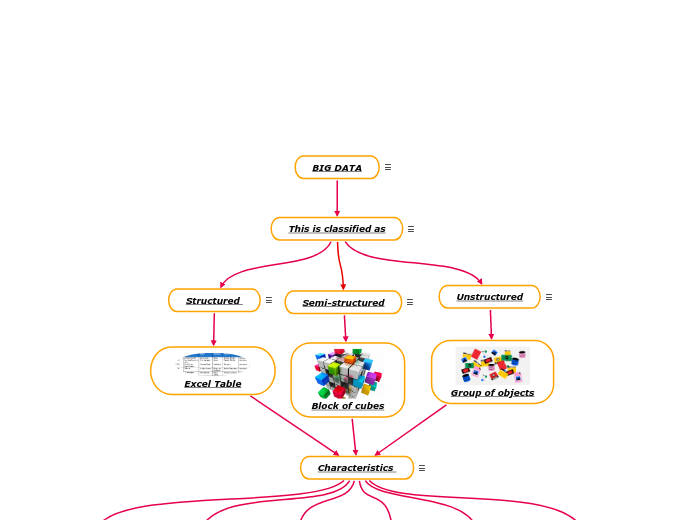
BIG DATA
Big data refers to a complex analysis of a large volume of data to obtain valuable information that can be used for the development and evolution of a business.
This is classified as
The data can be found in three categories:StructuredSemi-struturedUnstructured
Structured
These are those data that are found with a solid structure. Generally, these are organized in rows and columns, which makes their handling and management much easier.
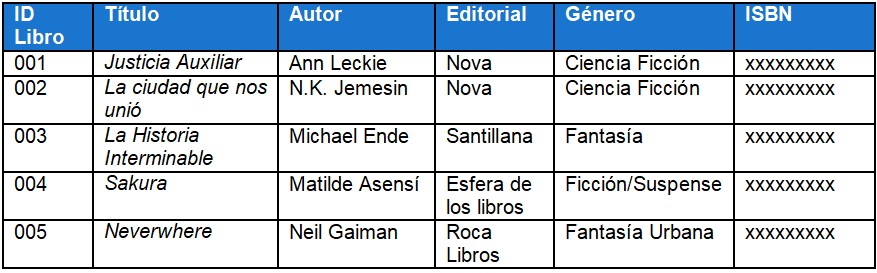
Excel Table
Characteristics
Big Data works on the basis of the so-called "6 Vs":Volume VarietyVelocityVeracityValue Visualitation
Volume
This topic refers to the large volume of information and data that make up the "Big data", often exceeding the measures of terabytes and peta bytes, which makes necessary the use of various more advanced and specialized technological equipment, compared to conventional data storage and management procedures used in the traditional way.

Visualitation
Visualization is centered on how information is presented and explained to us. The big data, exhibits us, in a visual and explicit way, the information that we want to obtain, because, it has been determined that the human being, in general terms, collects and understands better the information that is presented visually, than having to read different formats full of text and numerical formulas that demand much more attention.

Value
Generally in Big data there are some data that really have valuable information for those who need it, but to obtain this information it is necessary to use certain mechanisms of standardization, processing and proper and efficient management of such data, which promotes the use of varied and complex technological systems and specialized algorithms.

Veracity
This term alludes to the veracity (quality) of the data being manipulated and analyzed, since such data can be used with absolute confidence due to the remarkable results that have been extracted from them, and the legitimacy of the data to be management and used can also be verified.

Velocity
This characteristic refers to the speed with which the data is generated, which is distinguished by the high speed at which data is generated and distributed.
Variety
Big data is constituted by a great variety of information and data extracted from different sources of registration and management of such data, which explains the great capacity of information management within Big data. This data, in general, can be classified as: structured, semi-structured and unstructured. For the management of this kind of data, we need to use several types of process and technologies more developed and capable.
Semi-structured
They are those with a medium level of structuring and organizational rigidity. They have a certain level of structure, hierarchy and organization, although they lack a fixed scheme.

Block of cubes
Unstructured
These data types have an internal structure, but are not structured through fixed and predefined data models or schemas. They can be textual or non-textual and generated by humans or machines.

Group of objects