TOURISM
RISK
Grammar
Modal Verbs
Subtopic
To refer to the past
Subtopic
Vocabulary
Type of risk
Natural
Avalanches

Hurricanes

Floods

Subtopic
Tsunami

Subtopic
Earthquake

Health
Infectious diseases
Pandemics
.jpg)
Personal Injuries

Subtopic
Skin Infections

Economic
Currency fluctuations

Recession

Rising fuel prices
Civil unrest
Demonstrations

Riots

Subtopic
Strikes

Subtopic
Crime
Fraud

Subtopic
Hijacking

Subtopic
Kidnapping

Subtopic
Risk prevention
Spread the risk
Monitor the risk
Warn the risk
Protected place
Enabled
Level of risk
Remote
Slight
Acceptable
Considerable
Huge
Adventure Sports
Bungee jumping

Subtopic
Horseback riding

Subtopic
Hot-air ballooning

Subtopic
Mountaineering

Subtopic
Subtopic
Potholing

Subtopic
Skiing

Subtopic
Skydiving

Subtopic
Whitewater rafting

Subtopic
Professional skills
Dealing with crises
Crisis Managment Plan
Before the crisis
Prepare your organization`s contingency plans for handling emergency situation
Identify the types of records that must be completed in the event of an emergency and how to complete and submit them
Develop a media communications strategy in the event of a major crisis
Anticipate every imaginable situation that might arise, man-made or natural, starting with those that are most likely to happen
During the crisis
Produce an immediate plan of action that prioritizes needs and is based on an accurate assessment on the emergency situation
Provide prompt and effective action to prevent escalation of the situation
Set up a hotline to keep relatives and friends adequately informed
After the crisis
Work out an action plan to make sure the disaster does not happen again
Conduct a post-crisis review to learn the lessons of the past
Facing the media
Be quick to relay the information at your disposal
Deal with the facts of the situation and express your concern
point out
State the facts relating to the location and casualties, as well as the history of such disasters
Inform all the measures you take to ensure the safety of your passangers or visitors
GASTRONOMY
Grammar
Relative Clauses
Defining and non-defining relative clauses
Vocabulary
Culinary tourism
Tempt the palate

Appeal to the sense of taste
Bland

having very little taste
Savour

Fully enjoy the taste or smell of food
Wine and dine

Entertain someone with an enjoyable meal
Palate

The sense of taste, especially the ability to
enjoy good food
Gourmet products

Excellent quality food and drink
Forked out

Spent
Whet the appetite

Increase the desire
Produced

Food that has been grown on a farm to be sold
Fare

The type of food usually servved in a restaurant
Describing food

Positive
Appetizing
Delicious
Done to a turn
Mouth-watering
Succulent
Tasty
Tender

Negative
Bland
Greasy
Insipid
Rancid
Ripe
Rotten
Tough
Ways of cooking food

Bake

Boil

Fry

Grill

Poach

Roast

Simmer

Steam

Stew
What makes a good restaurant?

Atmosphere

Background music

Décor

Food quality
Price

Service

Wait time
Professional Skills
Giving feedback
Create a dialogue
Listen attentively
Don´t assume you know
why a mistake has been
made
Ask questions
Choose the right time
Regular intervals
Don´t wait if something
important needs to be said

Put forward solutions
Channel the conversation
Listener can make progress
Recommendations for improvement

Use the feedback sandwich

Include positive feedback
mix negative comments with praise

Focus on the problem,
not the person
Make it clear that you are talking
about specific actions that could be
improved
Not criticizing
ORGANIZATION
A NEWS ORGANISATION
Departments in a Company

FINANCE
This department is in charge of cash flow, verifying and controlling prices, and making invoices.

HUMAN RESOURCES
This department is in charge of the health and safety of employees and the correct recruitment of future employees of the company.
MARKETING
This department is in charge of creating a recognized brand image and the promotion to the products or services offered by the company.
OPERATIONS
This department is in charge of quality control of the company's products or services and of the supply chain.
PRODUCTION
This department is in charge of manufacturing

SALES
This department is in charge of the costumer service
Jobs
Director of Human Resources
Has several strategic and operation priorities
Finance Supervisor
The most important thing about the job is to ensure that payments are made on time

News Edior
Gives a reporter the task of covering a news story.
Programme Director
Lead the production team. This job is similar to the conductor of an orchestra

News Reporter
Works with a camera operator to make sure they are getting the right pictures.
Expressions people use to talk about their jobs
Report to
I report to the IT Director
Head of
I´m the head of Sales.
Work closely with
I work closely with the Head of Marketing
Look after
I look after the company website
Take care of
I take care of the export decumentation.
Responsible for
I´m responsible for coordinating the production team.
In charge of
I´m in charge of the research and development team.
Coordinate with
I coordinate with all departments to ensure customer satisfaction
Organizational structures

Grammar
FUTURE FORMS
Subtopic
Subtopic
COMMUNICATION SKILLS
Managing First Meetings: Functional Language

Meeting and Greeting
-How's it going?
-[Did you have] a good trip?
-Can I get you [anything to drink]?
-[Good/Great/Lovely/Nice] to finally meet you in person.
-[Good/Great/Lovely/Nice] to see you again.
-So, first time in [London]?

Introducing People
-Let's go and [meet the rest of the team...]
-I'd like to introduce you to...
-Have you met [Miranda] before? She works for/works with/runs...
-Do you know [the design guys]?
-[Guys,] this is Stefanie.

Saying Goodbye
-Excuse me. [I must take this call].
-OK, so we need to leave it there.
-Sorry to [be in a rush like this/rush off so soon].
-Thank you for coming and have a [safe trip/good weekend]
BUSINESS SKILLS
Small Talk in First Meetings: Functional Language

Asking and Answering Questions

Offer help/Hospitality.
-Can I take your [coat/bag]?
-Can I offer you [something to drink/a coffee/a glass of water]?
-Can I order you a taxi?

Journey
-Did you have a good [flight/journey/trip]?

Experience
-Is it your first time [in the London office/at the conference]?
Place of work
-Where do you work exactly?
-Where are you based?
-Are you in the [Zurich] office at the moment?

Time with Company
-When did you join de company?

Colleagues
-Do you report to [Paul Blaetther]?
-Do you work with [Dave in the Mexico office]?

Socialising
-Are you free for [lunch today/dinner this evening]?
EMAILS - ORGANISING INFORMATION
Ordering Information in an email: Functional Language
Greeting/Opening
-Dear Sir/Madam...
-Good Morning...
-Hello/Hi...
Reason for Writing
-Just a quick email to let you know...
-I'm writing to inform you that...
Ordering Information
-Firstly
-Then
-Thirdly
-After that
-Finally
Concluding Email
-Let me know...
-Hope to hear from you soon.
-I look forward to hearing from you.
-Thank you for your email.
-Please do not hesitate to contact me if you have any questions.
Closing
-All the best.
-Yours,
-Kind regards,
-Regards,
-Yours sincerely,
Channels
Advertising
The obvious and the most complex aspect
of e-commerce and digital marketing
Ads are presented in many ways

Native ads
adds that appear to be part of the
content that the user is consuming
Retargeting ads
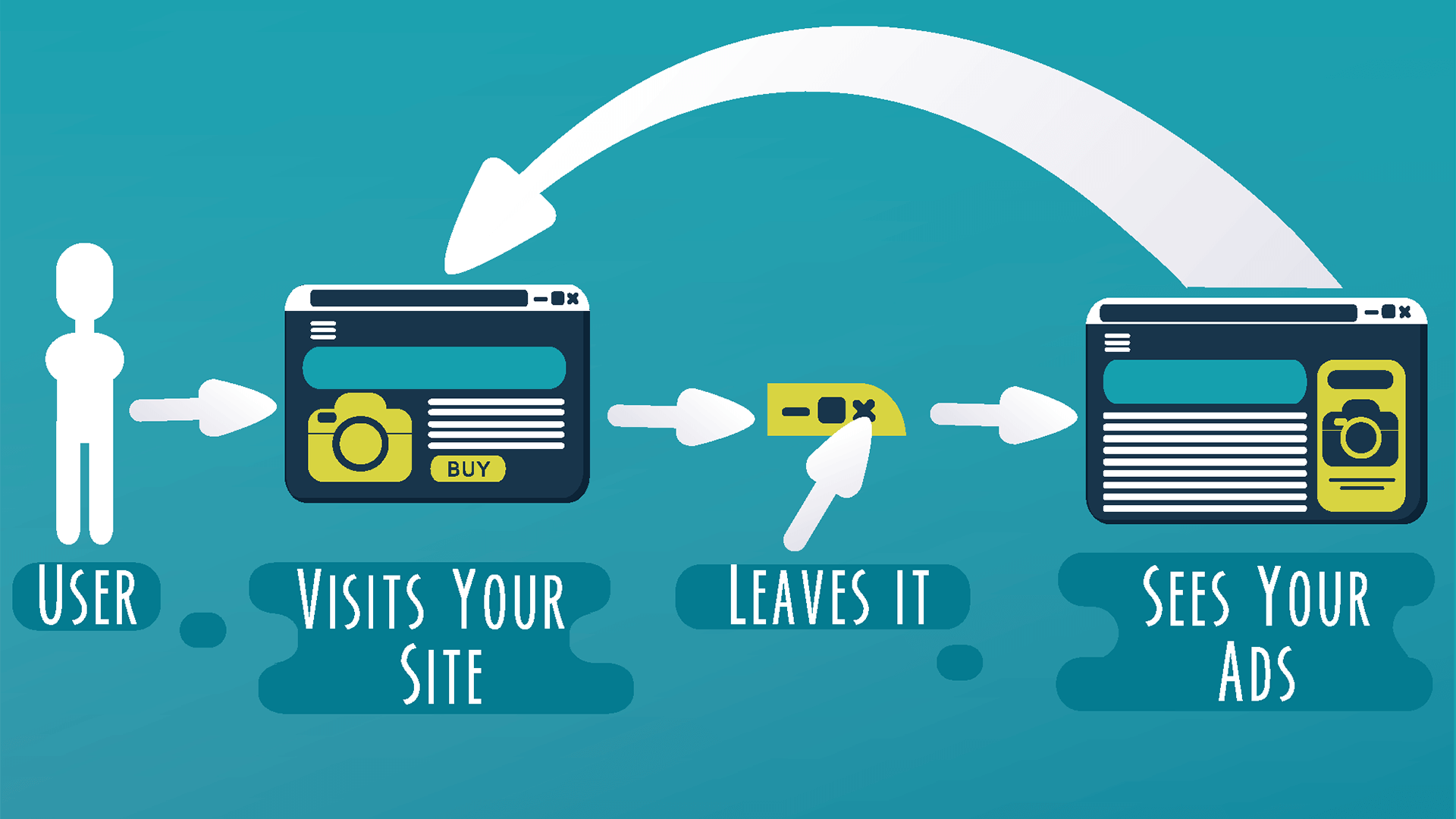
Auctioning

The internet created a market that brings
sellers and buyers together instantly
Mobile Commerce

A consumer´s mobile phone is the most
accesible device for stepping into the buying
circle that exists in the world nowadays
Social Commerce

To buy or sell via social media plattforms
messaging apps
Content used for customer attraction
on social sites
User-Generated Content

Created by
unpaid fans
Brand advocates
consumers
Can act as a
marketing
research
Giving valuable feedback
Giving new directions or
concerns that need to be
discussed
E-COMMERCE AND DIGITAL MARKETING IN PRACTICE.

SECURITY CONCERNS

Security of Your Electronic Transactions
Major risks associated with e-commerce and its security include:
1. Spoofing: create illegitimate sites that appear to be published by established organizations, to obtain information.
2. Unauthorized Action:alter your website and refuse to potential clients
3. Unauthorized Disclosure:Hackers intercept a transmission to obtain sensitive information
4. Data Alteration: The content of a transaction can be intercepted and altered.

Securing Your Web Site
Server ID: is the electronic equivalent of a buniness license
Certification authority (CA): issue the server ID to use the company name and Web address. Review credentials to ensure that organizations are what they claim to be.

Message Security
Secure sockets layer (SSL): is the industry-standard protocol for secure. The result is a secure communications channel between a server and a costumer.
Components of secure online transactions:
-Authentication: The costumer can verify that the Web site not belong to an impostor
-Message Privacy: SSL encrypts all information using a unique session key.

Message Integrity
When a message is sent, the sending and receiving computers generate a code. With message integrity both parties know that what they are seeing is exactly what the other party has sent.

E-Commerce Security Trends
Weak password and email attachments: most common methods that allow cybercriminals
Growth in Cyber Crimes: Cybercrimes are growing continuosly. Some motivations include corporate espionage, social justice and identity theft.
Types of malicious software or cryptoviruses that execute an unlawful act on an unsuspecting cyber victim:
-Ransomware: involves a threat to publish personal data in return for ransom.
-Malware: disrupts or damages computer systems or data within computer systems.
-Adware or Spyware: displays advertising materials.
Exploiting Social Commerce: Criminals will also use social platforms to spread fake news to manipulate stock prices for financial gain. Much social trust will be destroyed for these.
Zero-Day Exploits: A zero-day vulnerability refers to a hole in software that is unknown to the vendor. This is then exploited by hackers.
Fake Reviews: Hackers create fake news endorsing a product. Reviews make people buy things and if they are bad, people choose other product.
E-COMMERCE TECHNOLOGIES
Servers

Web server
Stores web pages
Provides the requested Web
pages to the end user
e-commerce server
Is used to handle everything, from
online reservations to purchasing

E-Commerce Web Apps and Tools
They will work together as a coherent strategy
for converting and retaining your atrracted
traffic.

Conversion Rate Optimization
Is the process or set of systems required to help you improve how many sites visitors decide to act on your various prompts and messages

Analytics
Is a system for finding, understanding and using important data and the patterns that will give your brand insight into how best to improve conversions and sales across the board


Social Sharing
The act of social sharing needs to be taken into account when creating your content

Browser Notifications
Powerfull method of attracting consumers back to yourr Web site and other media
Email Subscriptions
All a subscription requires is an email sign up page and permission from your consumer to become part of your list

Social Buy Buttons
Social Buy Buttons allow the consumer to buy something they like directly from the platform they are on from their own mobile phone, conveniently using a simple, direct buy button.
Live Chat
Live chat and multi-channel assistance offers consumers a reliable, convenient, and instant method of acquiring the answer to questions they need, to complete planning and make the purchase.
Dynamic Landing Pages
Dynamic Landing Pages are very useful because convince your target demographic to buy or act on your buying segments, according to what they want and what they searched for, they show the individual consumer exactly what they are looking for, using the media that will work best
Content Management and E-Commerce Platforms
Social Media

Subscriptions

Loyalty Programs
Inbound marketing
Affiliate Marketing

Internet of Things (IOT)

Messaging Apps and Chatbots
DIGITAL MARKETING
Introduction to the Topic of Digital Marketing and its Impact on Hospitality
When a hospitality brand markets online using digital technologies and online strategy- this is considered digital marketing.
Digital marketing has significantly impacted the hospitality space, making critical features like bookings, accommodation selection, and loyalty rewards delivery instant and easy for the consumer.
As the hospitality industry continues to innovate, so will marketing practices like SEO, search engine marketing, paid advertising, email and content marketing, reputation management, and Web analytics, which means that staying ahead of trends is key if you want to enhance your ability to sell online.
Practices to sell online
SEO
SEM
Paid Advertising
Media buying
Pay-per-click
Cost per action
Shopping Ads
Pay per view
Paid social advertising
Native Ads
Mobile ads
Retargeting
Email marketing
Content marketing
Video marketing
Podcasting
Conversion optimization
web analitics