LLS Typology
Oxford (1990)
It is according to purpose and use and based on research on cognitive & educational psychology.
Direct
Have direct impact with target language and require mental processing
Memory
Cognitive
Compensation
Indirect
Provide indirect support to language learning
Metacognitive
Social
Affective
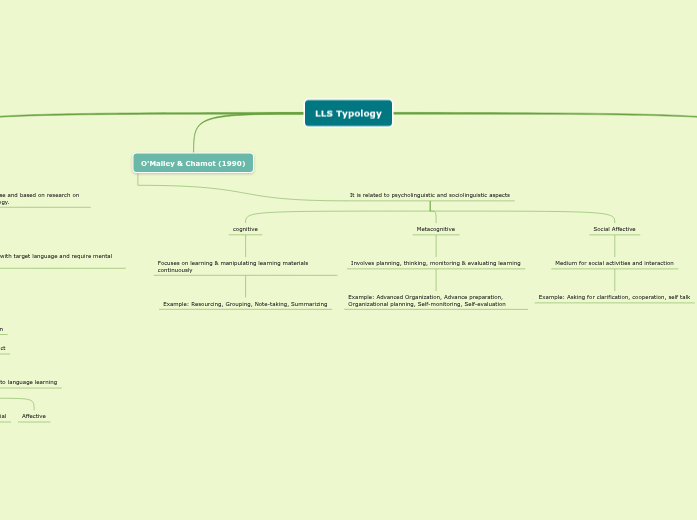
O'Malley & Chamot (1990)
It is related to psycholinguistic and sociolinguistic aspects
cognitive
Focuses on learning & manipulating learning materials continuously
Example: Resourcing, Grouping, Note-taking, Summarizing
Metacognitive
Involves planning, thinking, monitoring & evaluating learning
Example: Advanced Organization, Advance preparation, Organizational planning, Self-monitoring, Self-evaluation
Social Affective
Medium for social activities and interaction
Example: Asking for clarification, cooperation, self talk
Mohamed Amin Embi (1996)
It is based on influence of learning environment, setting and atmosphere.
Classroom LLS
Example: Sitting near to proficient students, asking for clarification, answer silently to oneself
Out-of-class LLS
Conversing with parents at home, discussing with friends after class, watch movies
Exam LLS
Joining group discussion, doing exercises in workbooks, memorising essay format