Blood
1.White Blood cells are immunity cells and they can eventually attack healthy cells and take over and cause issues like cancer such as they're other name leukocytes
2.Red blood cells are biconcave and they transport oxygen to he lungs and heart as well as all other parts of the body
3.Plasma Cells are the cells that distribute water and nutrients to your cells and tissues that need it
4. Platelet cells are cells that form blood clots and stop or prevent bleeding
Blood Vessels
Arteries: Are multi layered they are the thickets blood vessel and or vein and they are the vessel that carry blood away from your heart
Veins: Only blood vessel that contain valves they are all oxygenated other then your pulmonary veins and they carry blood back to the heart
Capillary's: Blood Vessels that are in charge of the exchange of materials and the meeting or link between the arteries and veins.
Heart
Our heart is a 4 chamber heart that pumps blood through our body. When tor heart pumps it makes two noises, The "lub" noise and the "dub" noise. when the "lub" noise is occurring it is when your tri and bi cuspid valves are closing. When the "dub" noise is happening your pulmonary valves and aortic valves are closing.
Pharynx
Carries air, food and fluid down from the mouth and nose.
Tongue
Facilitating the movement of food during mastication and assisting swallowing.
Esophagus
Moves food into the stomach
Lower esophageal sphincter
Allows food transit from the esophagus into the stomach and prevents the reflux of gastric contents back into the esophagus
Stomach
Holds the food and mixes it with acid and enzymes that continue to break the food down into a liquid or paste.
Small intestine
Helps to further digest food coming from the stomach.
Large intestine
Absorbs water and changes the waste from liquid into stool.
Rectum
Receives stool from the colon, sends signals to the brain if there is stool to be evacuated, and holds stool until evacuation can happen.
Anus
To detect rectal contents, whether they are liquid, gas or solid, and then control when stool should and shouldnt be excereted from your body
Mouth
Chews foodAllows food onto tongue
Sublingal salivary gland
Salivary gland located under the floor of the mouth
submond bular
contribute to the production of saliva which lubricates the oral cavity and aids in chemical digestion
salivary gland
Exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts
Bile duct
Helps digest fat
Gallbladder
Stores bile produced in liver
Liver
Stores glycogen as well as vitamin A, D, E KMakes bile which is stored in the gallbladderDetoxify poisons that are ingested (alcohol)
Duodenum
complete first phase of digestion
Jejunum
helps further digest food coming from the stomach
caecum
Beginning of large intestine (pouch)Located on right side of the body
Appendix
Hollow tube that is closed at one end and is attached to caecum at the other
Pyloric sphincter
ring of smooth muscle that governs the passage of food out of stomach into the small intestine
Chyme
Mass of food (bolus) that passes from the stomach into the small intestine
Pancreas
Produces enzymes, makes insulin and releases sodium bicarbonate
Transverse colon,Ascending colon, Decsending colon
Transverse colon: digestion and excretion of waste productsAscending colon: absorb the remaining water and other key nutrients from indigestible material Descending colon: stores feces that will eventually be emptied into rectum
Iluem
Final section of the small intestine
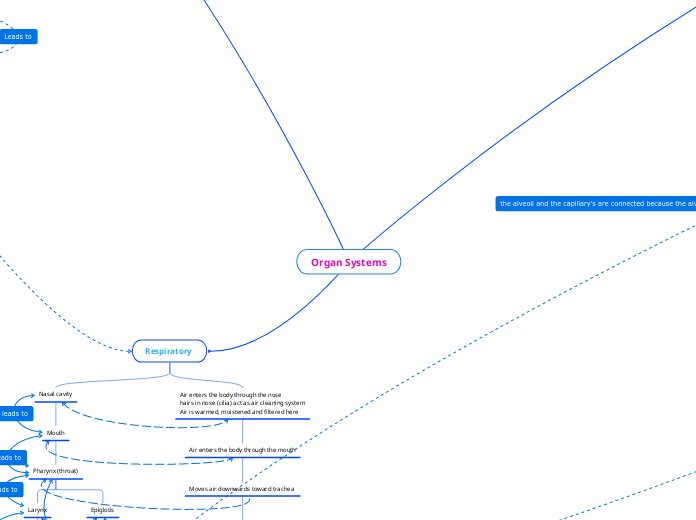
Nasal cavity
Mouth
Pharynx (throat)
Larynx
Trachea (windpipe)
Lungs
Left and Right Bronchus
Bronchioles
Alveoli
Diaphragm
Epiglotis
Air enters the body through the nose
hairs in nose (cilia) act as air cleaning system
Air is warmed, moistened and filtered here
Air enters the body through the mouth
Moves air downwards toward trachea
Conducts air in and out of trachea
Site of vocal cords
Made up of muscles and cartilage
Epiglottis allows air to enter larynx during swallowing
Presses downward and prevents food from entering air passages
(Windpipe) the trachea is wrapped in c shaped cartilage to protect and prevent its collapse
Air travels down the trachea until it reaches the bronchi
Encased by rib cage
Left lung has two lobes , right lung has three lobes
Each lung is surrounded by pleural membrane
Outer layer of membrane is attached to chest wall
Inner layer covers lungs
At the lungs the trachea divides into two bronchi (left and right) which are cartilaginous tubes
The two bronchi divide further into bronchioles
The bronchioles divide even further
Alveoli are small sacs that branch off the terminal bronchioles
It is estimated there are 150 million alveoli per lung
They are extremely thin (one cell thick)
Surrounded by capillaries
Site of gas exchange
Contracts and relaxes and the chest cavity enlarges
Contraction creates a vacuum which pulls air into the lungs
The diaphragm relaxes which makes it return to its dome like shape