Music Theory Fundamentals Website Project
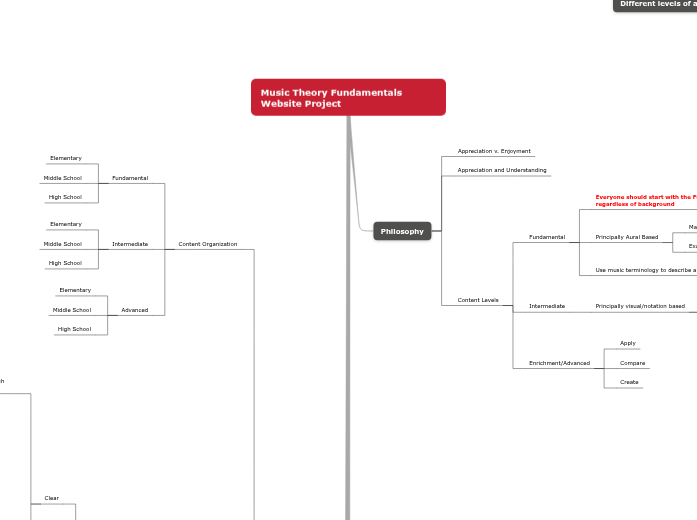
Philosophy
Appreciation v. Enjoyment
Appreciation and Understanding
Content Levels
Fundamental
Everyone should start with the Fundamental level, regardless of background
Principally Aural Based
Many different examples
Examples of varied historical period and genre
Use music terminology to describe aural experiences
Intermediate
Principally visual/notation based
Aural examples to support
Could re-use aural examples from fundamental level
Examples from scores
Enrichment/Advanced
Apply
Compare
Create
Content Organization
Fundamental
Elementary
Middle School
High School
Intermediate
Elementary
Middle School
High School
Advanced
Elementary
Middle School
High School
Rhythm
Fundamental
Pulse/Beat
Clear
Clear beats are most clearly identified by a listener through consitent, regular pulses in a specific timbre(s)
How is pulse perceived when a consistent pulse in a specific timbre is NOT present? Is beat perceived?
If yes, then what allows the listener to perceive beat?
No? Then does an absence of a consistent, regular pulse mean that no beat is present? Always?
Examples
Pop
Jump On It - Sir Mix-A-Lot
Rock
Country
Classical
Jazz
Traditional/Folk
Musical Theatre
not clear
Examples
Pop
Rock
Country
Classical
Jazz
Traditional/Folk
Musical Theatre
How Beats Group
What defines beat grouping in practice?
Repetition
Accent
Repetition of accent pattern defines beat grouping
Types of Accents
Pitch
Aggoic
Proximity
Timbre(?)
Melodic/Rhythmic Patterns
Lyrics
Groups of 2 or 4
Examples
Pop
Rock
Jazz
Country
Children's/Folk
Classical
Musical Theatre
Groups of 3
Examples
Pop
"Hayley Westenra" - Dark Waltz
Rock
Jazz
Country
Children's/Folk
"Amazing Grace"
Classical
Musical Theatre
How Beats Divide
2 parts (simple)
Examples
Pop
Rock
Jazz
Country
Hicktown
Children's/Folk
Classical
Musical Theatre
Subtopic
3 parts (compound)
Examples
Pop
Rock
Jazz
Country
Children's/Folk
Classical
Musical Theatre
Tempo
Tempo = relative speed to perceived beat
Speed defined
Beats per minute = measurement
Gradations between fast and slow
tempo changes
EXAMPLES
Pop
Rock
Live and Let Die
Country
Jazz
Jazz Festival Drum Solo
Night in Tunisia - Dizzy Gilespie and Arturo Sandoval
Children's/Folk
Classical
Chopin - Nocturne in Db
Bach - Toccata & Fugue in d
Musical Theatre
"I'll Cover You (Reprise)" -RENT
fast tempo
EXAMPLES
Pop
"contagious" avril lavigne
Rock
"wipeout" toy dolls
Country
"Wanna Talk About Me"- Toby Keith
Jazz
Branford Marsalis Trio - Cherokee
Ellington Caravan - Oscar Petereson Trio
Children's/Folk
micke y mouse march
"chicken dance"
Classical
Mozart - Overture "Marriage of Figaro"
Rimsky-Korsakov - Flight of the Bumblebee
Musical Theatre
"you can't stop the beat" hairspray
"What You Own" -RENT
slow tempo
EXAMPLES
Pop
Broken - Lifehouse
24-switchfoot
Rock
"Wish You Were Here"-Pink Floyd
Country
The Longer the Waiting (The Sweeter the Kiss) - Josh Turner
Jazz
Chet Baker - My Funny Valentine
Ella Fitzgerald - Misty
Miles Davis - The Man I Love
Thelonius Monk - Round About Midnight
Ellington "Tqake the A Train" - Oscar Petereson Trio
Children's/Folk
"amazing grace"
Classical
Bach - Brandenburg Concerto No. 2 - Mvt. 2
Schubert - Serenade
Musical Theatre
"Sunrise Sunset" -Fiddler on the Roof
"I Dreamed a Dream" -Les Miserables
Simple v. Complex
Syncopation
Durations
Sound
Silence
Intermediate
Durations (Beat tree)
The Measure
Meter
Time Signature
Syncopation
Changes of elements within a composition
Beat
Unclear
Beat present but not celarly defined by a timbre OR beat can be perceied differently OR no clear beat at all
Examples
Vesuvlus - Frank Ticheli
Wild Nights! - Frank Ticheli
Variable/Changing
Examples
Stravinsky Firebird, Finale
Advanced
Assymentrical tme signatures
Hemiola
Metric modulation
Melody
Harmony
Texture
Timbre
What Defines Formal Structures
Contrast and Repetition
Tension and Release
How Form is Achieved
Motives/Patterns
Syncopation
Hemiola
Repitition / Contrast
Meter
Change of Accented Beats
Time Signature
3/4 to 6/8
Tempo
Accelerando
Sudden Change
Hyper rhythm
Ritardando
Timbre
Contour
Range/Tessitura
Complexity
NCTs
Dynamic Level
Modulation/Tonicization
Cadence
must have a sence of closure at the end of a phrase
rhythmic cadence
harmonic cadence
four main types of cadence
(divides according to harmonic progression)
authentic cadence
(V or a V7 to I)
most direct way to establish the pitch as tonic
Perfect authentic cadence (PAC)
strongest type of cadence
creates complete melodic
and harmonic closure
Imperfect authentic cadence (IAC)
root position IAC
like PAC but the high voice (Soprano)
does not contain root
Inverted IAC
one or both chords must be inverted
Leading Tone IAC
the V chord is replaced with a viiio/sub V chord
and still ends on I
Evadence Cadence
creates extention (V42 to I6)
because the seventh must fall stepwise it forces
the cadence to resolve to a less stable first inversion chord
to achieve : the root position V must change
to a V42 before resolution therby evading the cadence.
plagal cadence
half cadence
ends on V
considered weak cadence
deceptive cadence
phrase in
relation to
cadence
are sections that an instrumetalist or singer
can play or sing on one breath.
generally end on the authentiv or half cadence
Plagal and deceptive avoid or follow a phrase ending cadence.
antecedent phrase
doesnt end on tonic
consequent phrase
ends on tonic
Voicing/Voice Leading
Open v. Closed Structures
Chromaticism
NCTs
Chromatic harmonies
Monophonic
Homophonic
Polyphonic
"Thick" v. "Thin"
Subtopic
Formal Structure Heirarchy
Motive
Phrase Segment
Phrase
Period Structures
Parallel v Contrasting
Period v. Double Period
Small Forms
Characteristics
Types
Binary
Ternary
Rounded Binary
Large Forms
Sonata
Rondo
Sonata-Rondo
Theme & Variations
Compound Forms
Minuet-Trio
Concerto
Symphonic Poem (Thorugh Composed)
Multi-Movement
Sonata
Symphony
Suite
Song Forms
Strophic
Modified Strophic
Through Composed
DaCapo Aria
Process/Procedure as Form
Countrapuntal Procedures
Invention
Fugue
Contemporary
Minimalism
Serialism
Context-defined Formal Structures
Instrumental v. Vocal
Western v. Non-western
Style/Genre
Genre Differences
Jazz
Pop/Rock
Country/bluegrass
Classical
Musical Theatre
Children's/Folk
Western Style Periods
Medieval
Renaissance
Baroque
Classical
Romatic
Contemporary
Composer?
Resources Link