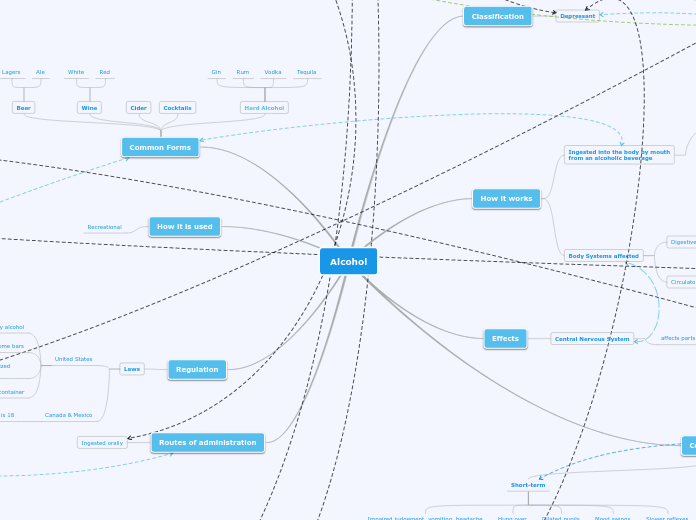
Depressant
Ingested into the body by mouth
from an alcoholic beverage
Gets absorbed in bloodstream
by the stomach or small intestine
Once in blood stream, travels to brain
Acts like a depressant & slows down body reaction time
and slows body functions
Body Systems affected
Digestive System
Alcohol irritates the stomach, causing
more stomach acid
Liver
Circulatory System
Increases blood pressure and heart rate
Central Nervous System
affects parts of the Brain
Difficulty walking, blurred vision, slurred speech,
slowed reaction times, impaired memory
alcohol is a drepressant
affecting our thoughts, feelings and actions
Short-term
Impaired judgement, vomiting, headache
Hung over
Dilated pupils
Mood swings
Slower reflexes
Long term
Family or work problems
Cardiovascular disease
Dependence
Depression
Addiction
Liver disease
Beer
Lagers
Ale
Wine
White
Red
Cider
Cocktails
Hard Alcohol
Gin
Rum
Vodka
Tequila
Recreational
Laws
United States
Must be 21 years old to consume & buy alcohol
Must be 18 years old to enter some bars
Against the law for all ages to drink and drive a motorized vehicle (BAC @ 0.08)
Most states it is illegal to have open container
Canada & Mexico
Legal drinking age is 18
Ingested orally
Marijuana
Dried leaves & buds
Hash Oil
Liquid form, very potent
Concentrated
Dabs or wax
If smoked
Enters lungs -> into bloodstream -> into brain
If ingested
Enters stomach -> into liver -> absorbed into bloodstream -> brain
Depressant
Acts likes Hallucinogenic or a Stimulant
Short Term
Spontaneous excitement and laughter
Increased appetite
Dry mouth
Muscle Relaxation
Increased Heart rate
Sleepiness
Pain relief
Long Term
Temporary hallucinations
Heart disease or persistent cough
Addiction
Bronchitis
Recreational
Medical
United States
At least 10 states legalize marijuana
(must be 21 or older to use marijuana)
33 States allow for medical marijuana
Mind
Affects memory
Brain Function
Brain receptors
Body
Smoked
Ingested
Lotions
Vaporized
Brain
Caffeine blocks adenosine receptors in the brain
(adenosine is a transmitter that makes us tired)
Headaches (dehydration)
Enters the brain -> increase Bp -> stimulate the release of stress hormones
Circulatory System
Increase heart-rate & blood pressure
Digestive System
Stomach, caffeine may reduce feelings of hunger and your desire to eat for a brief time.
Activates colon aka makes you poop
Increase urination too
Mind
Makes you feel more alert
Athletic performance
Short term
Headaches
Rapid heart rate & breathing rate
Feeling more alert
Dehydration
Long term
Dependence
Fatigue
Irregular heart rate
Difficulty sleeping
Nervousness
Oral
Coffee
About 1 cup has 95 mg of caffeine
Tea
Black tea has 60-75 mg of caffeine
Green tea has 15-30 mg of caffeine
Energy Drinks
Redbull has about 111 mg of caffienie
Soda
Pepsis can has 37.6mg of caffeine
Caffeine foods
Ice cream, chocolate, candy
Energy Bars
Medication
Vivarin
Excedrin
Supplement/Power
Recreational
Medically
Stimulant
FDA
Regulates the amount in food, drinks and medicine
Caffeine power is not regulated
Almost anyone @ any age can buy coffee, tea, candy, energy drinks
Alcoholic beverages with caffeine is banned
Brain
causing the brain to release a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and motivation (dopamine)
Circulatory System
Cause blood vessels to contrict/narrow
Increases risk of blood clots
CO2 from smoke & nicotine makes the heart
work harder & faster
Respiratory System
Irritation to trachea, larynx and lungs
Creates extra mucus in lung passages
Damage airoli (air sacks in lungs)
Reproduction System
Damage blood supply to penis
Reduces fertility in women
Mind
Addictive
"Stress reliever"
Body
Damages body systems
Short Term
Bad breath & taste in mouth
Smelly clothes and hair (smoking)
Addiction
Receding gums/sores in mouth from chewing
Long Term
Several Cancers
Lung disease / Emphysema
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
"Smokers Cough"
Bronchitis
Gingivitis
At risk for stroke & heart attack
Oral
FDA
requires health warning statements on tobacco packages & advertisements
Unites States
Must be 21 years to purchase tobacco in
(Arkansas, California, Illinois, New Jersey, Massachusetts, Oregon, Hawaii, Maine, Utah, Washington and Virginia)
Many states schools prohibit tobacco on the property
Bartering or selling tobacco products is regulated and taxed
World Health Organization:
Only 1 in 3 countries, representing 39% of the world's population, monitors tobacco use by repeating nationally representative youth and adult surveys at least once every 5 years.
Cigarettes
Cigars
Smokelss
Pipe
Hookah
E-cigarettes
Dissolvable
Recreational
Stimulant
Pills
Waxy/Gooey oil meth base
Crystal Form
Powder
Recreational
Medically
Treatment of ADHD
Stimulant
Illegal in the United States
for recreational use
5 grams = 5 yrs of jail
(if distributing it)
15 grams = 10 yr of jail
(if distributing it)
Brain
Increases the amount of dopamine
to be released in the brain
Kidneys
Urine retention can occurs
Cardiovascular System
Elevates blood pressure
Blood vessels constrict
Can develop clots
Increases risk of strokes
Brain
Impair cognitive functioning
Increase risk of stroke
Release the neurotransmitter dopamine
Short Term
Boost energy levels
Increased blood pressure
Rapid heart rate, irregular heartbeat
Lose appetite
Violent rages
Long Term
Meth Sores
Weight loss
Tooth Decay
This is from restriction of saliva flow
Deep Depression
Damage to motor skills
Damage Dopamine Receptors
Hallucinations
Paranoia
Snorted
(powder)
Injected
(dissolved)
Swallowing
(pill)
Smoking
Tablets
Capsules
Suppositories
Soluble powders & tablets
Liquids
Medically
Pain
Diarrhea
Cold & Flu
Dry irritating cough
Recreational
Purple drank
(codeine, cough syrup, & soft drink)
Opiate
Depressant
Legal for medications
Prescribed by doctors
Regulated under narcotic controls laws
Some is available w/o prescription
Nerve endings
Brain
Bonds to opioid receptors in the brain
blocks the triggering of neurons,
stopping the brain to process pain.
(Stops/dulls pain)
Circulatory system
Slows breathing rate
Slows heart rate
Blood pressure
Digestive System
Nerve ending are slowed
Constipation
Abdominal cramps
Brain
High doses of promethazine-codeine cough syrup can produce a high similar to that produced by other opioid drugs
Short term
Nausea
Euphoria
Dry mouth
Drowsiness
Long Term
High risk of building a tolerance
Possible dependence
Bradycardia
Liver & Kidney Damage
Reduce sex drive
Constipation
Oral
Opium Plant
Pain Medications
(Chemicals in this plant)
Codeine
Tablets, cough syrup
Thebaine
Morphine
Pills, tablets, liquid form
Semi-Synthetic opioids
(man-made chemicals)
Herion
Can be a white or brown powder, or black tar
Oxycodone
Fentanyl
Strongest opioid drug
Liquid, patch, powder, pills,
Medically
Recreational
Depressant
Prescription/Medication opioids
are legal in the US
Using opioids w/o prescription is illegal
Herion is illegal
Kidney
Opioids get filtered through the kidneys,
long term use can cause toxin exposure,
kidney stones and kidney failure
Heavy heroin use can cause
rhabdomyolysis
Liver
Liver filters out toxins and constant abuse of the drug
can damage the liver
Circulatory System
Painkillers that are crushed up and dissolved them
in water, the pill clumps can cause blockages & damage veins
Heart rate slows down, decreases blood pressure
Skeletal Systems
Bone thinning and impairment of regrowth,
more likely to break bones
Digestive System
Brain
Blocks pain & slows breathing
Opioids can destroy neurotransmitters and receptors
in the brain responsible for pleasure
Makes the body feel "relaxed"
Short term
Dry mouth
Unconsciousness
Coma
Constipation
Pupil Dilation
Slowed breathing
Nausea
Bloating
Long term
Weaken bones
Restlessness
Insomnia
Addiction
Physical dependence
Pain Medications
Injection
Rectal
Oral
Herion
Injecting
Snorting
Smoking
Marijuana
Dried leaves, oil, wax
LSD
(Lysergic acid diethylamide)
Capsules, absorbent paper, liquid, powder
Mushrooms
Molly/Ecstasy
(3,4-methylenedioxy-methamphetamine MDMA)
Tablet, capsule, liquid, powder
Recreational
Psychedelic drug/Hallucinogenic
Mushrooms are legal in Oregon
LSD & Molly are illegal
Circulatory System
Increased heart rate & blood pressure
Brain
Affects the pathways of the brain
(serotonin pathway & glutamate system)
Brain
Experiences are unpredictable & depends on
amount ingested and the user’s personality, mood, expectations, and surroundings
"Good trips" = pleasant hallucinations
"Bad trips" = bad thoughts & nightmare feelings
Mood
Sensory perception
Short term
Nervousness
Increased energy
Increased heart rate & body temp.
Impulsive emotions
Mixed senses/Hallucinations
(seeing sounds, hearing colors)
Sweating
Nausea
Long term
Paranoia
Addiction
B
Smoked
Injected
Oral
Snorted