Big Data
Is a term that describes large volumes of data, both structured and unstructured.It is also determined by data sets or combinations of data sets whose size (volume), complexity (variability) and speed of growth (velocity) make them difficult to capture, manage, process or analyze using conventional technologies and tools.
the characteristics of big data
The characteristics of Big Data are commonly referred to as the seven
Variety of data
The data received in a Big Data project is generally very diverse. This data can come from different sources and can be found in different formats. For this reason we need to integrate different technologies and applications to be able to organize, process and integrate the different data and to be able to draw effective conclusions or identify useful patterns.
Example
Social media data includes text, images, videos, links and comments.Sensor data can be temperature readings, pressure, geographic location, among others.

pressure readers
Veracity of the data
Veracity is the quality and reliability of the data we receive. Today, it is complex to ensure that all the information obtained is highly reliable and of optimum quality. For this, it is necessary to invest some time in trying to clean up and eliminate data that is not correct.
Example
Survey data may contain biased or inaccurate responses due to the subjectivity of human responses.Sensor data may contain errors due to technical problems or device failures.
Feasibility
Feasibility is the company's ability to manage and handle the large amount of data available to us. It is necessary that they have the appropriate skills, so that their use is as profitable as possible, both with appropriate technological programs and efficient work teams.
Data visualization
After data processing, visualization is the way in which we present the data, with the objective that this representation is done in a simple way so that anyone can access this data. Thanks to this representation, it is possible to detect hidden patterns that we would not have detected before.
Example
Line and bar charts are used to visualize trends and patterns in numerical data sets.Heat maps are used to visualize the density and distribution of geospatial data.
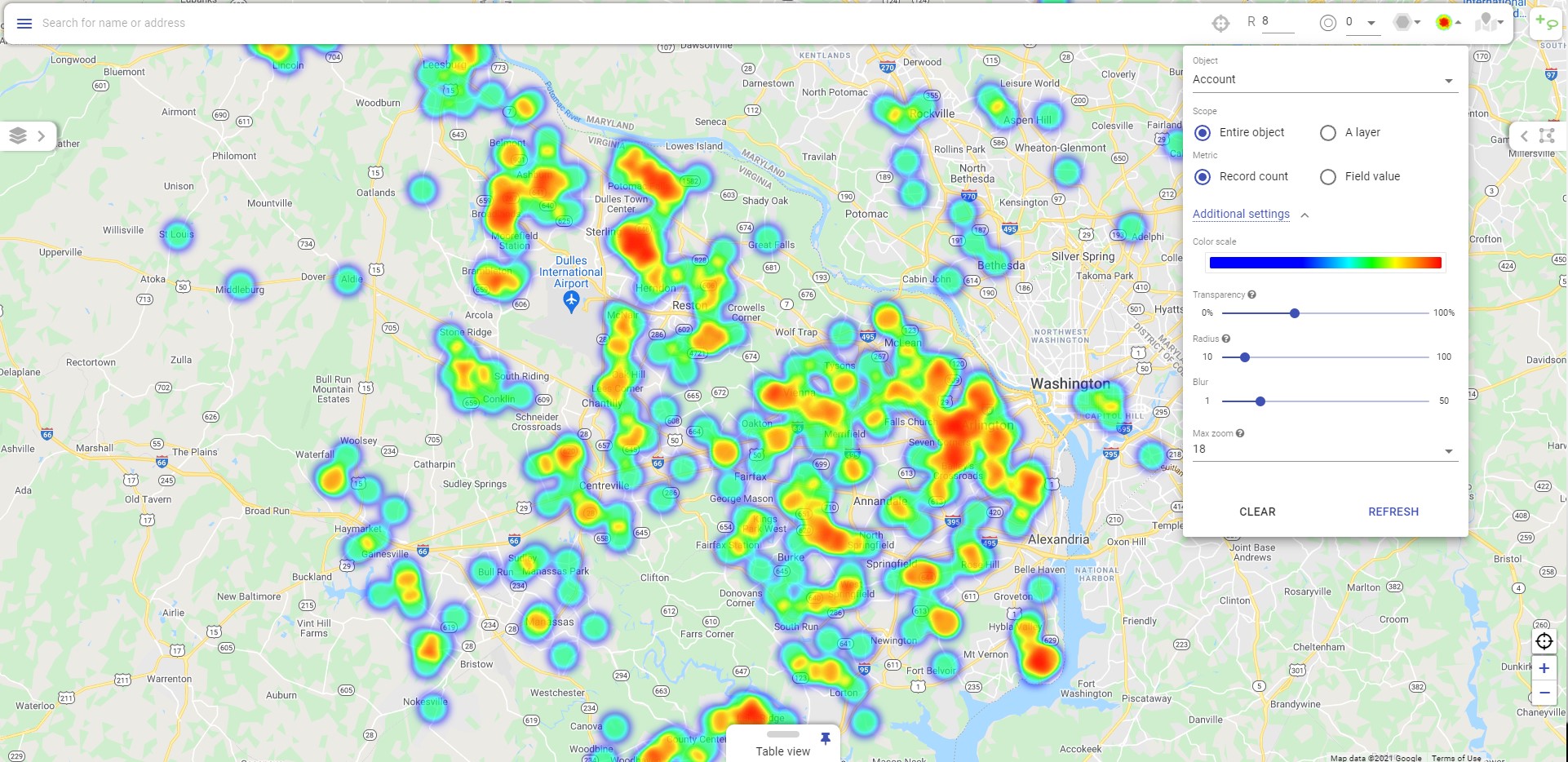
heat maps

line and bar charts

Data value
This feature is perhaps the most valued by organizations and businesses looking to improve. Once we have obtained the data and transformed it to make it readable, it is time to make useful and profitable decisions that can help us.Therefore, the value is the information obtained from the data, with which we can improve the benefits and performance of the business.
Example
Analysis of online shopping data can reveal patterns of consumer behavior and product preferences.Analysis of patient data in the healthcare field can help identify trends and improve treatments.
Volume
This characteristic refers to the large amount of data that is generated and available in our environment. In a Big Data project, the amount of information that is produced is enormous and keeps growing. As the databases grow in size, so do the applications and infrastructure designed to capture and store such data.
Examples
For example, a company that sells its products only through an online channel, it would be convenient to implement Big Data technology to process all the information collected on its website, tracking all the actions carried out by the customer; to know where he/she clicks most often, how many times he/she has gone through the shopping cart, which are the most viewed products, the most visited pages, etc.

iCloud
Human genome sequencing
Human genome sequencing can generate up to 200 gigabytes of data per individual
Velocity
We talk about the speed with which data is created, stored and processed. and processed. In some processes, time is of the essence and a delay in processing would be fatal. If data is not received, stored and processed in real time, it will become obsolete and its usefulness will be lost.
Examples

Financial transactions
Online financial transactions require real-time processing to detect fraud immediately.

Sensors in vehicles
Sensors in autonomous vehicles generate and transmit data at high speed to make real-time decisions.