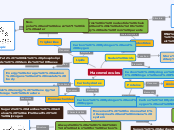
Macromolecules
Carbohydrates
Monosacharides
Always in a 1:2:1: ration for Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen

Subtopic
Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen
Quick energy, energy storage, structure
Sugars, starches, cellulose (cell wall), Glycogen
Proteins
Amino Acids
Creates 20 types of amino acids, which are determined by shape

Subtopic
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen
Movement, hormones, enzymes and immune system
Sugars, starches, cellulose (cell wall), Glycogen
Nucleic Acids
Nucleotides
Forms in nucleotide chains and is able to carry traits from parents

Subtopic
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen and Phosphates
Store and transmit hereditary information
RNA (ribonucleic acid), DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
Lipids
Triglicerides
Non-polar and doesn't like water

Subtopic
Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen
Energy storage, cushion organs and insulate body
Fats, Oils, phospholipids, Steroids, Waxes

Dehydration Synthesis