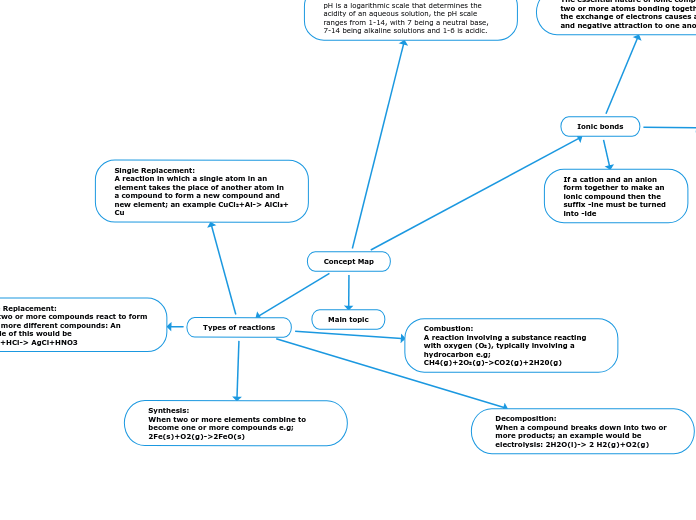
Combustion:
A reaction involving a substance reacting with oxygen (O₂), typically involving a hydrocarbon e.g;
CH4(g)+2O₂(g)->CO2(g)+2H20(g)
Synthesis:
When two or more elements combine to become one or more compounds e.g;
2Fe(s)+O2(g)->2FeO(s)
Decomposition:
When a compound breaks down into two or more products; an example would be electrolysis: 2H2O(l)-> 2 H2(g)+O2(g)
Single Replacement:
A reaction in which a single atom in an element takes the place of another atom in a compound to form a new compound and new element; an example CuCl₂+Al-> AlCl₃+ Cu
Double Replacement:
When two or more compounds react to form two or more different compounds: An example of this would be
AgNO3+HCl-> AgCl+HNO3
Stable Octet
This is an example of an Ionic bond where the Chlorine atom receives an electron becoming Chloride, satisfying the Chloride and Sodium's octets.
https://gyazo.com/d5dee62aecb70f6baa76b979798bb776
If a cation and an anion form together to make an ionic compound then the suffix -ine must be turned into -ide
The essential nature of ionic compounds is two or more atoms bonding together after the exchange of electrons causes a positive and negative attraction to one another.