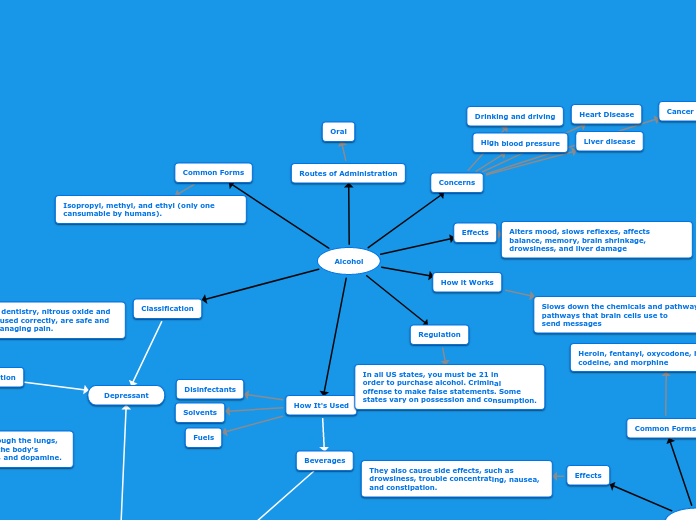
Isopropyl, methyl, and ethyl (only one cansumable by humans).
Disinfectants
Solvents
Beverages
Fuels
Depressant
In all US states, you must be 21 in
order to purchase alcohol. Criminal
offense to make false statements. Some
states vary on possession and consumption.
Slows down the chemicals and pathways
pathways that brain cells use to
send messages
Alters mood, slows reflexes, affects balance, memory, brain shrinkage, drowsiness, and liver damage
Drinking and driving
High blood pressure
Heart Disease
Liver disease
Cancer
Oral
Sativa
Indica
Hybrid
Recreational
Medical
Recreational Use States:
Washington, Oregon, California,
Nevada, Colorado, Illinois, Michigan,
Vermont, Massachusetts, and Maine
Medical Use States:
Montana, Utah, Arizona, New Mexico,
North Dakota, Minnesota, Missouri, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Louisiana, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Maryland, New Jersey, Rhode Island, New Hampshire, West Virginia, Connecticut, and Delaware
THC's chemical structure is similar
to the brain chemical anandamine,
which allows the body to accept it.
Affects brain areas that influence
pleasure, memory, thinking, concentration
movement, coordination, and sensory/time
perception.
Pain relief
Increased Appetite
Addiction
Psychiatric Disorders
Oral
Transdermal
Inhalation
Sublingual
Energy Drinks
Coffee
Alertness
Wakefulness
Stimulant
Caffeine is currently not regulated. Recognized as "safe", but it is quite addictive, especially when it comes to coffee and energy drinks.
Fools adenosine receptors, and binds to them. Causes drowsiness by slowing nerve cell activity
Can cause agitation
Cigarettes
Cigars
Pipe Tobacco
Chewing Tobacco
Snuff
Affects behavior, mood, and emotions (ex. anxiety
Linked to social activities and usage during work breaks
The FDA has the ability to regulate tobacco products
Most states require users to be 18, while some require them to be 21
Nicotine acts in the brain by stimulating the adrenal glands to release adrenaline and dopamine.
Gives similar feelings to caffeine
Reduces appetite
Nicotine inside tobacco is highly addictive
Smoking is the number one cause for lung cancer
Chewing
Smoking
Snorting
Crystalline Powder
Crystal Meth
Pills
Meth Base
This is a drug that people can snort, smoke, orally take, or inject and causes a false sense of happiness and well-being.
An illegal drug in the same class as cocaine and other harmful street drugs.
Illegal, but used by many people of all ages
It is a dangerous and very potent chemical that first acts as a stimulant and uses the body's resources.
Memory loss
Aggression
Heart and Brain damage
Psychotic behavior
Addiction
Destroys the body
Injection
Oral
Propane tanks
Whipped cream aerosols
Chloroform
Medical Anesthetics
Mostly used in dentistry, nitrous oxide and oxygen, when used correctly, are safe and effective for managing pain.
Enters the bloodstream through the lungs, and triggers the release of the body's natural opioids, endorphins, and dopamine.
Feelings of euphoria
Relaxation
Calmness
Dizziness
Laughter
Long term exposure can lead to infertility, short term effects include dizziness, unconsciousness, and even death.
Inhalation
Heroin, fentanyl, oxycodone, hydrocodone, codeine, and morphine
Medically, opioids are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia.
Opioids need to be properly prescribed to patients. That is the only way they can receive them. Possession without a prescription is illegal.
These drugs bind to opioid receptors in the brain, spinal cord, and other areas of the body. Restrict pain messages from being sent to the brain.
Pain medication
Because opioids can cause physical dependence and addiction, it is difficult to prescribe them properly, which later translates into improper pain management.
They also cause side effects, such as drowsiness, trouble concentrating, nausea, and constipation.
Intramascular
Intravenous
Subcutaneous
LSD
MDMA
Psilocybin
PCP
DMT
Peyote
Rituals/Religious reasons
Boredom relief
Hallucinogen
Oregon has determined that it is currently a schedule one drug (there is no medical value)
Alters a person's perception, mood, and other mental processes.
Visual disturbance
Disorganized thinking
Paranoia
Mood changes
HCPP
Toxicity and Overdose
Self harms caused by changes in perception
Are one of the most "safest" drugs
Sublingual
Snorting
Held in cheek