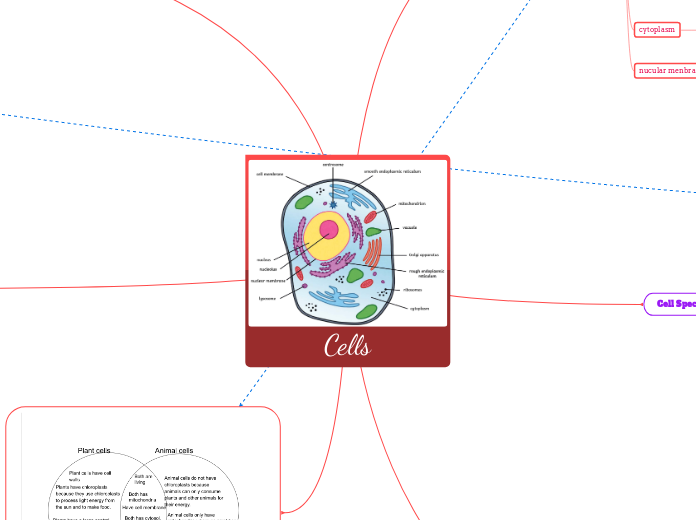
Cells
organelles
nucleus
serves both as the repository of genetic information and as the cell's control center.
cell wall
provids strength and structure for cell, also gives semi-pemuble surface for things to pass.
Cell membraine
the cell membraine is to protect the cell from its surroundings
mitochondria
Transfers water,glucose, oxgen and protins
chloroplasts
using photosynthesis it absorbs energy from the sun.
vacuole
To store food, waste and water for cells.
ribosome
Small structure that synthesizes proteins.
cytoplasm
thsi is for cell shape, material transport like genetic material and products for cellular respiration, and storage
nucular menbraine
this acts as a barrier that separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm.
Cell Specialization and Organization
What is cell specialization and how does it happen? Cell specialization refers to the unique structure and function of cells, resulting from the presence of different amounts of organelles. This allows for more complex organisms, larger growth, easier survival, and adaptability to diverse environments.
examples specialized cells in the human body:Blood cells, surface skin cells, Bone cells, Epithelial cells, Neurons, Cardiac muscle cells, Skeletal muscle cells,
organ systems in the human body
Skeletal system:gives the body structure and protects organs.
Muscular System: Suports the body and helps it move.
Digestive system: Breaks down food and absorbs nutrients.
Circulatory system: Helps to move nutrients and waste products into and out of your body.
4 basic types of Human tissue
Epithelial tissue: The layer of cells on the outside and inner body surfaces.
Connective tissues: Bones and cartilage.
Muscle Tissue: Made of cells that can get contract and helps your body to move.
Nervous Tissue: made of netrons cells that can send messages to many parts of the body. That includes the brain.
how organisms are organized from cell to organism: It goes from cell, to tissue, to organ to organ system .
Cells: cells are the basic building blocks if life. Cells can specialize and be different from each other.
Tissue: A tissue is a group of cells that have a similar function. they do the same job. For example, the lens in your eye.
Organs: Organs are structures that are made of two or more types of tissues working together to do a job. For example, your eye is an organ that has cells in the lens, it also has nerve cells and muscle cells to help it function properly.
Organ systems: Organ systems are made up of two or more different organs working together to do different jobs.
cell theory
There are 3 tenets of cell theory
All living things are composed of one or more cells.
Animal and Plants are made out of cells, even you are made
of cells. Some orgnisams can even be only one cell.
The cell is the basic unit of structure and function of living things.
Cells are the building blocks of living things, with different cells possessing unique organelles that enable them to perform specific functions.
All cells come from pre-existing cells.
In all living things, cells divide, or produce duplicates of themselves. Cells do not appear out of thin air.
Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms
Unicellular organisms: Unicellular organisms are Organisms with only one cell.Examples: Such as amoeba and bacteria.
How unicellular organisms eat their prey: An amoeba captures prey by stretching pseudopods from its membrane, wrapping them around the prey, creating a vacuole inside, and introducing enzymes to break down the prey.
Multicellular organisms: Multicellular organisms are organisms that have more than one cell.
how multicellular organisms are different from unicellular organisms, and what advantages or disadvantages they have:Multicellular organisms have specialized cells that enable them to have diverse tissues, become more complex, and grow larger. They can lose cells without dying. Unlike unicellular organisms which are limited to organelles in one cell and can die if the cell membrane is damaged however they are more simple.
diffusion and omosis
diffusion: DIffuison is when a more concentrated particle goes to a less concentrated area because partcles are bumping into each other so they are moving around
dynamic equilibrium: When Diffusion happens, the particle will continue mixing until it reaches dynamic equilibrium. dynamic equilibrium is when 2 sides are equal. even though it is equal, the particles will still moving,however the concentration will remain around the same .
some examples: spraying perfume into the air, scented candles, the smell of cooking spreading through the house, a drop of food colouring spreading in water. In all particles are mixing with the particles around it.
Osmosis: Osmosis is a special type of diffuson for water where water particles is moving through a semi-permeable surface to a place of lower concentration
Solvent and solute: This is when Water molecules travel over a semi-permeable membrane, moves them from an area of low solute concentration to one of high solute concentration.