Elementary Mathematics
Adding/Subtracting Integers
Chip Model
Charged-Field Model
Number-Line Model
Pattern Model
Missing Addend Approach
Multiplication/Division
of Integers
Chip Model
Charged-Field Model
Pattern Model for Mult.
Def. for Division
Scientific Notation
Small #s
Large #s

Mental Computation w/ Decimals
Breaking and Bridging
Using Compatible #s
Making Compatible #s
Balancing w/ Decimals in Division
Balancing w/ Decimals in Subtraction
Converting Decimals,
Fractions, and Percentages
Decimals
Fractions
Percentages
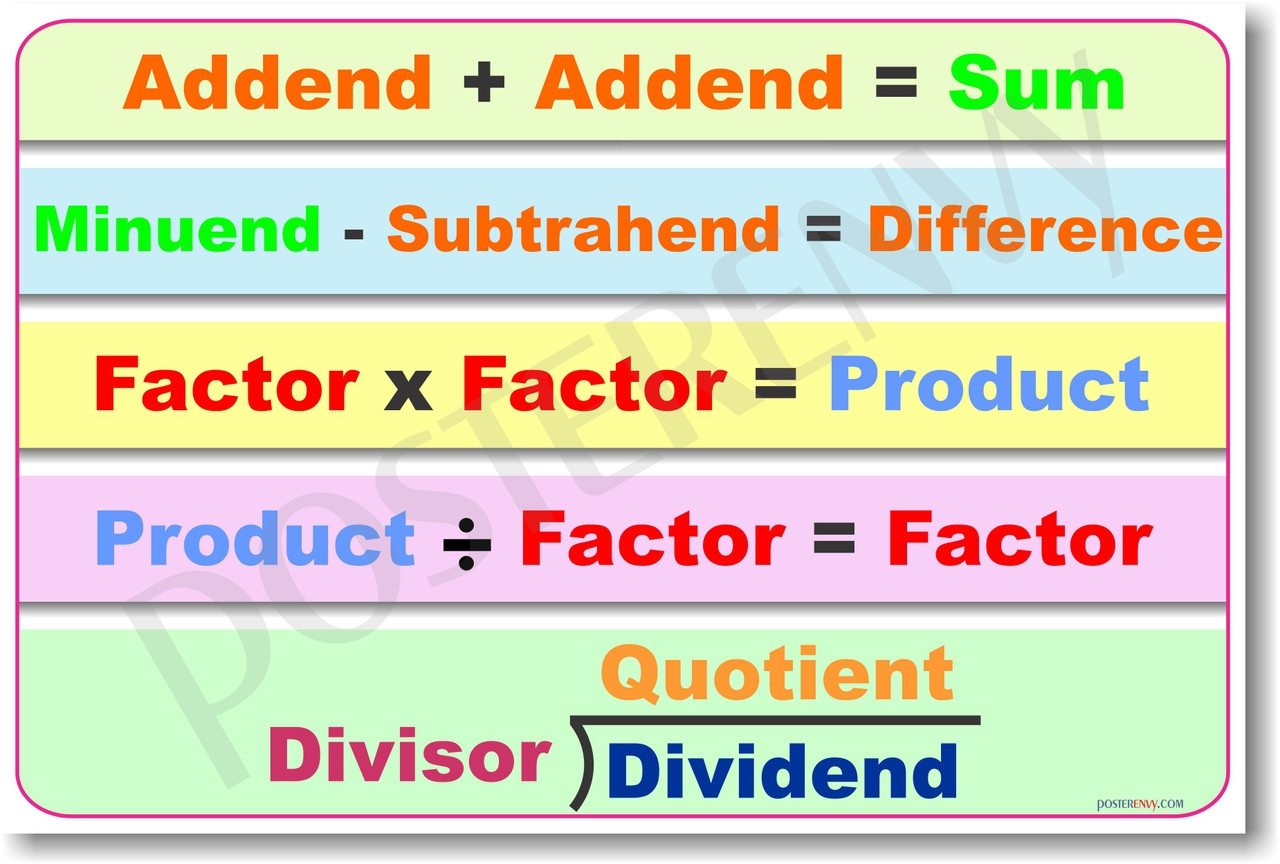
Operations with
Whole Numbers
Addition
Counting on
Set model
Number-line model
Making 10
Counting back
Subtraction
Take-Away Model
Missing Addend Model
Comparison Model
Number-line model
Multiplication
Repeated Addition Model
Array and Area Model
Cartesian-Product Model
Division
Set Model
Missing-Factor Model
Repeated Subtraction Model
Additive Inverse
Expression
Number
Factoring
Difference of squares
Common factors

Numeration Systems
Hindu-Arabic numerals
Roman numerals
Egyptian
Mayan
Babylonian
Tally
Divisibility Rules

Rules
Greatest Common Divisor
Colored Rods Method
Factor Tree Method
Number Line Method
Least Common Multiple
Prime Factorization Method
Number Line Method
Factor Tree Method
Division-by-Primes Method