced to NADPH
ATP
PSI (happens second)
700 nm
PS II (happens first)
680 nm
Calvin Cycle
needed to reduce CO2
intracellular membrane
diffuse directly through lipid bilayer
nonpolar
steroid hormones (aldosterone)
passes through plasma membrane
aldosterone binds to receptor protein activating it
hormone receptor complex enters nucleus &' binds to specific gene
bound protein acts as a transcript factor &' stimulates the transcripts of the gene into mRNA
mRNA is translated into a specific gene
molecule released by a cell which is received by another cell
transduction
inactive g protein
active g protein (10 to the 2 molecules)
Inactive adenylyl cyclase
Active adenylyl cyclase (102)
ATP
Cyclic AMP (104)
Inactive protein kinase A
Active protein kinase A (104)
Inactive phosphorylase kinase
Active phosphorylase kinase (105)
inactive glycogen phosphorylase
Active glycogen phosphorylase (106)
cAMP can activate an enzyme called protein kinase A
This allows the same cAMP second messenger to produce different responses in different contexts
adenylyl cyclase converts ATP into cAMP
Helicase
DNA Primase
DNA Polymerese III
Okazaki fragments
Ligase
Histones
ORI C
Cell division
Double Helix
Sperate Strands
New Strands
A T C G
A T C U
monomer
DNA
Deoxyribose
Nucleobase
MRNA
Ribose
Eukaryote
nucleus
pre-mRNA
RNA polymerase II
transcription/translation
5'-3'
5' CAP
introns/exons
RNA Splicing
Spliceosomes
RNA + protiens
Okasaki fragments
ligase
3' PolyA Tail
polyA polymerase
AAUAAA
Gene Expression
Proximal
sequences in DNA
Transcription factors
Distal
enhancers
close/far from gene
transcription factors
H1, H2, H2B, H3, H4
activator
repressors
Prokaryote
cytoplasam
RNA Polymerase
mRNA
5'-3'
transcription/translation
Gene Expression
operon
activator (positive)
LAC operon
permease
LAC Y
B-galactosidase
glucose
galatose
LAC Z
transacetylase
LAC A
RNAP
CAP
CAMP
repressor (negative)
RNA polymerase
Initiation
RNA polymerase binds to promoter
Elongation
unwinds DNA, elongating RNA transcript
Termination
RNA transcript released, polymerase detaches
Initiation
brings together mRNA
small ribosome subunit
initiator tRNA carrying Met or F-Met then scans the mRNA to find start codon
F-Met is found in Eukaryotes
Eukaryotes
80s ribosomes
translation &' transcription occur at different times
mRNA is in nucleus
Met is found in Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes
70s ribosomes
translation &' transcription occur at the same time
mRNA is in cytoplasm
large ribosome subunit
joins complex to form a translation intiation complex
Elongation
next tRNA carrying correct amino acid comes to A site
a peptide bond forms between 2 amino acids
peptidyl transferase
tRNA that is now empty is in P site
moves to E site to be released
tRNA from A site moves to P site &' a new tRNA comes to A site
E site
exit site
discharged tRNAs leave the ribosome
P site
peptidyl-tRNA binding site
hold tRNA that carries the growing polypeptide chain
A site
aminoacyl-tRNA binding site
does correct match between a tRNA &' amino acid
a chain of amino acids attached
holds tRNA that carries the next amino acid to be added to the chain
Termination
once stop codon reaches A site
NO tRNA responds to a stop codon
a release factor sits in the A site
breaks up the complex stopping translation
GTP driven process
enzymes
ribosomes
composed of proteins &' RNA
made of 2 parts/subunits
large
come together during translation of mRNA
small
golgi
secretory vesicles
lysosomes available for fusion
transport vesicles carry proteins
plasma membrane
secretion
plasma membrane expands
proteins secreted from cell by exocytosis
SRP binds signal peptide
SRP binds to receptor protein
SRP leaves, polypeptide synthesis resumes
signal peptide cleaved by enzyme
completed polypeptide leaves the ribosome
at final conformation
mitochondria
chloroplast
peroxisomes
nucleus