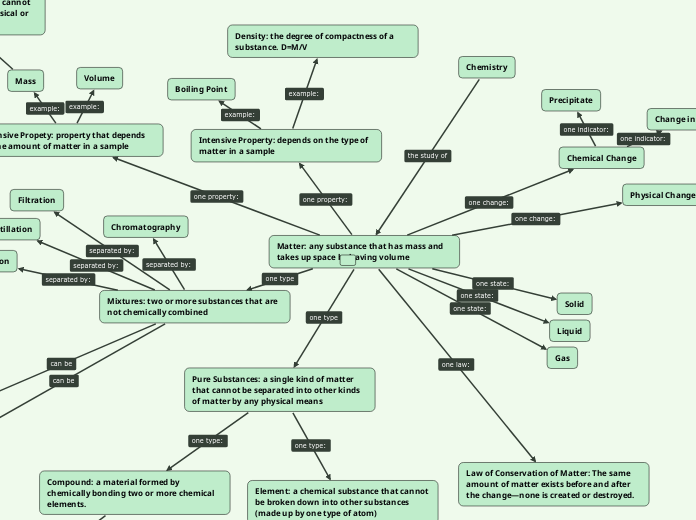
Chemistry
Matter: any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume
Mixtures: two or more substances that are not chemically combined
Heterogeneous Mixtures
Granite
Homogeneous Mixtures
Solution
Air
Alloy
Kool-Aid
Filtration
Distillation
Sublimation
Chromatography
Liquid
Pure Substances: a single kind of matter that cannot be separated into other kinds of matter by any physical means
Compound: a material formed by chemically bonding two or more chemical elements.
Sodium Chloride
Element: a chemical substance that cannot be broken down into other substances (made up by one type of atom)
Periodic Table of Elements
Neon
Silicon
Copper
Gas
Solid
Extensive Propety: property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample
Mass
law of conservation of mass: mass cannot be created or destroyed in any physical or chemical change
Volume
Physical Change
Chemical Change
Precipitate
Change in Color
Intensive Property: depends on the type of matter in a sample
Density: the degree of compactness of a substance. D=M/V
Boiling Point
Law of Conservation of Matter: The same amount of matter exists before and after the change—none is created or destroyed.