Macromolecules
Proteins
Amino Acids
A carboxyl group and
an amino group
As the monomer
subunit of proteins
Disulfide bridges
Peptide bonds
Peptides
Polypeptides
Denature
The loss of
Structure
Function
Beta-pleated sheet
Side by side of the
amino acid chain
Secondary structure
Alpha helix
A delicate coil held together
by hydrogen bonds.
Amino Acid
Non-protein component
Prosthetic groups
Protein function
Structural
Defensive
Signal
Carrier
Recognition &
Receptor
Enzyme
Motile
Movement
Actin & Myosin
Catalyst
Amylase
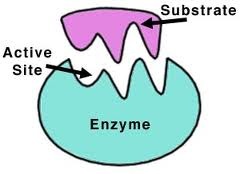
Speed up this reaction
Cellular Markers
Major histocompatibility
complex
Material transport
Hemoglobin
Messenger
Hormones
Fighting infections
Antibodies
Framework support
Ligaments
Structure
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
More than one amino
acid chain
3D-folding pattern
hydrogen bonds,
ionic bonds,
sulfur-sulfur covalent bonds,
hydrophobic interactions
H-bonds
in the peptide
amino acids to fold
in a repeating pattern
Sequence chain
of amino acids
Lipids
Energy sources
Insulation
Waterproofing qualities
Protection
Fatty acids
Carboxyl group linked
to a hydrocarbon chain
Stearic acid

Trans
One or more double
bonds in trans config.
Straight stucture
Fats
Saturated
Solid at room temp.
Straight structure
No double bonds
Unsaturated
Liquid at room temp.
Monounsaturated
One double bond (cis config.)
Bent structure

Polyunsaturated
Multiple double bonds
(cis config.)
More bent than monounsaturated

This specific example
is Linoleic acid
Triglycerides
3 fatty acid chains
linked to a glycerol
molecule

Triglyceride structure
Phospholipids
Steroids
Wax
Soft
Long fatty acid chains
Carbon rings
or alcohols
4 hydrocarbon
rings
Good
HDL
Regulates LDL storage
Promotes excretion
Bad
LDL
Storing cholesterol
in the bloodstream
Hormones, cholesterol,
membrane strength and
Vitamin D
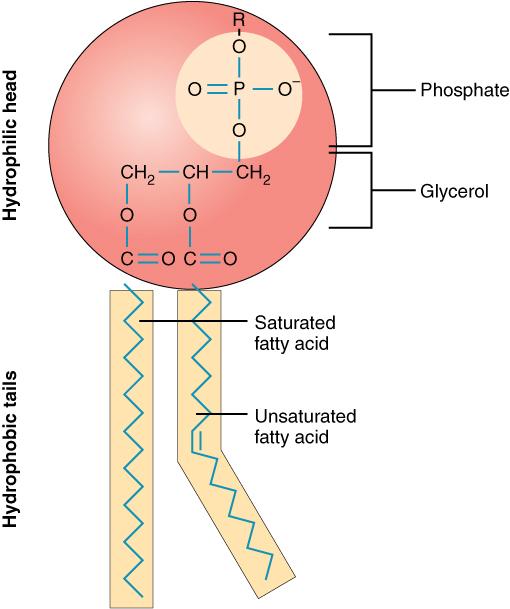
2 fatty acid chains
Hydrophilic head
Soluble in water
Flexibility and formation
Hydrophilic tail
Insoluble
Plasma membranes
Groups of polar lipids
Carbon, hydrogen
and oxygen atoms
Non-polar
Insoluble
Carbohydrates
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides
joined together
Dehydration synthesis reaction
2 sugar bases
Glycosidic Linkages
1-->4
1-->6
Branching structure
Linear structure
Beta
Orientation of the
-OH group
Alpha
Maltose
Lactose
Sucrose
Quick energy
Polysaccharides
Starch
Glycogen
Cellulose
Chitin
Structural complex carbohydrates
Storage carbohydrates
Amylopectin
80% of starch
1-->4, 1-->6 bonds
(linkages)
Short energy storage
Amylose
20% of starch
1-->4 bonds
(linkages)
Alpha glucose
Long energy storage
Energy source, structural
support and cell to cell
communication
Very long chain/branching chain
with alpha/beta linkages
Many bases
>10 sugars
Hydrolysis
Glucose
Energy
Condensation
Reaction
Joins monomers
together
Monosaccharides
Simplest form of a carbohydrate
Single sugar unit
Hexose sugar
Six carbon atoms
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
Forms a ring structure
Alpha Glucose
Glycogen in animals
1-->6 linkages
A branching structure
Short term energy storage

Glycogen structure
Starch in plants
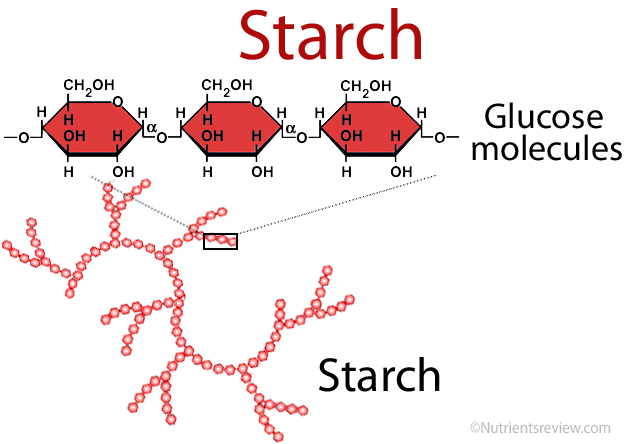
Starch structure
1-->4 linkages
Strong fibres
Hydrogen bonds
Beta Glucose
Cellulose in plants
Pentose sugar
Five carbon atoms
Deoxyribose
Ribose
Glycosidic bonds
Complex carbohydrates
100-1000s of linked
monosaccharides
Quick energy
Building blocks
Energy storage
(Short + Long Term)
Structural support
Cell-cell
communication
Carbon, hydrogen
and oxygen atoms
Polymerization
Subunits link to form
a large molecule
Nucleic Acids
Nucleotides
Building block of
nucleic acids
5-carbon sugar
Nitrogenous base
1-3 Phosphate groups
Pyrimidine
Uracil, thymine, cytosine
Purine
Adenine, guanine
ATP, GTP
Transport chemical energy
Phosphodiester bonds
Phosphate bridge
5'-carbon
3'-carbon
Deoxyribose sugar end
End with the
phosphate group
H bonds
Complementary strands
of nucleotides
"Assembly instructions" for
all proteins in living organisms
Backbone
Alternating sugar &
phosphate groups
RNA
Takes on a
variety of structures
DNA
Double helix shape
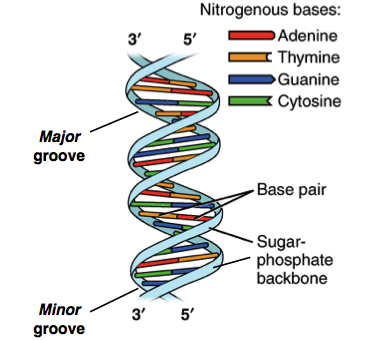
Double helix (DNA shape)
By base pairs
2 nucleotides
Organic molecules
Carbon in ring, or chain form
Covalent bonds

The -OH group placement

Sucrose structure

Lactose structure

Maltose structure
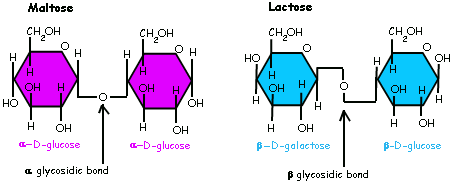
Glycosidic linkage
Cholesterol
Floating topic