Blood
Heart
Blood vessels
Carry oxygen, nutrients and hormones to the cells and also removes waste products such as carbon dioxide.
What is?
It is a hollow muscular organ the size of the fist that is divided into four chambers (2 atriums and 2 ventricles).
Right side
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Tricuspid valve
Left side
Left atrium
Left ventricle
Mitral valve
Location
Is in the chest in the space between the lungs called the mediastinum.
It has 3 layers.
Epicardium
Myocardium
Endocardium
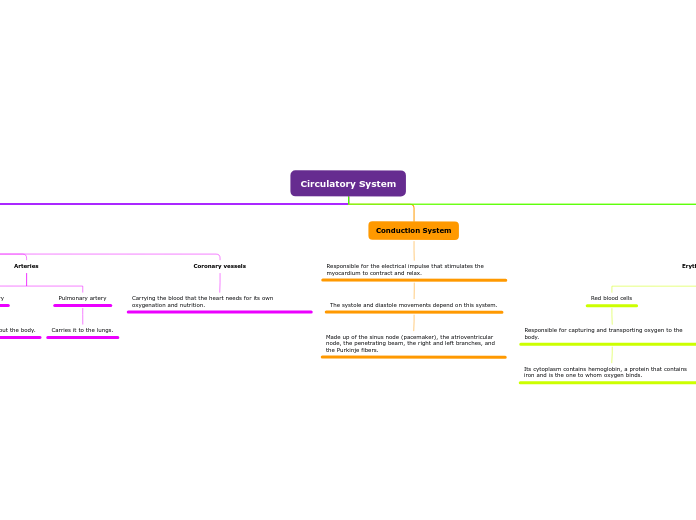
Arteries
Aorta artery
Carries blood throughout the body.
Pulmonary artery
Carries it to the lungs.
Coronary vessels
Carrying the blood that the heart needs for its own oxygenation and nutrition.
Responsible for the electrical impulse that stimulates the myocardium to contract and relax.
The systole and diastole movements depend on this system.
Made up of the sinus node (pacemaker), the atrioventricular node, the penetrating beam, the right and left branches, and the Purkinje fibers.
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells
Responsible for capturing and transporting oxygen to the body.
Its cytoplasm contains hemoglobin, a protein that contains iron and is the one to whom oxygen binds.
Types or blood groups
ABO system
A
B
AB
O
Rh system
Positive
Negative
Leukocytes
White blood cells
Are the defense cells.
Granulocytes
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
Agranulocytes
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
Platelets
Facilitate clotting by joining each other.
Actived
Form extensions and become sticky to be able to join and form the clot.
Circulatory system
Coronary artherosclerosis
Myocardial infarction
Heart failure
Arterial hypertension
Congenital heart disease
Cerebral vascular disease
Varicose veins
Blood
Anemia
Leukemia