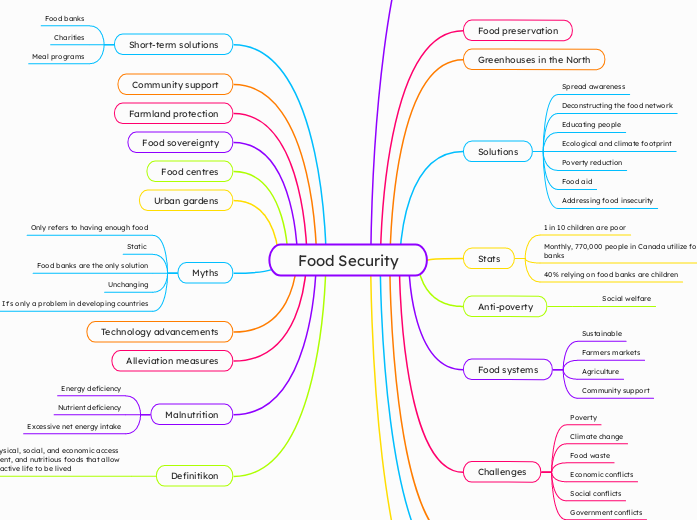
Food Security
Enhancing Food Security
Increased accessibility
Safe to consume
Transportation
Nutritious
Availability
Diversity
Food distribution
Agriculture productivity
Trade policies
Dietary needs are met
Acceptability
Affordability
Sustainable
Stability
Maintained despite food security factors
Climate change
Natural disasters
Economic fluctuations
Food preservation
Greenhouses in the North
Solutions
Spread awareness
Deconstructing the food network
Educating people
Ecological and climate footprint
Poverty reduction
Food aid
Addressing food insecurity
Stats
1 in 10 children are poor
Monthly, 770,000 people in Canada utilize food banks
40% relying on food banks are children
Anti-poverty
Social welfare
Food systems
Sustainable
Farmers markets
Agriculture
Community support
Challenges
Poverty
Climate change
Food waste
Economic conflicts
Social conflicts
Government conflicts
Improved government and political policies
Food diversity
Five trends
Population growth
Change in diets/food
Global food pricing
New technology
Climate change
Short-term solutions
Food banks
Charities
Meal programs
Community support
Farmland protection
Food sovereignty
Food centres
Urban gardens
Myths
Only refers to having enough food
Static
Food banks are the only solution
Unchanging
It's only a problem in developing countries
Technology advancements
Alleviation measures
Malnutrition
Energy deficiency
Nutrient deficiency
Excessive net energy intake
Definitikon
Having the physical, social, and economic access to safe, sufficient, and nutritious foods that allow for a healthy, active life to be lived