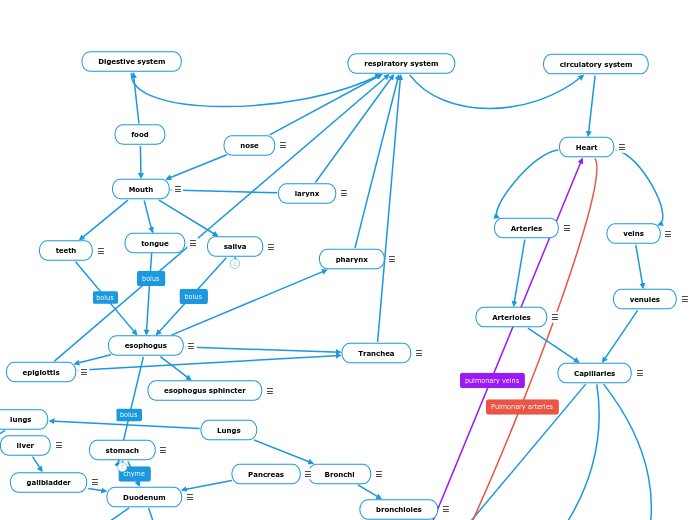
respiratory system
circulatory system
Heart
Made with thick muscle and has 4 chambers,right atrium,right ventricle,left atrium,left ventricle.pumps oxygenated blood from lungs to all body cells,pumps deoxygenated blood from body cells to lungs,has valves to prevent backwards flow of blood.
Arteries
carry blood away from heart,specifically from from the left ventricle.pulmonary arteries-carry deoxygenated blood from heart to each lung,specifically from the right ventricle.Aorta-carries oxygenated blood from heart to other arteries in the bodystrong thick elastic walls withstand high pressure
Arterioles
smaller branches off arteries,leading to capillaries
veins
carry blood toward the heartpulmonary vein-carries oxygenated blood from lungs to heart Vena Cava-carry deoxygenated blood from body cells to heart specifically to the right ventricle.thinner walls than arteriesvalves prevent backward flow of blood
venules
smaller branches of veins,leading to capillaries
Physical/chemical breakdown,salivary enzymes
teeth
bites food into smaller pieces to go down esophogus
esophogus
smooth muscleperistalsis wave like muscular contraction,moves bolus
pharynx
pharynx is shared by digestive/respiratory system divides into the esophagus or trachea.
Tranchea
long tubeair passes through into lungs lined with cartilage to keep airway open mucus and cilia protect
esophogus sphincter
muscle between esophogus and stomach.opens to allow bolus to enter stomach stays closed to prevent stomach acid from bubbling up into the esophogus.
epiglottis
epiglottis-directs food into esophagus and protect the trachea
stomach
physical=paristalsis,chemical=HCI(aq),smooth muscle,mucus lining,chyme
saliva
chemically breaks down foodmoistens your mouth, reduces infections in the mouth and throat, and helps protect your teeth and gums.
tongue
helps break down food
The liver processes blood, breaking down the nutrients and chemicals your blood carries. produce bile
stored bile
Duodenum
digestive chemicals are injected into the duodenum from accessory organs.bile made from liver and stored in the gall bladder breaking down into smaller pieces (Pancreatic juices).
jejunum
Nutrients in intestine,diffuse through the villi,capillaries,cells of the body
peristalsis;long,coiled tube,villi,High SA,low V,thin membrane,capillary;duodenum,jejunum,ileum,The small intestine has three parts: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. It helps to further digest food coming from the stomach. It absorbs nutrients
Nutrients in intestine,diffuse through the villi,capillaries,cells of the body
Large intestine(Colon)
paristalsis;long tube,water absorbed through osmosis,dehydrates chyme and forms into stool absorbs water through osmosis,absorbs electrolytes,bacteria breaks down into waste(chemical)
Rectum
feces(undigested materials)are stored in the rectum and eliminated through the anus.
produce insulin,enzymes,neutralize chyme
disposes feces at end of cycle
inhales air nose hairs and mucus trap dirt and other particles strong cartilage to keep airway open
contains vocal cordsair causes vibration to create sound
Bronchi
two branches airways leading to each lung also lined with cartilage
bronchioles
smaller and smaller branches leading to alveoli
Diaphragm
Upon inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and flattens and the chest cavity enlarges. This contraction creates a vacuum, which pulls air into the lungs.
two branches airways leading to each lung also lined with cartilage
bronchioles
smaller and smaller branches leading to alveoli
tiny branches of arterioles & venules,surrounding tissueseasy diffusion of O2,CO2,glucose,other nutrients & wastesone cell thickmillions of themcover almost all the tissueshigh surface area,low volume
flexible tiny air sacs at the end of bronchioles,walls are one cell thick,surrounded by capillaries (circulatory system)allows for easy diffusion for gas exchange.