Green Supply Chain Management
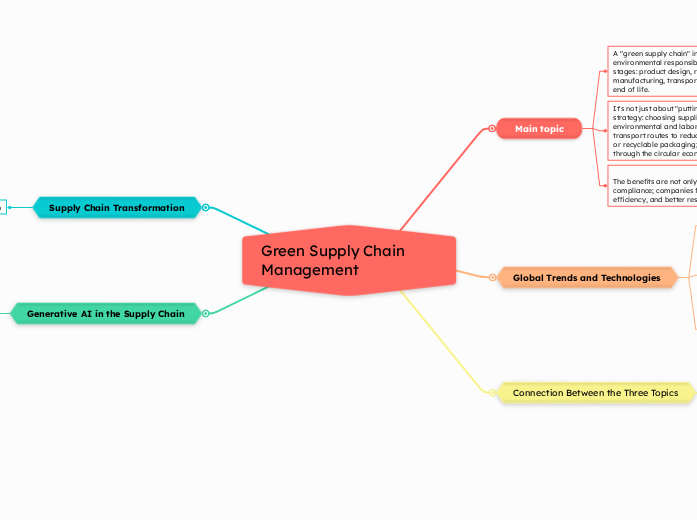
Main topic
A "green supply chain" involves integrating environmental responsibility principles into all stages: product design, raw material sourcing, manufacturing, transportation, distribution, and end of life.
It's not just about "putting on a green filter," it's a strategy: choosing suppliers that comply with environmental and labor standards; optimizing transport routes to reduce emissions, using lighter or recyclable packaging; and closing the loop through the circular economy.
The benefits are not only related to image or compliance; companies find savings, greater efficiency, and better resilience against disruptions.
Global Trends and Technologies
Total digitalization of the supply chain.
Key technologies:
Automation and robotics
Digital Twins (scenario simulation)
Blockchain (traceability and security)
IoT (sensors and real-time monitoring)
Objectives: resilience, visibility, speed, cost reduction.
Connection Between the Three Topics
Sustainability needs technology to measure and improve.
Technology drives efficiency and global competitiveness.
Generative IA combines data and decisions for a smart, flexible, and green supply chain.
Supply Chain Transformation
Green Supply Chain
Integrate sustainability throughout the entire process: design, production, transport, and recycling.
Focus on: emissions reduction, traceability, circular economy.
Challenges: initial investment, reliable data, coordination with suppliers.
Benefits: efficiency, reputation, regulatory compliance.
Generative AI in the Supply Chain
redicts demand, optimizes routes, manages risks.
Creates scenarios and "what-if" solutions.
Provides speed, accuracy, reduced waste.
Challenges: data quality, technological integration, specialized talent.