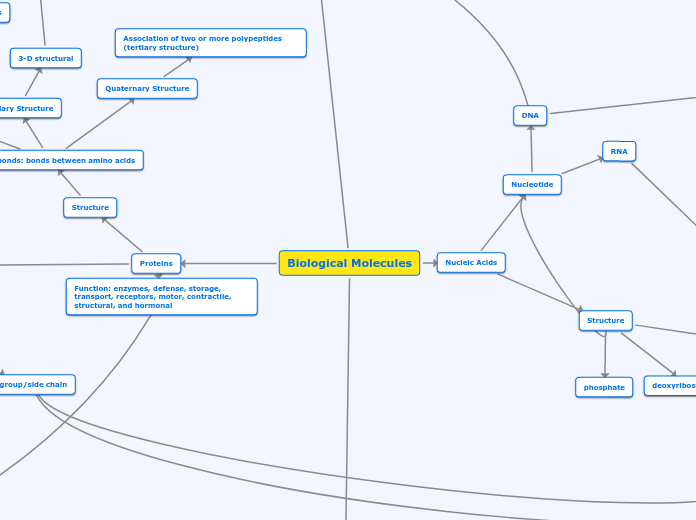
Function: enzymes, defense, storage, transport, receptors, motor, contractile, structural, and hormonal
Amino acids
Polar: hydrophilic
Nonpolar: hydrophobic
Acidic: (-) charge
Basic: (+) charge
Parts of an amino acid
Hydrogen
Amino group
Carboxyl group
r group/side chain
Structure
Peptide bonds: bonds between amino acids
Primary Structure
linear amino acid chain
DNA
DNA Replication: The division of DS DNA into 2 single-stranded pieces of single-stranded DNA
Enzymes
Helicase: Responsible for splitting DS DNA
DNA Polymerase I: Replaces RNA primer with complimentary nucelotides in 3'-5' direction
Topoisomerase: Relieves overwinding of newly separated DNA
SSB: Keeps single stranded DNA separated
Nuclease: Cuts out damaged/incorrect DNA
Primase: Responsible for laying primers in 5'-3'
DNA polymerase III: 5' to 3' polymerization of DNA
Ligase: Joins Okazaki fragments
Subtopic
ORI: Gene sequence that signals
for location of DNA replication
Replication fork: The corners of the separated DNA
Semi-conservitive
Template Strand: The original strand of DS anti-parallel DNA that is later separated into leading and lagging strands
Leading and lagging strands
Okazaki Fragments: DNA replicated on the lagging strand
Replication direction: DNA synthesized
in 5'-3' direction
Secondary Structure
H- bonds: Coils and Folds
Alpha helices
Beta pleated sheets
Tertiary Structure
3-D structural
different interactions to help it fold (different r groups)
Quaternary Structure
Association of two or more polypeptides (tertiary structure)
Function: Gives energy and support
Structure
Monosaccharides
Glucose: Type of monosaccharide made up of Oxygen, Hydrogen, & Carbon
Step 1: Glycolysis
Energy Investment Phase
Glucose to Glucose 6-phosphate using 1 ATP and hexokinase enzyme
Glucose 6-phosphate to Fructose 6-Phosphate using ezyme Phosphoglucoisomerase
Fructose 6-phosphate to Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate using ATP & enzyme phosphofructokinase
Enzyme aldolase makes 2 molecules of Glyceraldehyde 3- phosphate
Energy Payoff Phase
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate forms 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate using enzyme Triose phosphate dehydrogenase
2 NADH+ form 2 NADH
1,3-bisphophoglycerate from 3- phosphoglycerate with enzyme phophoglycerokinase
2 ADP to 2 ATP
Forms 2-phosphoglycerate with enzyme phosphoglyceromutase
Enolase helps remove 2 H2o molecules to make Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
Pyruvate kinase adds 2 p groups to ADP to from ATP to form 2 Pyruvate
Net: 2 pyruvate, 2 H2O, 2 ATP, & 2 NADH+
Disaccharides: 2 monosacchardies
Maltose: made from glucose+glucose
Sucrose: glucose+ fructose
Polysaccharides: Multiple monosaccharides
Storage
Glycogen
Starch
Dextran
Structure
Cellulose
Chitin
Function: energy storage and structure
Fat (Triacylglycerol)
1 glycerol group and 3 fatty acid groups connected
fatty acids
Saturated fats
Unsaturated fats
Steroids
Cholesterol
Testosterone
Phospholipid
1 glycerol group, 2 fatty acid groups, and a phosphate
Amphipathic: hydrophobic & hydrophilic regions
Makes phospholipid bilayer
Structure
phosphate
deoxyribose sugar
Nitrogen bases
purines
guanine & adenine
pyrimidines
cytosine uracil & thymine
Nucleotide
RNA
Gene Expression
Central Dogma
Transcription: Producing mature mRNA to carry genetic info out of the nucleus, into the cytoplasm to be used for translation
Promoter: Initiated by TATA box
& begins upstream
Transcribes downstream
Terminator: Ends transcription
RNA transcript: 5' cap and poly A tail
Pre-mRNA: Consisists of introns and exons
RNA splicing: Removes introns via lysosomes
RNA polymerase II: Moves in 3'-5' direction
and breaks DS
Transcription factors
Translation: mRNA codons coded by tRNA for protein and are produced via ribosomes
tRNA: Decodes mRNA into protein
anti-codon: Complimentary to codon
APE site: Where tRNA binds on ribosome
to make protein
Ribsosomes: Site of translation
Codons: 3 nucleotides that code
for amino acid
Protein released through stop codon
Aminoacyl tRNA Synthetase: Attaches correct
amino acid to its tRNA
Initiation, elongation, termination
Initiated by start codon
Subtopic
DNA
DNA Packaging
Metaphase Chromosome
700 nm
Looped Domain
300 nm
Fibers
30 nm
Nucleosomes
10 nm
Beads on a String
DNA wrapped around Histones twice
Linker DNA is Coiled
Histones
Histone Cores
H2A
H2B
H3
H4
Binds Linker DNA
H1
Heterochromatin
Tightly Packed
Genes Not Expressed
Euchromatin
Loosely Packed
Genes Expressed
Stages
Interphase
G1
Cell Growth & Accumulates
materials for DNA Synthesis
S
DNA Synthesis and Replication
G2
Synthesizes Proteins
for Cell Division
Mitosis
Prophase
Nucleoli Begins to Disappear
Chromosomes Begin Condensation
Centrosomes move to Opposite ends
Mitotic Spindle Begins to form
Prometaphase
Nuclear Envelope Degraded
Chromosomes Fully Condensed
Microtubules conect to Kinetochores
Metaphase
Centrosomes at Opposite ends
Chromosomes align in center
Anaphase
Sister Chromatids separated by Microtubules
Telophase
Spindle Fibers disperse
Nuclear Envelope forms around
Chromosome groups at Opposite poles
Cytokinesis
Cytoplasm Divides
End Result
2 Cells
Diploid (2n)
Identical
Somatic Cells
Stages
Interphase
G1
Cell Growth & Accumulates
materials for DNA Synthesis
S
DNA Synthesis and Replication
G2
Synthesizes Proteins
for Cell Division
Meiosis
Meiosis I
Prophase I
Homologous Chromosomes
pair up and Cross Over
Metaphase I
Homologous Pairs align in center
Anaphase I
Homologous Pairs separated by Microtubules
Telophase I
Nuclear Envelope forms around
Chromosome groups at Opposite poles
Cytokinesis
Cytoplasm Divides
Meiosis II
Prophase II
Nuclear Envelope disappears
Centrosomes move to Opposite ends
Mitotic Spindle Begins to form
Metaphase II
Centrosomes at Opposite ends
Chromosomes align in center
Anaphase II
Sister Chromatids separated by Microtubules
Telophase II
Spindle Fibers disperse
Nuclear Envelope forms around
Chromosome groups at Opposite poles
Cytokinesis
Cytoplasm Divides
End Result
4 Cells
Haploid (n)
Different
Sex Cells
Autosomes
22 Pairs (1-22)
Homologous Pairs
Sex Chromosomes
1 Pair (23)
NOT Homologous Pairs