Channels Of Distribution
Direct distribution
Distribution is how products get from the manufacturer to the consumer. It involves things like transportation and logistics
Two examples of direct distribution are, where the manufacturer sells directly to the consumer, and indirect distribution, where products go through peacemakers like retailers.
Subtopic
Subtopic
Indirect distribution
Indirect distribution is when products go through abitur like retailers before reaching the consumer. It involves using channels such as wholesalers, distributors, or online marketplaces
Two examples of indirect distribution are when a clothing brand sells its products through department stores or when a tech company sells its products through online platforms like Amazon.
Subtopic
Wholesalers
Wholesalers are middlemen who buy products in bulk from manufacturers and sell them in smaller quantities to retailers. They help bridge the gap between manufacturers and retailers, ensuring a smooth distribution process.
For example, companies like Costco and Sysco are well-known wholesalers that supply a wide range of products to various retailers.
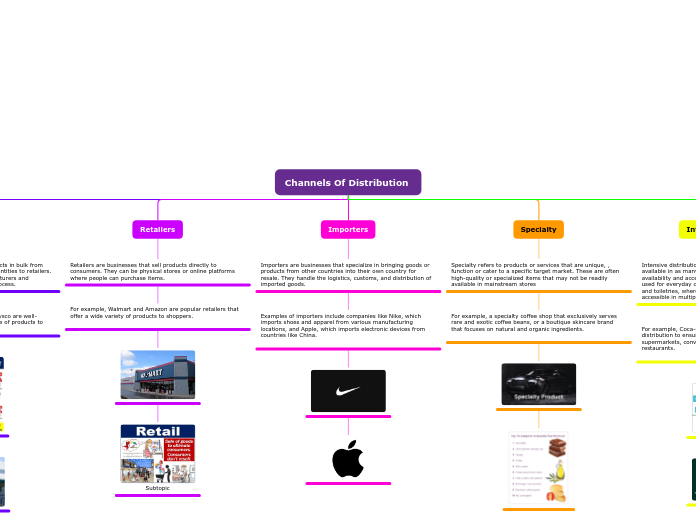
Retailers
Retailers are businesses that sell products directly to consumers. They can be physical stores or online platforms where people can purchase items.
For example, Walmart and Amazon are popular retailers that offer a wide variety of products to shoppers.
Subtopic
Importers
Importers are businesses that specialize in bringing goods or products from other countries into their own country for resale. They handle the logistics, customs, and distribution of imported goods.
Examples of importers include companies like Nike, which imports shoes and apparel from various manufacturing locations, and Apple, which imports electronic devices from countries like China.
Specialty
Specialty refers to products or services that are unique, , function or cater to a specific target market. These are often high-quality or specialized items that may not be readily available in mainstream stores
For example, a specialty coffee shop that exclusively serves rare and exotic coffee beans, or a boutique skincare brand that focuses on natural and organic ingredients.
Intensive distribution
Intensive distribution is a strategy where a product is made available in as many outlets as possible to maximize its availability and accessibility to consumers. It is commonly used for everyday consumer goods like soft drinks, snacks, and toiletries, where the goal is to have the product easily accessible in multiple locations.
For example, Coca-Cola and PepsiCo employ intensive distribution to ensure their beverages are widely available in supermarkets, convenience stores, gas stations, and restaurants.
Selective distribution
Selective distribution is a strategy where a product is made available in a limited number of outlets that are carefully chosen based on specific criteria. This approach is often used for products that require more specialized knowledge or cater to a specific target market
For example, luxury brands like Louis Vuitton and Rolex use selective distribution to maintain exclusivity by only selling their products in high-end boutiques and authorized retailers.
Exclusive distribution
Exclusive distribution is a strategy where a product is made available through a single outlet or a limited number of outlets in a particular market. This approach is often used for high-end or luxury products to maintain a sense of exclusivity and prestige
For example, a luxury car brand like Rolls-Royce may use exclusive distribution by selling their vehicles only through a select network of authorized dealerships. Similarly, a high-end fashion brand like Chanel may choose to distribute their products exclusively through their own flagship stores.