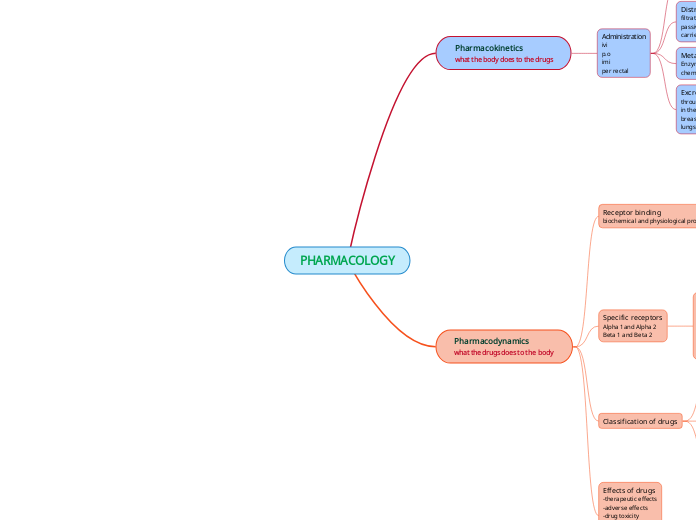
Administration
ivi
p.o
imi
per rectal
Absorption
1st pass effect(enterohepatic cycle
Distribution
filtration
passive diffusion
carrier -mediated transport
Metabolism /Biotransformation
Enzyme system
chemical reactions
Excretion
through urine
in the bile and faeces
breast milk
lungs
Receptor binding
biochemical and physiological processes
Transmembrane receptors
Transmit information from one side of the membrane
Enzyme receptor
they respond to extracellular signals of proteins that promote growth
Transport carrier receptor
they move particles through diffusion to increase the level of
transmitter sin blood stream
Storage receptors
present in nerve endings in which endogenous neurotransmitters are stored for binding
Specific receptors
Alpha 1and Alpha 2
Beta 1 and Beta 2
Alpha
more responsive to norepinephrine than epinephrine
smooth muscle contraction
pupil contraction alpha
Beta
more responsive to epinephrine than norepinephrine
smooth muscle relaxation
Classification of drugs
Agonist
they activate receptors and produce desired effects
eg morphine
Antagonist
they stops the action or effects of other drugs
eg naltrexone
Partial antagonist
they partially binds and activate given receptor
eg pentazocine
Effects of drugs
-therapeutic effects
-adverse effects
-drug toxicity
-drug intolerance
-drug dependence
-drug abuse