Carbohydrates
Polisaccharides
Made of thousands of Monosaccharides linking together
They can be divided by
Main topic
Disaccharides
Made up of two monosaccharides where they bond to create new sugars
Maltose
Monosaccharids
simple sugars, they are the smalls units that make up any carbohydrates. They also contain carbon hygrogen's oxygens
Types
Glucose
Main source of energy for humans.
properties
Glucose has an OH bond, which is polar. The covalent bonds can break down easily. No Toxic
Glucose types
Alpha
The alpha configuration in the chemical formula is pointing in the opposite direction to the carbon number six.
Structure
Structural Formula
Beta
The Beta configuration is the opposite to the alpha. Hydroxyl group of carbon number 6 are pointing towards the same direction
Structure

Subtopic
Galactose
Fructose
Energy production. Is involved actively in the reproduction of the cells and MRNA
Properties
Higher solubility than other sugars. Soluble in water It bonds with glucose to forma disaccharides saccarose. Covalent bond
Structure

Subtopic
Condensation happens between two alpha glucose monosaccharide, then water is released and hydrolysis occurs so water breaks down (a 1 to 4 bonds)

Beta and Glucose bonds to each other, through the condensation and hydrolysis process Lactose is created (B 1 to 4 bonds)
Is found in milk to create energy. Used to serve in neural and immunological processes.

Lactose
Reduces sugar. Covalent bond. soluble in water
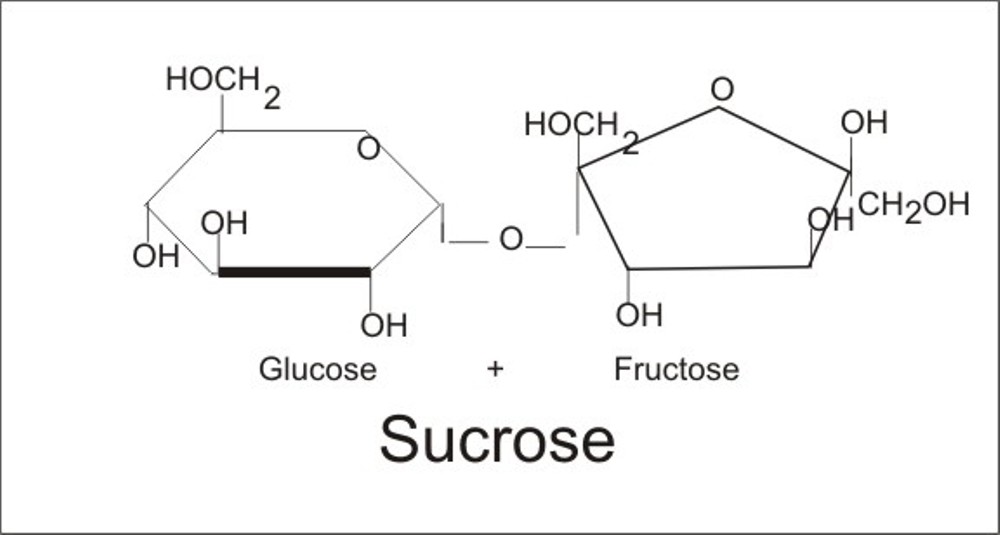
Sucrose
Alpha glucose and Beta Fructose link through condensation. The bond between glucose and fructose is more complicated because fructose has to flip over to allow sucrose to do the hydrolysis. (Glu1 and B2 Fruct)
Sucrose is formed by plants, not by animals. They are monomers.
Homopolysaccharides
Two or more different types of saccharides
Unbranched
Branched
Glucose links with Glycosidic to form Glycogen (1-4 Beta Glycosidil bonds)
Water soluble. It's a storage compound in animal tissues and is found mainly in the liver and muscle cells. Covalent bond.
Heteropolysaccharides
Single