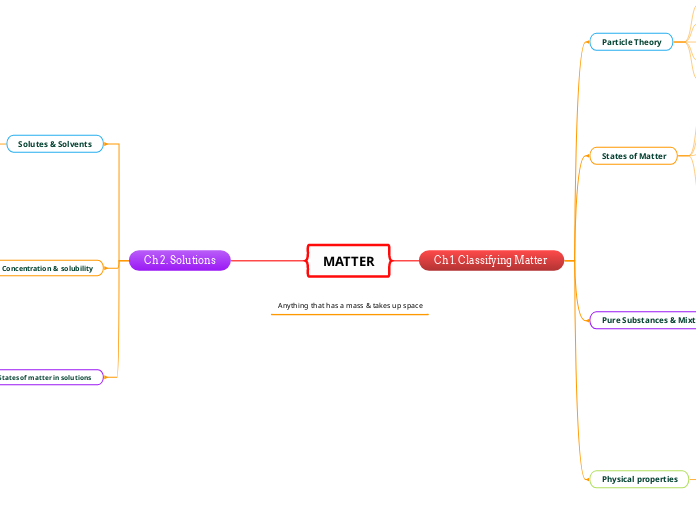
MATTER
Ch 1. Classifying Matter
Particle Theory
All matter is made of tiny particles
Paricles have empty space in between them
Particles are moving randomly all the time
Particles move faster & spread farther apart when heated
Particles are attracted to eachother
States of Matter
Solids
Particles have a definite shape and volume
Liquids
Particles have a definite volume, but not definite shape
Gases
Particles do not have a definite shape or volume
Changes in states
melting
Freezing
Boilling
Evaporation
Pure Substances & Mixtures
Pure Substances
A Type Of Matter That contains Only One Kind Of Particle
An example is salt
Mixtures
mechanical Mixtures
Also Heterogeneous Mixture
A mixture Where you Can see the Different kinds Of Particles
Granola bars are an example
A type of Matter That Contains More Than One kind Of Particle
Solutions
Also Homogeneous Mixture
A Mixture Where The Different Kinds of particles are mixed Evenly, Causing it To look Like a Pure Substance.
An example is apple juice
Physical properties
Properties of matter that we can observe without changing the substance
Examples: color, hardness, melting & boiling point
Ch 2. Solutions
Solutes & Solvents
Solutes
Dissolves in Solvent
Example: In sugar-water, sugar=solute
Solvents
Dissolves Solutes
Example: In sugar-water, water=solvent
Concentration & solubility
Concentration
Formula = amount of solute in g/100ml of solution
Concentrated solution=solution with a lot of solute particles
Dilute solution=solution with minimal solute particles
Concentration means amount of solute in the solution
Solubility
Formula=max amount of solute that will dissolve in g/100ml of solvent
Solubility is whether or not a solute can dissolve in specified substance
States of matter in solutions
Gaseous solutions
EX: the air we breathe
Liquid solutions
EX: iced tea
Solid solutions
EX: 14-karat gold