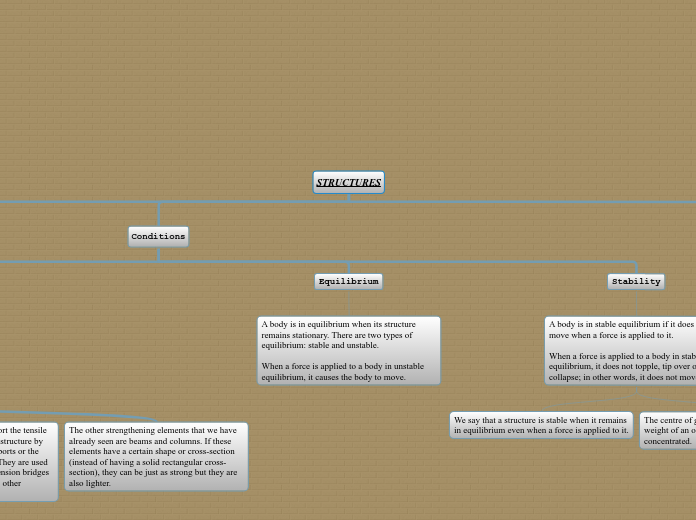
STRUCTURES
Basic definitions
Force
A force is an influence that can deform a body or change its movement, or produce motion in a body at rest
Stress
Stresses are the physical demands that a body or object must withstand when one or more external forces are applied to it
Strength
The strength of a material is its ability to withstand external forces without breaking.
Conditions
Rigidity
If a material is rigid, it does not change shape when force is applied to it. By contrast, if the material does change shape, we say that it is deformable.
Not all materials are suitable for building structures
Trussing is a method for making weak structures more rigid. It works because the triangle is the only figure that cannot be deformed. Therefore, structures that have a triangular shape are rigid.
By contrast, when a force is applied to a quadrilateral structure, it can be deformed because it is not rigid. How can we make it rigid? By adding a diagonal bar to the polygon, we divide the figure into two triangles, i.e. we triangulate the structure.
A brace is a part that is positioned diagonally between two bars to connect them by forming a right angle. It is used to reinforce and join together the elements of a structure.
Stay cables are used to help support the tensile stresses in other components of a structure by distributing the weight to the supports or the terrain where they are anchored. They are used in suspended structures like suspension bridges and they help to reinforce or truss other structures
The other strengthening elements that we have already seen are beams and columns. If these elements have a certain shape or cross-section (instead of having a solid rectangular cross-section), they can be just as strong but they are also lighter.
Equilibrium
A body is in equilibrium when its structure remains stationary. There are two types of equilibrium: stable and unstable.
When a force is applied to a body in unstable equilibrium, it causes the body to move.
Stability
A body is in stable equilibrium if it does not move when a force is applied to it.
When a force is applied to a body in stable equilibrium, it does not topple, tip over or collapse; in other words, it does not move
We say that a structure is stable when it remains in equilibrium even when a force is applied to it.
The centre of gravity is the point where the weight of an object is considered to be concentrated.
Types of strees
Compresion
This is caused by forces acting on a body that tend to flatten it or reduce its length or thickness
Tension
This is caused by forces acting on a body that tend to stretch it.
Bending
This is caused by forces acting on an element that make it curve or bend
Torsion
This is caused by forces acting on a body that make it twist
Shear
This is caused by two equal forces applied in opposite directions that act on lines of action close to each other.