Phospholipid Bilayer
Glycolipids
Cholesterol
Channel Proteins
Carrier Proteins
protein structures
secondary
hydrogen bonds
tertiary
quaternary
hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces between nonpolar side chains.
primary
peptide bonds
Cell shape, facilitates chromosome movement, cilia and flagella
Myosin and actin, muscle contraction, resists external tension
anchorage of nucleus, lamina formation
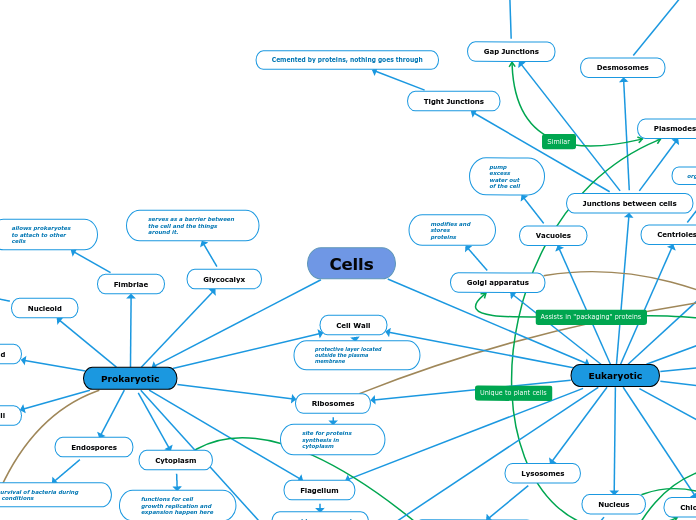
Cemented by proteins, nothing goes through
Everything goes through
Semi-permeable, certain molecules go through
Everything goes through
enables movement
site for cellular respiration, production of energy
functions for cell growth replication and expansion happen here
Calcium Channel opens
Calcium causes vesicles to attach at membrane and release neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter binds to adjacent neurotransmitter and depolarization occurs
The unphosphorylated dimer becomes
phosphorylated (fully activated) ,
Inactive relay proteins bind to phosphate
groups on the dimer and become active when there a total of 6 phosphates (3 on each side of molecule)
Active enzyme catalyzes phosphorylation within the cell
Replication bubble
Leading strand
Lagging strand
Prokaryotes
occurs in the cytoplasm
INITIATION
RNA polymerase binds to the promoter resulting in new RNA 5'-3'
DNA unwinds and RNA synthesis starts at start point of the template strand
ELONGATION
New RNA nucleotides are added to 3' end of growing chain
condensation/dehydration occur using RNA polymerase
New nucleotides are added in 5' to 3'. Once RNA polymerase reaches termination site, transcription stops
TERMINATION
proceeds through terminator sequence in DNA
transcribed terminator functions terminator signal
polymerase detaches from DNA releasing the transcript
RNA SPLICING
pre mRNA with 5’cap and 3’polyA tail
RNA processing
introns are removed and exons are joined together to form a mature mRNA
TRANSLATION
INITIATION
Prokaryotes
occurs in the cytoplasm
small ribosomal unit binds to mRNA, initiator tRNA base pairs with the start codon (in the P site), and the large subunit binds to form translation initiation complex
Ribosomal subunits=
70S (50S + 30S)
ELONGATION
initiator tRNA sits in the P site
and carries the amino acid Met
carry fMet (formal methionine)
GTP is hydrolysized
aminoacyl tRNA base pairs with
complimentary mRNA codon in
the A site
peptide bonds form between the
polypeptides carried by the tRNAs
tRNAs shift to the left, so that the P site
tRNA is now in the E site, and A site is
now in the P site
new aminoacyl tRNA is brought into
the A site to repeat the process
TERMINATION
a stop codon is reached in the A site,
so a release factor sits in the site
the complete polypeptide is freed and the complex is dissociated, stopping translation
carry Met (methionine)
Ribosomal subunits=
80S (60S + 40S)
Eukaryotes
RNA Polymerase II transcribes polyadenylation signal sequence
AAUAAA specified in pre-mRNA
six RNA nucleotides appears and are bound by certain proteins in the nucleus.
10–35 nucleotides downstream from the AAUAAA signal
RNA transcript is set free from the polymerase releasing the pre-mRNA
RNA Polymerase II and transcription factors bind to the promoter resulting in new RNA 5'-3'
Eukaryotes
occurs in the nucleus
Osmosis
Facilitated Diffusion
Simple Diffusion
Endocytosis
pinocytosis
receptor-mediated
phagocytosis
Exocytosis
Cotransport
Electrogenic Pump