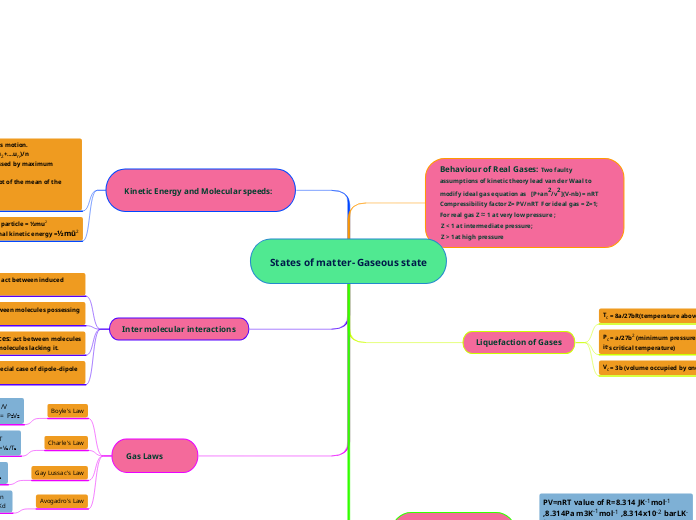
Molecules of gases remain in continuous motion.
Average speed of molecules, uav = (u1+u2+....un)/n
Most probable speed, ump: speed possessed by maximum number of molecules
Root mean square speed: The square root of the mean of the squares of speeds, urms= √ū2
urms > uav > ump
Kinetic Energy of a particle = ½mu2
Average translational kinetic energy =½mū2
Dispersion or London Forces: act between induced momentary dipoles.
Dipole-Dipole Force: act between molecules possessing permanent dipoles.
Dipole- Induced Dipole Forces: act between molecules having permanent dipole and molecules lacking it.
Hydrogen Bonding: It is a special case of dipole-dipole interactions.
Boyle's Law
P ∝ 1/V P₁V₁ = P₂V₂
Charle's Law
V ∝ T V₁/T₁=V₂/T₂
Gay Lussac's Law
p ∝ T P₁/T₁=P₂/T ₂
Avogadro's Law
V = Kn M = Kd
Tc = 8a/27bR(temperature above which gas can not be liquified)
Pc = a/27b2 (minimum pressure required to liquify a gas at it's critical temperature)
Vc = 3b (volume occupied by one mole of a gas at Tc and Pc)
PV=nRT value of R=8.314 JK-1mol-1 ,8.314Pa m3K-1mol-1 ,8.314x10-2 barLK-1mol-1 and 0.0822 atmK-1mol-1
Equation of state P₁V₁ = P₂V₂
T₁ T₂
Dalton's Law PTotal = P₁+P₂+P3+....... (at const. T,V)