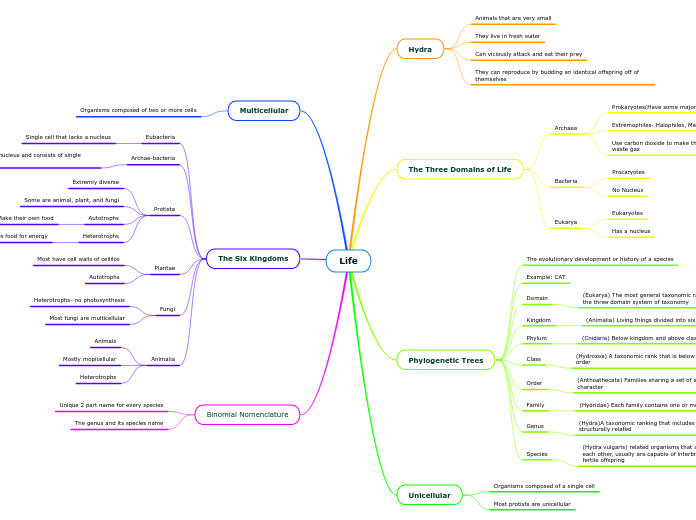
Animals that are very small
They live in fresh water
Can viciously attack and eat their prey
They can reproduce by budding an identical offspring off of themselves
Archaea
Prokaryotes(Have some major DNA instructor differences
Extremophiles- Halophiles, Methanogens, Thermophiles
Use carbon dioxide to make their energy instead and produce waste gas
Bacteria
Procaryotes
No Nucleus
Eukarya
Eukaryotes
Has a nucleus
The evolutionary development or history of a species
Example: CAT
Domain
(Eukarya) The most general taxonomic rank of organisms in the three domain system of taxonomy
Kingdom
(Animalia) Living things divided into six kingdoms
Animalia
Phylum
(Cnidaria) Below kingdom and above class
Chordata
Class
(Hydrozoa) A taxonomic rank that is below phylum and above order
Mammalia
Order
(Anthoathecata) Families sharing a set of similar nature or character
Carnivora
Family
(Hydridae) Each family contains one or more genera
Felidae
Genus
(Hydra)A taxonomic ranking that includes species that are structurally related
Felis
Species
(Hydra vulgaris) related organisms that are very similar to each other, usually are capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring
Catus
Organisms composed of a single cell
Most protists are unicellular
Organisms composed of two or more cells
Eubacteria
Single cell that lacks a nucleus
Archae-bacteria
Are prokaryotes that lack a nucleus and consists of single celled organisms
Protista
Extremly diverse
Some are animal, plant, and fungi
Autotrophs
Make their own food
Heterotrophs
Can consume other things besides food for energy
Plantae
Most have cell walls of cellilos
Autotrophs
Fungi
Heterotrophs- no photosynthesis
Most fungi are multicellular
Animalia
Animals
Mostly mopicellular
Heterotrophs
Unique 2 part name for every species
The genus and its species name