2. Digital Commerce: electronic transactions
Be aware of issues involving electronic transactions
There are goods and services which conflict with laws and morals
Learn to be effective consumers

3. Digital Communication: electronic exchange of information
Everyone has the opportunity to communicate and collaborate with anyone from anywhere and anytime
Many users have not been taught how to make appropriate decisions when faced with so many different digital communication options

4. Digital Literacy: keeping up to date with technology
New technologies are finding their place into the workplace that are not being used in schools (ie. videoconferencing)
Workers in many different occupations need immediate information (just-in-time information), which requires sophisticated searching and processing skills (ie. information literacy)
Learners must be taught how to learn in a digital society; taught how to learn anything, anytime, anywhere
As new technology emerges, learners need to learn how to use technology quickly and appropriately
Digital citizenship involves educating people in a new way
Individuals need a high degree of information literacy skills

5. Digital Etiquette: electronic standards of conduct or procedure
Before using technology people are not taught digital etiquette (ie. appropriate conduct)
People must be taught how to be responsible
1. Digital Access: full electronic participation in society

Not everyone has the same opportunities when it comes to technology
Work toward equal digital rights
Supporting electronic access
Goal: help and provide access to technology
Productive citizens make sure no one is denied digital access
9. Digital Security (self-protection): electronic precautions to guarantee safety

Responsible citizens protect their information from outside forces that might cause disruption or harm
Must have virus protection, backups of data, and surge control of equipment
8. Digital Health & Wellness: physical and psychological well-being in a digital technology world
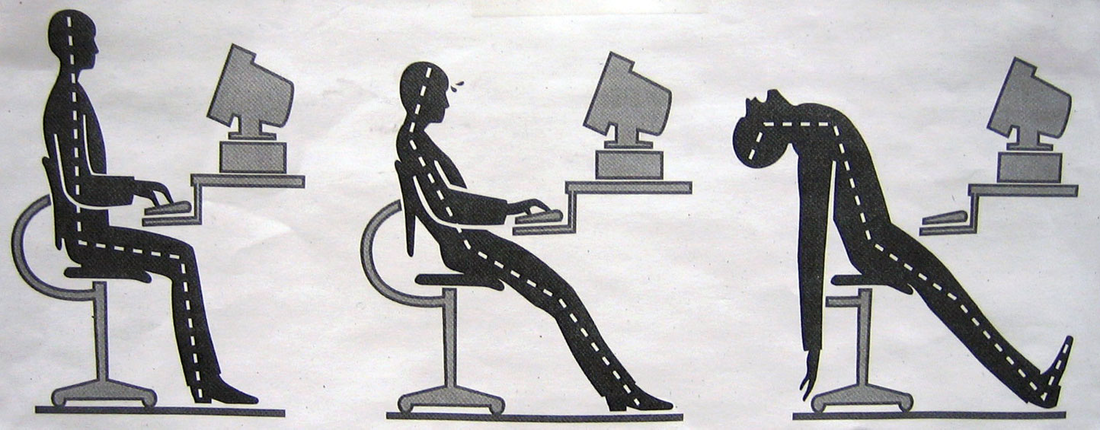

Users need to be taught the inherent dangers of technology
Physical → eye safety, repetitive stress syndrome ,sound ergonomic practices
Psychological → internet addiction
Digital citizenship includes a culture where technology users are taught how to protect themselves through education and training
7. Digital Rights & Responsibilities: those freedoms extended to everyone in a digital world

Digital citizens have the right to privacy, free speech, etc.
Basic digital rights must be addressed, discussed, and understood in the digital world
Users must help define how the technology is to be used in an appropriate manner
6. Digital Law: electronic responsibility for actions and deeds

Digital laws deal with ethics of technology within a society
Unethical → theft and/or crime
Ethical → abiding by the laws of society
Stealing and sabotaging people’s information and data is a crime, and is unethical
“Nine Elements.” Digital Citizenship, www.digitalcitizenship.net/nine-elements.html.