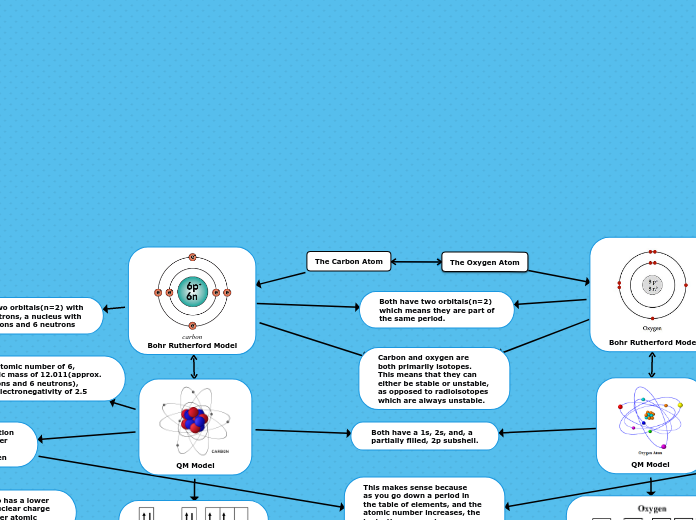
The Carbon Atom
The Oxygen Atom

carbon
Bohr Rutherford Model

QM Model
Carbon
Both have a 1s, 2s, and, a
partially filled, 2p subshell.
Has an atomic number of 6,
an atomic mass of 12.011(approx.
6 electrons and 6 neutrons),
and an electronegativity of 2.5
Has a lower ionization
energy but a greater
electron affinity
compared to oxygen
Carbon also has a lower
effective nuclear charge
and a greater atomic
radius than oxygen
Has two orbitals(n=2) with
6 electrons, a nucleus with
6 protons and 6 neutrons
Has 4 valence electrons making
it less reactive than oxygen
Carbon and oxygen are
both primarily isotopes.
This means that they can
either be stable or unstable,
as opposed to radioisotopes
which are always unstable.

Bohr Rutherford Model

QM Model
Has an atomic number of 8, an
atomic mass of 15.999(approx. 8
electrons and 8 neutrons) and an
electronegativity of 3.5
Has a greater Ionization energy and
a lower electron affinity than carbon
Oxygen has a greater effective nuclear
charge and a lower atomic radius than
carbon
Has two orbitals(n=2) with 8 electrons,
a nucleus with 8 protons and 8 neutrons
Has 6 valence electrons
making it more reactive
than carbon