Mind Mapping
Trigonometric functions
And Their Properties
Sine (sin) (y/r)
Reciprocal: Co-secant (csc) (r/y)
Example:
9pi/4
9pi/4-8pi/4
=pi/4
sin theta= sqrt 2/2
csc theta= sqrt 2
cos theta= sqrt 2/2
sec theta- sqrt 2
tan theta= sqrt 2/2/sqrt/2=1
cot theta= 1
Cosine (cos) (x/r)
Reciprocal: Secant (sec) (r/x)
Tangent (tan) (y/x)
Reciprocal: Cotangent (cot) (x/y)
Unit Circle

Where (x,y) is (cos,sin)
sin theta 30 (1/2) cos theta 30 (square root of 3/2)
cos theta 45 (square root of 2/2 sin theta 45 (square root of 2/2
sin theta 60 (square root of 3/2) cos theta 60 (1/2)
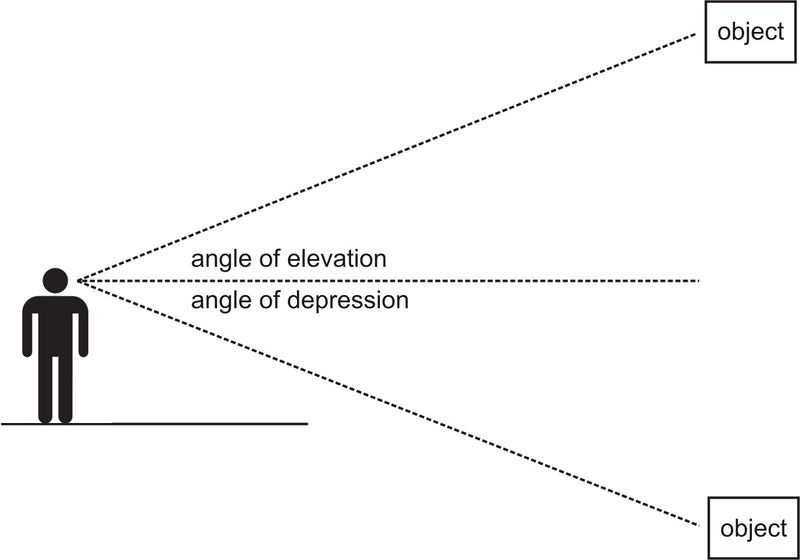
Angle of Elevation
Example:
A tree casts a shadow 21ft long. The angle of elevation of the sun is 51'. What is the height of the tree?
Solution:
tan(51)=v/21
v=21*tan(51)
v~25.93ft
Angle of Depression
Example:
A lighthouse operator 25yrds above the sea level sights a sailboat. The angle of depression of the sighting is10'. How far is the boat from the base of the lighthouse?
Solution:
tan(10)=v/25
v=25*tan(10)
v~4.41yrds
The Law of Sines and
Cosines
Law of Sines
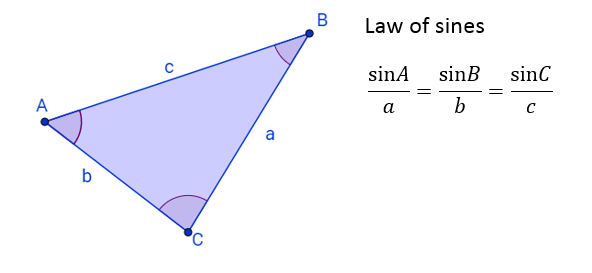
sin(A)/a=sin(B)/b
sin(A)/a=sin(C)/c
sin(B)/b=sin(C)/c
These equations can be used when:
1) One side and two angles are known (ASA/SAA)
2) Two sides and the angle opposite one of them are known (SSA)
Example: SAA
Solve the triangle: A=40', B=60', a=4
(FIND ALL MISSING SIDES)
Formula used: sin(A)/a=sin(B)/b
sin(B)/b=sin(C)/c
180=40+60+m<c
180=100+m<c
-100-100
m<c=80
sin(40)/4=sin(60)/b
(b)*sin(40)/4=sin(60)/b*(b)
(4/sin(40)*b* sin(40)/4=sin(60)(4/sin(4))
b=sin(60)(4/sin(40)
b~5.39
sin(40)/4=sin(80)/c
c*sin(40)=4*sin(80)
/sin(40) /sin(40)
c= 4*sin(80)/sin(40)
c~6.13
Example: SSA
Solve the triangle: a=3. b=2. A=40'
Formula used: sin(A)/a=sin(B)/b
sin(A)/a=sin(C)/c
Solution:
sin(40)/3=sin(B)/2
2*sin(40)/3=sin(B)/2*2
2*sin(40)/3=sin(B)
sin^-1(2*sin(40)/3=sin^-1(sin(B))
B=sin^-1(2*sin(40)/3
B~25.4
m<C=180-40-25.4
m<C=114.6
sin(40)/3=sin(114.6)/c
c=sin(114.6)(3/sin(40)
c~4.24
Law of Cosines
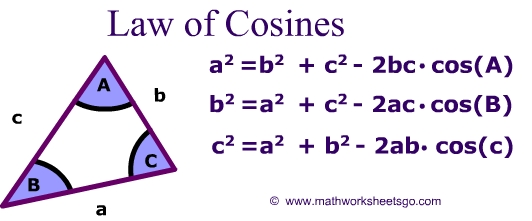
These equations can be used when:
1) Two sides and the included angle are known (SAS)
2) Three sides are known (SSS)
(when all sides are know use cos(B)=b^2-(a^2+c^2)/-2ac to find the angles)
Example: SAS
Solve the triangle: a=2, b=3, C=60'
Formula used: c^2=a^2+b^2-2ab*cos C
sin(A)/a=sin(C)/c
Solution:
c^2=2^2+3^2-2(2)(3)*cos(60')
c^2=4+9-12*(1/2)
c^2=13-6
c^2=7
c= Square root of 7
sin(A)/2=sin(60)/square root of 7
A=sin^-1(2(sqrt3/2/sqrt.7)
A=40.9'
B=180-60-40.9
B=79.1'
Example: SSS
Solve the triangle: a=4, b=3, c=6
Formula used: a^2=b^2+c^2-2bc*cos(A)
cos(B)=b^2-(a^2+c^2)/-2ac
Solution:
4^2=3^2+6^2-2(3)(6)*cos(A)
16=9+36-36*cos(A)
16=45-36*cos(A)
-45 -45
-29=-36*cos(A)
-36 -36
Cos(A)= 29/36
A=cos^-1(29/36)
A=36.3
cos(B)=b^2-(a^2+c^2)/-2ac
B=cos^-1(9-(16+36)/-2(4)(6)
B= 26.4'
C=180-36.3-26.4
C=117.3'
Fundamental Trigonometric
Identities
Quotient Ident.
cos^2(theta)+ sin^2 (theta)= 1
tan^2(theta)+1 = sec^2(theta)
cot^2(theta)+1= csc^2(theta)
Example:
Find the exact value of each Expression
a) tan(20)= sin(20) b)sin^2(pi/12)+ 1
------- ------
cos(20) sec^2(pi/12)
Solution:
a) tan(20)= sin(20)
----------
cos(20)
=tan(20)-tan(20)
=0
Solution:
b) sin^2(pi/12)+ 1
------
sec^2(pi/12)
=sin^2(pi/12)+ cos^2(pi/12
=1
Example:
Given that sin(theta)=1/3 and cos(theta)<0, find the exact value of the remaining trig function
Option1. Using the properties of the unit circle
ll Students | l All
sin(theta), csc(theta) | Trig. function
+ | +
--------------------------------------------------
lll Take | lV Calculus
tan(theta),cot(theta) | cos(theta),sec(theta)
+ | +
sin(theta)=1/3 csc(theta)=3/1
cos(theta)=2sqrt3/3 sec(theta)=3/2 srqrt3
=3/2sqrt3*sqrt2/sqrt2
=3 sqrt2/4
tan(theta)=1/2sqrt2* sqrt2/2 =sqrt2/4 cot(theta)= 2sqrt2/1
Option 2. Using Identities
sin^2(theta)+cos^2(theta)= 1
(1/3)^2+cos^2(theta)=1
1/9+cos^2(theta)=1
-1/9 -1/9
cos^2(theta)=8/9
sqrt cos^2(theta)= sqrt8/9
cos=2 sqrt2/3
Inverse of Sin, Cos, and Tan Functions
Inverse sin of x
Properties:
-pi/2 is less than or equal to x is less than or equal to pi/2
-1 is less than or equal to x is less than or equal to 1
Example:
Find the exact value of each of the following composite function: sin^-1(sin 5pi/8)
Solution:
sin^-1(sin 5pi/8)
8pi/8- 5pi/8= 3pi/8
= 3pi/8
Inverse cos of x
Properties:
-1 is less than or equal to x is less than or equal to 1
0 is less than or equal to y is less than or equal to pi
Example:
Find the exact value of: cos^-1 0
Solution:
cos^-1 0
cos(cos^-1(0)= cos (theta)
0= cos (theta)
cos(pi/2)=0
= pi/2
Inverse tan of x
Properties:
- infinity is less than x is less than infinity
-pi/2 is less than y is less than pi/2
Example:
Find the exact value of: tan^-1
Solution:
tan theta = y/x
tan(pi/4)=1
tan^-1(tan(pi/4))= tan^-1(1)
pi/4=tan^-1(1)
Trig. Identities
Example:
Establish the identity: tan(v)+cos(v)/sec(v)*csc(v)=1
Solution:
tan(v)+cos(v)/sec(v)*csc(v)=1
Remember: tan= y/x cot= x/y
sin(v)/cos(v)(sin(v)/sin(v)+cos(v)/sin(v)(cos(v)/cos(v)
____________________________________________
1/cos(v)*1/sin(v)
sin^2(v)+cos^2(v)
=________________
cos(v)*sin(v)
______________ = 1 1
1 __________ = __ = 1
______________ cos(v)*sin(v) 1
cos(v)*sin(v)
Sum and Difference
cos(a+B)=cos(a)*cos(B)-sin(a)*sin(B)
cos(a-B)=cos(a)*cos(B)+sin(a)*sin(B)
Example:
Find the exact value of cos(pi/12)
Equation used: cos(a-B)=cos(a)*cos(B)+sin(a)*sin(B):
Solution:
cos(pi/12) -> 15' =45'-30'
cos(pi/12)=cos(pi/4- pi/6)
=cos(pi/4)*cos(pi/6)*cos(pi/6)+sin(pi/4)*sin(pi/6)
=(sqrt2/2)(sqrt3/2)+(sqrt2/2)(1/2)
=sqrt6/4+sqrt2/4
+sqrt6 +sqrt2/4
sin(a+B)=sin(a)*cos(B)+cos(a)*sin(B)
sin(a-B)=sin(a)*cos(B)-cos(a)*sin(B)
Example:
Find the exact value of sin(7pi/12)
Equation used:sin(a+B)=sin(a)*cos(B)+cos(a)*sin(B)
Solution:
sin(7pi/12) -> 105' =60'+45'
sin(7pi/12)=sin(pi/3+pi/4)
=sin(pi/3)*cos(pi/4)+cos(pi/3)*sin(pi/4)
=(sqrt3/2)(sqrt2/2)+cos(1/2)*sin(pi/4)
=sqrt6/4+sqrt2/4
=sqrt6/4+sqrt2/4
=sqrt6+sqrt2/4
tan(a+B)=tan(a)+tan(B)
-----------------
1-tan(a)*tan(B)
tan(a-B)=tan(a)-tan(B)
----------------
1+tan(a)*tan(B)
Prove the identity: tan(theta+pi)=tan(theta)
Equation used: tan(a+B)=tan(a)+tan(B)
-----------------
1-tan(a)*tan(B)
Solution:
tan(theta+pi)=tan(theta)
tan(theta)+tan(pi)
---------------------
1-tan(theta)*tan(pi)
=tan(theta)
-----------
1
=tan(theta)
Finding the exact value of an Expression involving inverse trigonometric functions
Example:
Find the exact value of: sin(cos^-1(1/2)+sin^1(3/5)
Equation used: sin(a+B)=sin(a)*cos(B)+cos(a)*sin(B)
Solution:
cos(a)=(1/2) sin(B)=(2/5
sin(a)=y/r cos(B)=x/r
1^2+y^2=2^2 x^2+3^2=5^2
-1^2 -1^2 -3^2 -3^2
--------------------- ---------------
y^2=3 x^2=16
y=+/- sqrt 3= sqrt 3 x= +/-4 = 4
sin(a)=sqrt 3/2 cos(a)=4/5
=(sqrt3/2)(4/5)+(1/2)(3/5)
=4(sqrt 3)/16 + 3/5
=4(sqrt3)+3/10
Double-angle And Half-angle Fromulas
sin(2*theta)= 2*sin(theta)*cos(theta)
cos(2*theta)=cos^2(theta)-sin^2(theta)
cos(2*theta)=1-2*sin^2(theta)
cos(2*theta)=2*cos^2(theta)-1
Example:
If sin(theta)= 3/5, pi/2 < theta < pi, find the exact value of: cos(2*theta)
Equation Used: cos(2*theta)=1-2*sin^2(theta)
Solution:
cos(2*theta)= 1-2*sin(3/5)^2
= 1-2*sin(3/5)^2
= 1-18/25
= 25/25-18/25 -> 1=25/25
= 7/25
sin(a/2)= +/- sqrt 1-cos(a)
---------
sqrt 2
cos(a/2)=+/- sqrt 1+cos(a)
----------
sqrt 2
tan(a/2)=+/- sqrt 1-cos(a)
---------
sqrt 2
Example:
Use a half-angle formula to find the exact value of:
cos(15)
Equation used: cos(a/2)=+/- sqrt 1+cos(a)
----------
sqrt 2
Solution:
cos(15) = cos(30/2)
=+/- sqrt 1+ cos(30)
-----------
2
=+/- sqrt 1+ sqrt3/2
------------
2
=+/- sqrt 2+ sqrt3
----------
2
---------
2
=+/- sqrt 2+sqrt 3
---------
4
=+sqrt 2 sqrt3
----------
2
Area Formulas for Any Triangle

Example: SAS
Find the area K of the triangle for which a=8, b=6,C=30'
Formula used: A=1/28ab*sinC
Solution:
A=1/2(8)(6)*sin(30)
A=24*(1/2)
A=12units^2
Example: SSS
Find the area of a triangle whose sides are 4, 5, and 7
Formula used:K = Sqrt. s(s-a)(s-b))s-c)
s =1/2(a+b+c)
Solution:
s=1/2(4+5+7)
s=16/2
s=8
K= sqrt. 8(8-4)(8-5)(8-7)
K= sqrt. 8(4)(3)(1)
K= sqrt 96 = 4 sqrt. 6
K~9.8 units^2
Equation:
K=1/2*ab*sin(C)
K=1/2*bc*sin(A)
K=1/2*ac*sin(B)
Equations:
K = Sqrt. s(s-a)(s-b))s-c)
(This equation can only be used when ALL SIDES ARE KNOWN)
s= 1/2(a+b+c) (is used when you have to find s)