Ballance sheets
Owners equity
Net worth LEFT OVER
Own - owe = left over
Assets - Liabilities = networth
Liabilities (bad)
Debts OWED buy the business
EXAMPLE bills not paid yet, loans, taxes
Assets (good)
Anything OWNED that has $ value
EXAMPLE stocks, cash
Intro to balance sheet
formal financial statement shows what is owned, owed & networth
shows a financial picture as of a CERTAIN DATE
income statments
Formal financial statement
Shows how much profit or loss the business made over a period of time.
Shows a sheet of the profit or loss over time.
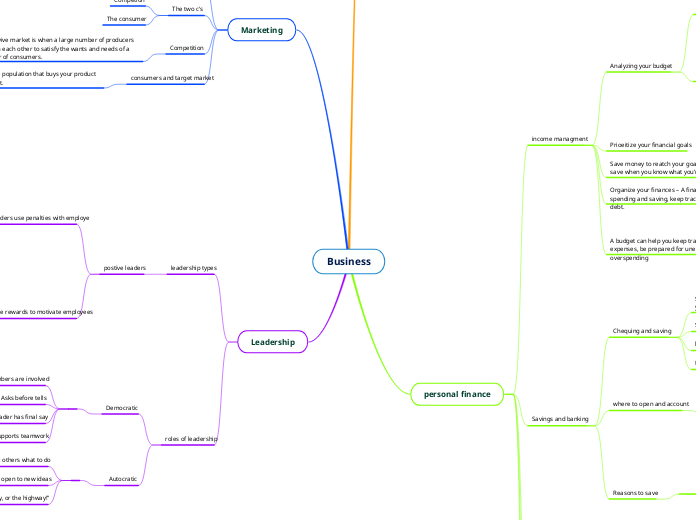
income managment
Analyzing your budget
Cut spending Making a small changes can add up to big savings
5 Questions to ask yourself
Do you eat out a lot? Could you cook more of your meals at home?
Do you buy coffee on the way to work each day? Could you briring coffee from home?
Do you pay a lot of fees for a cell phone? Could you get a cheaper plan? Do you still have a landline? WHY?
Could you cut back on cable or satellite service?
Do you spend a lot on gas for your car? Could you drive less?
Prioeitize your financial goals
Save money to reatch your goals – You may find it easier to save when you know what you’re saving for.
Organize your finances – A financial plan can help you balance spending and saving, keep track of expenses and manage debt.
A budget can help you keep track of your income and expenses, be prepared for unexpected expenses and avoid overspending
components of a budget
REVENUE Income after taxes (YOUR NET, NOT GROSS)
EXPENSES Fixed monthly expenses Variable expenses Occasional expenses
Budget surplus vs deficit
If your revenue>expanses you have a net income (like accounting)This means you have money leftover - a Budget surplus
If you spend more than you earn, you have a budget deficit
Savings and banking
Chequing and saving
Savings and chequing accounts are safe place to put money you plan to spend soon
Saving accounts – allow you to set money aside
build funds for your education
for emergencies, save for a large purchase or
where to open and account
You can open an account at any of these financial institutions. They provide the same kinds of banking services for chequing and savings accounts, but they are run differently
Banks and trust companies – make money for the people who own their shares.
Credit unions – owned and run by the members who bank there. They may charge a refundable membership fee to join.
Reasons to save
FINANCIAL SECURITY
Emergency funds
Buy a car
Buy a house
Pay for your kids to go to school
Retirement
Cheques
Before writing a cheque you must have a chequing account
A cheque is only valid for 6 months
On a cheque you need to (1) write your name (2) write the amount of money you want to pay and (3) the date
payroll and decoctions
By LAW, your employer must take each of the 3 deductions off of your paycheque and send the money to the government.
Health Care, Jails, Education, Roads, Welfare/Social Assistance
Government deductions pay for public services such as Police
CPP: Canada Pension Plan
- anyone who works & is over 18 years old contributes to CPP
- when you retire, become disabled, or should your spouse pass away, you can receive CPPEI:
El Employment Insurance
pay into it from EVERY paycheque, even if you are not yet 18.
interest
The rule of 72
Divide the rule number (72) by the annual interest rate (R) to find out the approximate time (T) required for doubling
The rule of 72 is useful for savings goals, retirment goals and comparing investments
The four p's
product, price, promtion, place
The two c's
Competion
The consumer
Competition
The competivive market is when a large number of producers compete with each other to satisfy the wants and needs of a large number of consumers.
Market share is the percentage of the market that a company or brand has.
consumers and target market
The specific segment of the population that buys your product is called your Target market.
leadership types
postive leaders
Negative leaders use penalties with employe
These leaders act domineering and superior with people Negative penalties include:
Days off without pay
repimanding in front of others
assigning unpleasant job tasks
Positive leaders use rewards to motivate employees
independence
development opportunities
acknowledgement
raises, bounses
time off
roles of leadership
Democratic
All members are involved
Asks before tells
Leader has final say
Supports teamwork
Autocratic
Tell others what to do
Not open to new ideas
“It’s my way, or the highway!”