Grade 10 Science
Optics
Mirrors
Convex Mirror
Concave Mirror
Lens
Concave Lens
Convex Lens
Eyes
Parts of the eyes
Hyperopia
Myopia
Reflections
Law of reflection
The law of reflection states that when a ray of light is reflected off a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Regular Reflections
Diffuse Reflections
Diagrams
Rules of drawing diagrams for mirrors
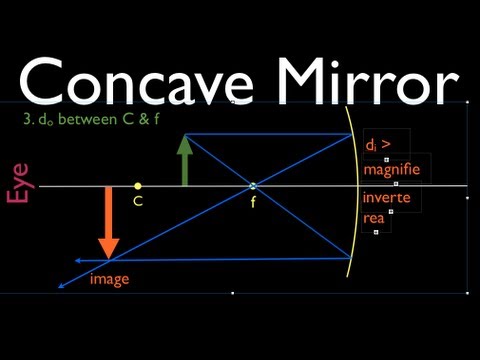
Concave
1. An incident ray which is parallel to the principal axis is reflected through the focus of the mirror.
2. An incident ray which passes through the focus of the mirror is reflected parallel to the principal axis.
3. An incident ray which passes through the centre of curvature of the mirror is reflected back along its own path.
4. An incident ray which strikes the mirror at its vertex is reflected such that its angle of incidence with respect to the principal axis is equal to its angle of reflection.
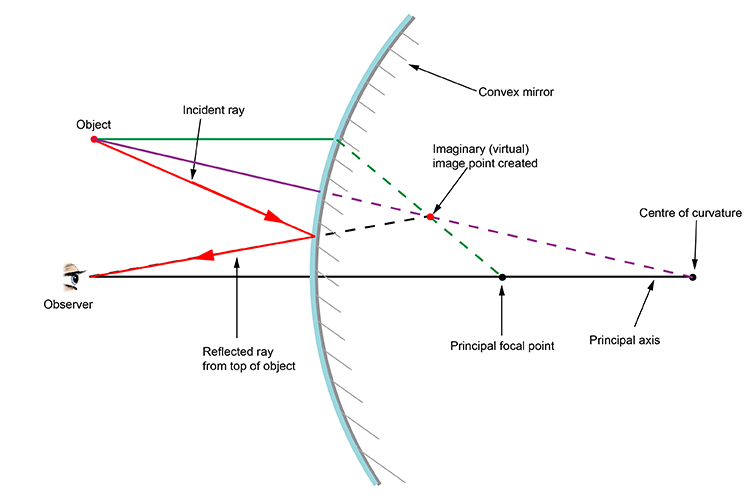
Convex
1. An incident ray which is parallel to the principal axis is reflected as if it came from the virtual focus of the mirror.
2. An incident ray which is directed towards the virtual focus of the mirror is reflected parallel to the principal axis.
3. An incident ray which is directed towards the centre of curvature of the mirror is reflected back along its own path.
4. An incident ray which strikes the mirror at its vertex is reflected such that its angle of incidence with respect to the principal axis is equal to its angle of reflection.
Concave mirror diagram
convex mirror diagram
Scientific Inquiry/ Investigation
Scientific Method
The scientific method is the process of objectively establishing facts through testing and experimentation.

Chemistry
Periodic Table
a table of the chemical elements arranged in order of atomic number, usually in rows, so that elements with similar atomic structure appear in vertical columns.
Bonding
Ionic
Occurs between metals and non-metals
Covalent
Electrons are shared between 2 non-metals
Steps for writing Ionic Formulas
1. Write the symbols of the 2 elements.
2. write the valance of each as subscripts.
3. drop the positive and negative signs.
4. crisscross the superscripts so they become subscripts.
5. reduce when possible.
Compounds
Ionic
Ionic compounds are compounds composed of ions, charged particles that form when an atom (or group of atoms) gains or loses electrons.
Molecular
Molecular compounds are chemical compounds that take the form of discrete molecules.
Diagrams
Bohr Rutherford
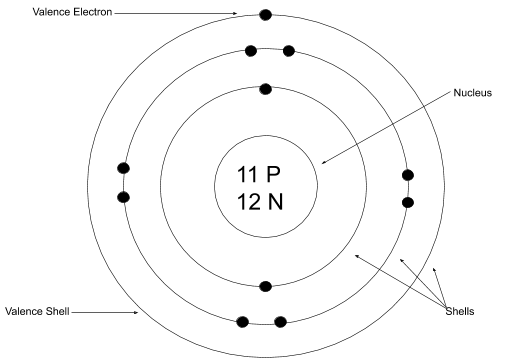
Lewis Dot

Reactions
Synthesis
A chemical process in which two or more simple elements or compounds combine to form a more complex product. It is represented by the equation: A + B → AB.
Decomposition
a reaction in which a compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances. The general form of a decomposition reaction is: AB→A+B.
Single replacement
when one element replaces another element in one compound. This type of reaction is represented by: A + BC → B + AC.
Double Replacement
occur when parts of two ionic compounds are exchanged, making two new compounds. The overall pattern of a double replacement reaction looks like this: A+B+C+D → A+D+C+B.
Chemical Formula
A chemical formula tells us the number of atoms of each element in a compound.

Equations
Converting
Step 1: Identify reactants and products and place them in a word equation. a
Step 2: Convert the chemical names into chemical formulas. Place them based on the chemical equation and write the state symbols. Step 3: Balance the chemical equation.
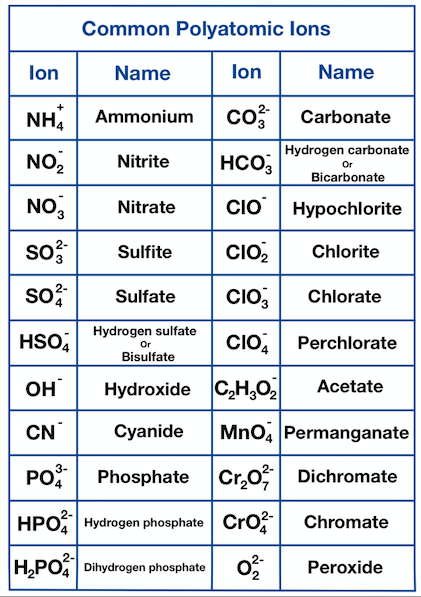
Polyatomic Ions
containing more than one and especially more than two atoms.
Cells/Systems of the Body
Systems
Skeletal
Supports the body, protects organs, movement, mineral and fat storage, blood cell formation and sound transmission.

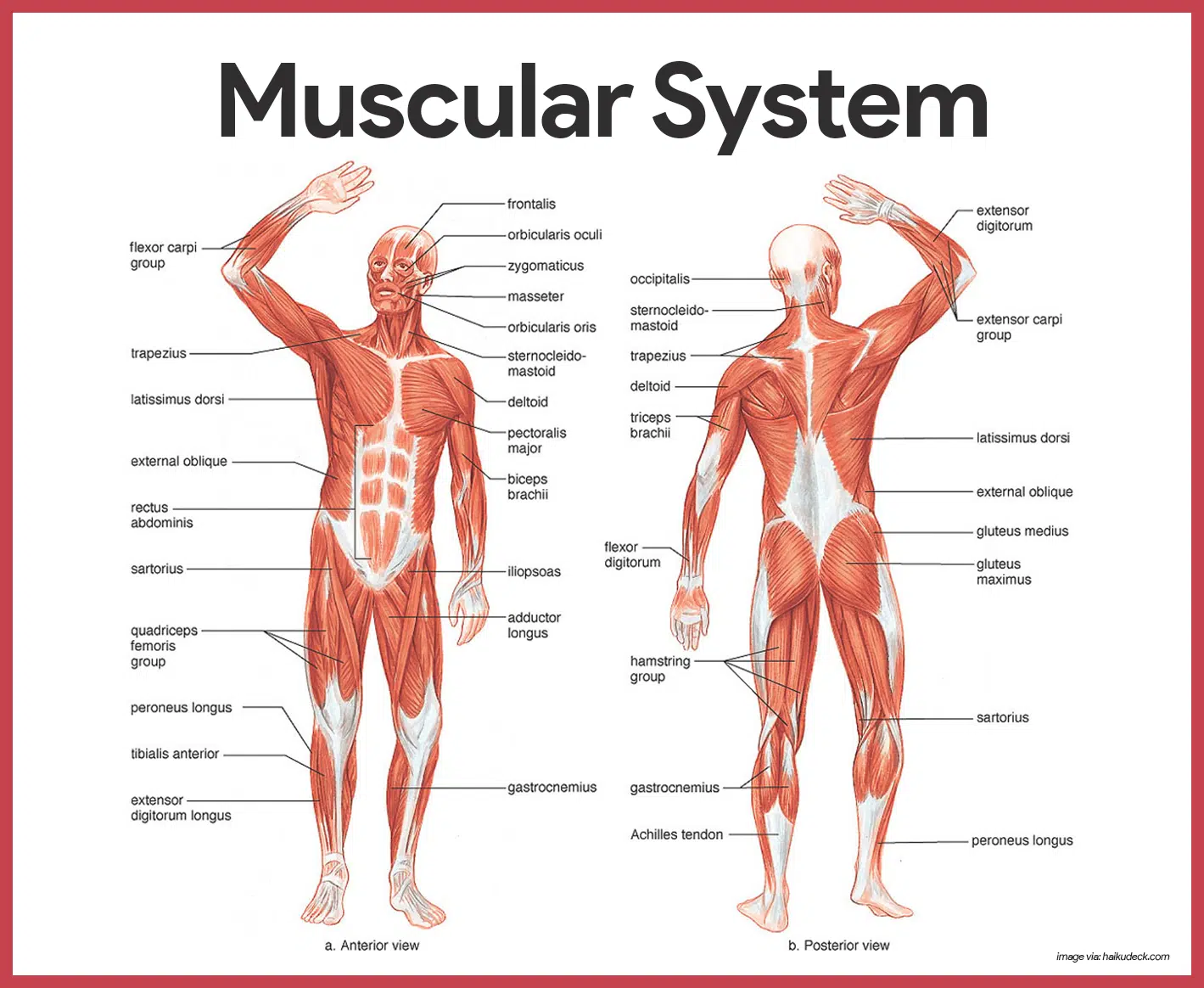
Muscular
Movement, maintains posture, generates heat, moves substances through the body, protects organs, stabilises joints.
Digestive
Turns food into nutrients then the body uses it for energy.

Respiratory
Take in oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide.

Cells
Plant
Plant cells have a cell wall, as well as a cell membrane. In plants, the cell wall surrounds the cell membrane. This gives the plant cell its unique rectangular shape.

Animal
Animal cells are the building blocks that make up all living organisms in the kingdom Animalia.

Mitosis
Mitosis is a process of cell duplication, in which one cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells.

Light
Types/Sources of lights
Types of light
Luminous
Any object that gives off its own light. (Sun, Stars, Torch, Candle, Fireflies)
Non-Luminous
An object that does NOT give off its own light. (Moon, Earth, Paper, Tree)
Sources of light
Natural
Light NOT made by human (Sun, Stars)
Artificial
Man made light (Light Bulbs, Torches, Fireworks)
Speed of light
299,792,458 meters/second
Electromagnetic Spectrum
the range of wavelengths or frequencies over which electromagnetic radiation extends.
production of light
Incandescent
An object heats up enough to emit light. (Sun)
Electric Discharge
Electricity passes through gas (Fluorescent light)
Phosphorescence
Emitting light after light has been shone on the object (Glow in the dark stickers)
-The object contains Phosphors which are particles that get excited and emit light.
Fluorescence
Emitting light while getting energy from another source. (Highlighters)
Chemiluminescence
Chemical energy is converted to light energy. (Glow sticks)
2 chemicals react and emit light -> Low Temperature
Bioluminescence
Living organisms produce light using chemicals in there bodies (Fireflies)
Climate Change
Water Pollution
Climate change is a long term change in climate and is a rise in global tempers.
Flooding
The overflow of water on regularly dry land.
Solar Panels
Solar panels are devices which are used to collect the sun's rays and convert them into electricity or heat.