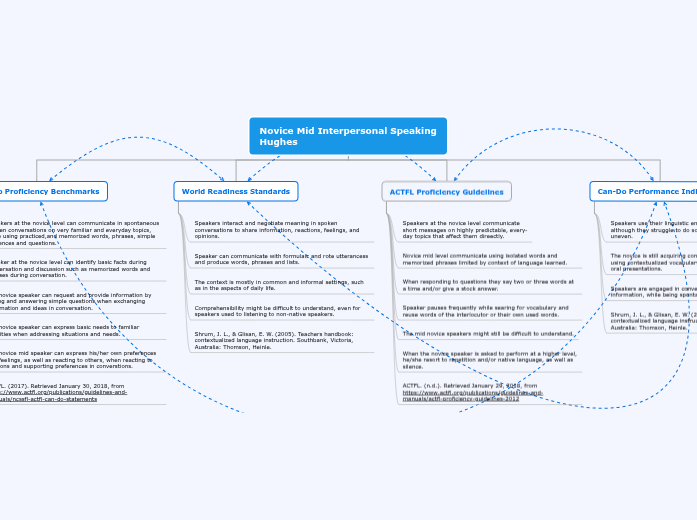
Novice Mid Interpersonal Speaking
Hughes
Can-Do Proficiency Benchmarks
Speakers at the novice level can communicate in spontaneous spoken conversations on very familiar and everyday topics, while using practiced,and memorized words, phrases, simple sentences and questions.
Speaker at the novice level can identify basic facts during conversation and discussion such as memorized words and phrases during conversation.
The novice speaker can request and provide information by asking and answering simple questions when exchanging information and ideas in conversation.
The novice speaker can express basic needs to familiar activities when addressing situations and needs.
The novice mid speaker can express his/her own preferences and feelings, as well as reacting to others, when reacting to opinions and supporting preferences in converstions.
ACTFL. (2017). Retrieved January 30, 2018, from https://www.actfl.org/publications/guidelines-and-manuals/ncssfl-actfl-can-do-statements
World Readiness Standards
Speakers interact and negotiate meaning in spoken conversations to share information, reactions, feelings, and opinions.
Speaker can communicate with formulaic and rote utterancess and produce words, phrases and lists.
The context is mostly in common and informal settings, such as in the aspects of daily life.
Comprehensibility might be difficult to understand, even for speakers used to listening to non-native speakers.
Shrum, J. L., & Glisan, E. W. (2005). Teachers handbook: contextualized language instruction. Southbank, Victoria, Australia: Thomson, Heinle.
ACTFL Proficiency Guidelines
Speakers at the novice level communicate
short messages on highly predictable, every-
day topics that affect them direectly.
Novice mid level communicate using isolated words and memorized phrases limited by context of language learned.
When responding to questions they say two or three words at a time and/or give a stock answer.
Speaker pauses frequently while searing for vocabulary and reuse words of the interlocutor or their own used words.
The mid novice speakers might still be difficult to understand.
When the novice speaker is asked to perform at a higher level, he/she resort to repetition and/or native language, as well as silence.
ACTFL. (n.d.). Retrieved January 29, 2018, from https://www.actfl.org/publications/guidelines-and-manuals/actfl-proficiency-guidelines-2012
Can-Do Performance Indicators
Speakers use their linguistic energy to sustain the level, although they struggle to do so. Performance might be uneven.
The novice is still acquiring concrete vocabulary in context and using contextualized vocabulary in short conversations and oral presentations.
Speakers are engaged in conversation and exchange of information, while being spontaneous.
Shrum, J. L., & Glisan, E. W. (2005). Teachers handbook: contextualized language instruction. Southbank, Victoria, Australia: Thomson, Heinle.