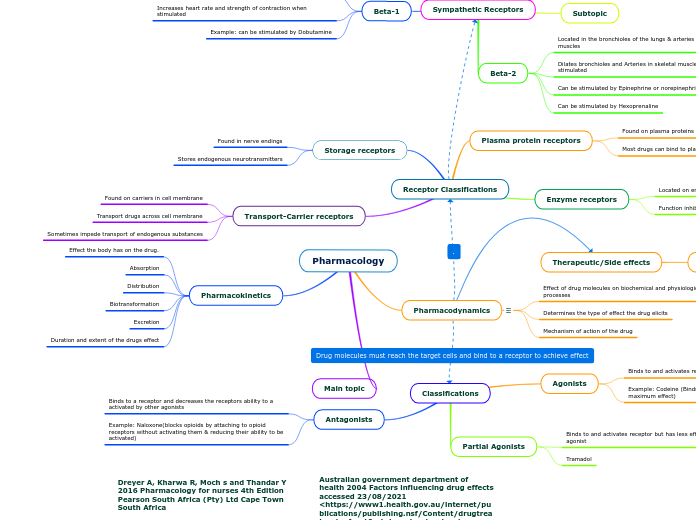
Effect the body has on the drug.
Absorption
Distribution
Biotransformation
Excretion
Duration and extent of the drugs effect
Dreyer A, Kharwa R, Moch s and Thandar Y 2016 Pharmacology for nurses 4th Edition Pearson South Africa (Pty) Ltd Cape Town South Africa
Effect of drug molecules on biochemical and physiological body processes
Determines the type of effect the drug elicits
Mechanism of action of the drug
Binds to and activates receptor
Example: Codeine (Binds tightly to receptors, produces maximum effect)
Binds to and activates receptor but has less effect than a full agonist
Tramadol
Binds to a receptor and decreases the receptors ability to a activated by other agonists
Example: Naloxone(blocks opioids by attaching to opioid receptors without activating them & reducing their ability to be activated)
Found on plasma proteins
Most drugs can bind to plasma proteins
Located on enzymes
Function inhibited when drugs bind to them
Found in nerve endings
Stores endogenous neurotransmitters
Found on carriers in cell membrane
Transport drugs across cell membrane
Sometimes impede transport of endogenous substances
Found in only arteries
Causes constriction of arteries when stimulated by Epinephrine or Norephineprine
Example: Stimulated by phenylephrine
Located in the bronchioles of the lungs & arteries of skeletal muscles
Dilates bronchioles and Arteries in skeletal muscles when stimulated
Can be stimulated by Epinephrine or norepinephrine
Can be stimulated by Hexoprenaline
Located in the heart
Increases heart rate and strength of contraction when stimulated
Example: can be stimulated by Dobutamine
Australian government department of health 2004 Factors influencing drug effects accessed 23/08/2021 <https://www1.health.gov.au/internet/publications/publishing.nsf/Content/drugtreat-pubs-front6-oh-toc~drugtreat-pubs-front6-oh-6~drugtreat-pubs-front6-oh-6-1>
aType of drug
Quantity of drug used
Method of administration
Gender, Mass
Drug interactions
Time taken to consume
Patient tolerance
Environment