English grammar
English words have few endings that could help us to understand how words connect into sentences. At the same time, English words have many meanings. Together, these two problems present the most difficulty for language learners, in many cases making it difficult to understand the meanings and functions of words in sentences.Английские слова имеют мало окончаний, которые могли бы нам помочь понять, как слова соединяются в предложения. В то же время, английские слова имеют много значений. Вместе, эти две проблемы представляют наибольшую трудность для изучающих язык, во многих случаях затрудняя понимание значений и функций слов в предложениях.Grammar helps us to understand how English works. Grammar brings order, logic, and clarity into the process of studying English. It specifies how sentences are built to make sense, identifies the meanings of individual words in a sentence and explains relationships between them, and gives you a set of rules for speaking and writing.Careful study of typical grammatical structures helps us to understand how meanings are created in English, and the ability to use such structures correctly and confidently is a huge step on the road to effective communication in English.
a
Articles
Using ArticlesWhat is an article? Basically, an article is an adjective. Like adjectives, articles modify nouns.English has two articles: the and a/an. The is used to refer to specific or particular nouns; a/an is used to modify non-specific or non-particular nouns. We call the the definite article and a/an the indefinite article.the = definite articlea/an = indefinite articleFor example, if I say, "Let's read the book," I mean a specific book. If I say, "Let's read a book," I mean any book rather than a specific book.Here's another way to explain it: The is used to refer to a specific or particular member of a group. For example, "I just saw the most popular movie of the year." There are many movies, but only one particular movie is the most popular. Therefore, we use the."A/an" is used to refer to a non-specific or non-particular member of the group. For example, "I would like to go see a movie." Here, we're not talking about a specific movie. We're talking about any movie. There are many movies, and I want to see any movie. I don't have a specific one in mind.Let's look at each kind of article a little more closely.
Articles-a,an,the

Articles in grammar, useful rules

Types of articles

ss
Verb TensesVerbs come in three tenses: past, present, and future. The past is used to describe things that have already happened (e.g., earlier in the day, yesterday, last week, three years ago). The present tense is used to describe things that are happening right now, or things that are continuous. The future tense describes things that have yet to happen (e.g., later, tomorrow, next week, next year, three years from now).
Top 100 verbs in English

English irregular verbs
Action verbs
English tenses
Часи в англійській мові – це достатньо об’ємна частина усієї граматики, яка налічує 12 часових форм, та ще чотири додаткові групи Future in the Past, які наведені нижче в таблицях. Вони поділяються на чотири групи та чотири види часів.Групи часів:Види часів:Минулий.Теперішній.Майбутній.Майбутній в минулому.Неозначений.Тривалий.Доконаний.Доконаний тривалий.
Rules
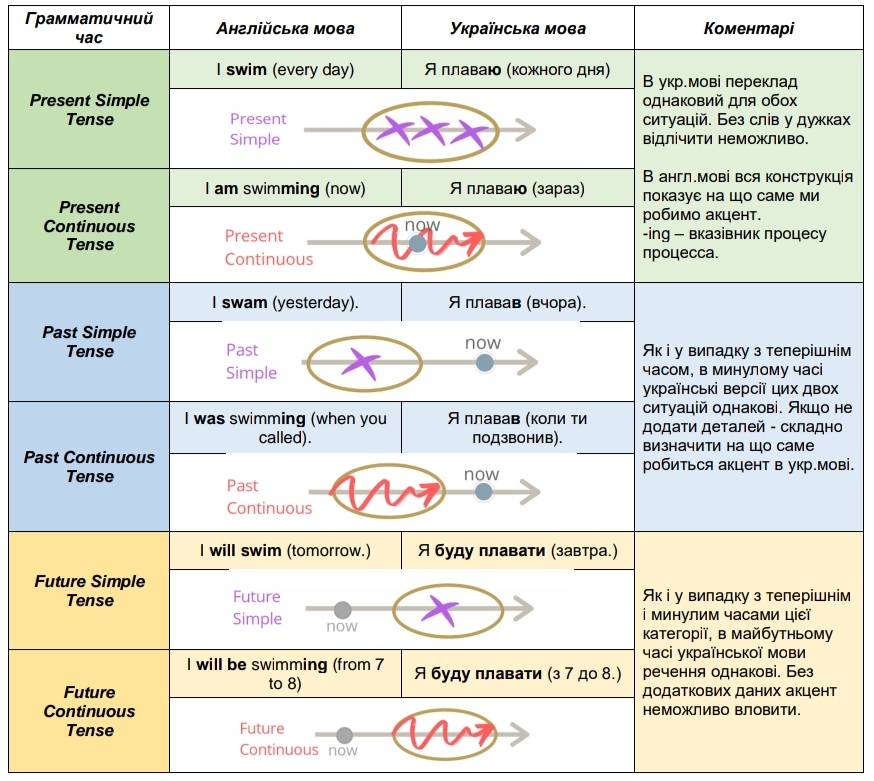
Table of English Tenses
Present Simple

Degrees of comparison
Degrees of ComparisonIn grammar, the degrees of comparison relate to adjectives and adverbs.Every adjective and adverb can be written in one of three degrees:The Positive Degree. This offers no comparison. It just tells us about the existence of a quality. For example:adjectives: slow, beautiful, happyadverbs: slowly, beautifully, happilyThe Comparative Degree. This compares two things to show which has the lesser or greater degree of the quality. For example:adjectives: slower, more beautiful, happieradverbs: more slowly, more beautifully, more happilyThe Superlative Degree. This compares more than two things to show which has the least or greatest degree of the quality.For example:adjectives: slowest, most beautiful, happiestadverbs: most slowly, most beautifully, most happily
aRules
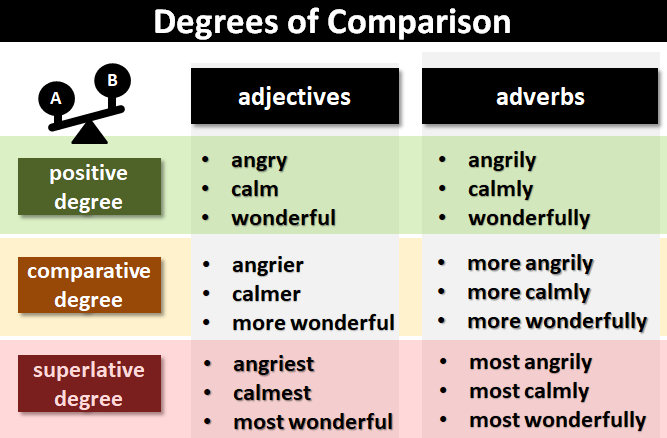
Usage table
Positive,comparative,superlative

Prepositions
A preposition is a word or group of words used before a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase to show direction, time, place, location, spatial relationships, or to introduce an object. Some examples of prepositions are words like "in," "at," "on," "of," and "to."Prepositions in English are highly idiomatic. Although there are some rules for usage, much preposition usage is dictated by fixed expressions. In these cases, it is best to memorize the phrase instead of the individual preposition.As we have learned, Prepositions are words that connect nouns/pronouns/phrases. It’s a bit tricky to explain the usage as it really has not many rules. But the wonders of logic will save this one. We will get into complete details of this part in our next chapter but let’s get introduced to the different kinds in this chapter:Simple Prepositions: Usually containing only two syllables, simple prepositions are words like for, by, at, out, in, of, off, through, till, up, to, with.The whale dived into the water creating a massive splash.I am from New Jersey.Martha is here till her brother gets into college.The moon does not shine by its own light.My niece is suffering from flu.I am working hard at Geography.
a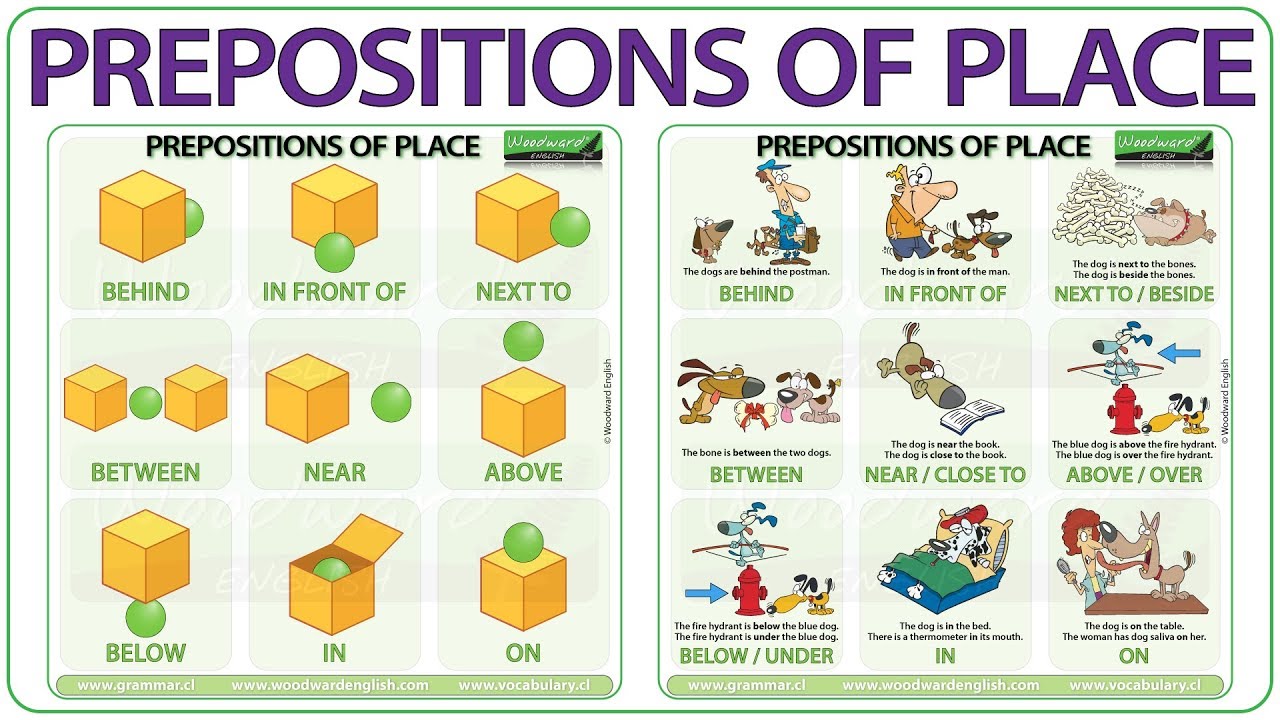
Structures
Rules

подтема

Essay
EssayAn essay is generally a short piece of writing outlining the writer’s perspective or story. It is often considered synonymous with a story or a paper or an article. Essays can be formal as well as informal. Formal essays are generally academic in nature and tackle serious topics. We will be focusing on informal essays which are more personal and often have humorous elements.Types of Essays1.Narrative Essays2.Descriptive Essays3.Expository Essays4.Persuasive Essays Topics:ArticleDescriptive EssayDialogueDiary EntryFormal LettersInformal LettersLetter WritingNon-Classified/Display AdvertisementsNoticeParagraphStoryStory: CharactersStory: SettingSummary
aFormal letter

Structure
ss