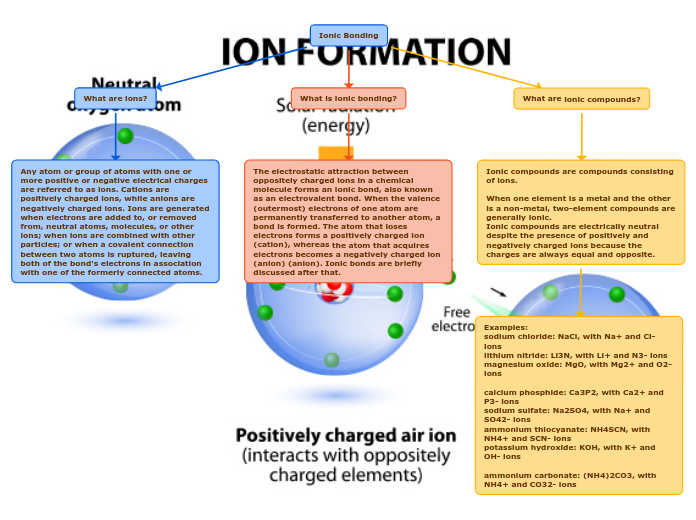
Any atom or group of atoms with one or more positive or negative electrical charges are referred to as ions. Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions. Ions are generated when electrons are added to, or removed from, neutral atoms, molecules, or other ions; when ions are combined with other particles; or when a covalent connection between two atoms is ruptured, leaving both of the bond's electrons in association with one of the formerly connected atoms.
The electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a chemical molecule forms an ionic bond, also known as an electrovalent bond. When the valence (outermost) electrons of one atom are permanently transferred to another atom, a bond is formed. The atom that loses electrons forms a positively charged ion (cation), whereas the atom that acquires electrons becomes a negatively charged ion (anion) (anion). Ionic bonds are briefly discussed after that.
Ionic compounds are compounds consisting of ions.
When one element is a metal and the other is a non-metal, two-element compounds are generally ionic.
Ionic compounds are electrically neutral despite the presence of positively and negatively charged ions because the charges are always equal and opposite.
Examples: sodium chloride: NaCl, with Na+ and Cl- ions
lithium nitride: Li3N, with Li+ and N3- ions
magnesium oxide: MgO, with Mg2+ and O2- ions
calcium phosphide: Ca3P2, with Ca2+ and P3- ions sodium sulfate: Na2SO4, with Na+ and SO42- ions
ammonium thiocyanate: NH4SCN, with NH4+ and SCN- ions
potassium hydroxide: KOH, with K+ and OH- ions
ammonium carbonate: (NH4)2CO3, with NH4+ and CO32- ions