Biology
cells
mitosis
Mitosis is cell division, it is done asexually
(by itself) it has seven phases;
Interphase: the cell grows and develops
Prophase: chromosomes start to form
Metaphase: chromosomes split to each side of the cell
Anaphase: spindle fibers attach to chromosomes
Telophase new nuclear membrane starts to form
Cytokinesis: mitosis is over and a new cell has been created
parts of the cell
both cells contain mostly the same
parts although there are a few differences
between animal and plant cells, notably
the presence of chloroplasts in plant cells.
asides from that, both cells contain; a cell membrane,
a rough ER and a smooth ER, microtubes, a nucleus,
cytoplasm, ribosomes, lysosomes, a vacuole, mitochondria,
chloroplasts, and a golgi body.
types of cells
Prokaryotes (single celled organisms)
Eukaryotes
(multiple celled organisms)
Animal cells
Plant cells
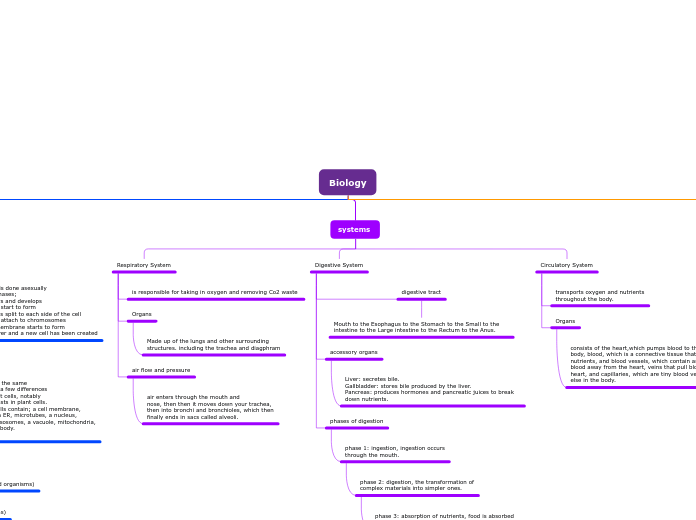
systems
Respiratory System
is responsible for taking in oxygen and removing Co2 waste
Organs
Made up of the lungs and other surrounding
structures. including the trachea and diagphram
air flow and pressure
air enters through the mouth and
nose, then then it moves down your trachea,
then into bronchi and bronchioles, which then
finally ends in sacs called alveoli.
Digestive System
digestive tract
Mouth to the Esophagus to the Stomach to the Small to the intestine to the Large intestine to the Rectum to the Anus.
accessory organs
Liver: secretes bile.
Gallbladder: stores bile produced by the liver.
Pancreas: produces hormones and pancreatic juices to break down nutrients.
phases of digestion
phase 1: ingestion, ingestion occurs
through the mouth.
phase 2: digestion, the transformation of
complex materials into simpler ones.
phase 3: absorption of nutrients, food is absorbed
in the intestines through villi and microvilli.
phase 4: elimination of waste, food is eliminated
the anus.
Circulatory System
transports oxygen and nutrients
throughout the body.
Organs
consists of the heart,which pumps blood to the rest of the body, blood, which is a connective tissue that is full of nutrients, and blood vessels, which contain arteries that push blood away from the heart, veins that pull blood back to the heart, and capillaries, which are tiny blood vessels everywhere else in the body.
plants
Plant Tissues
Vascular tissue
designed to transport water and minerals
throughout the plant.
Ground tissue
Manufactures nutrients, stores
carbohydrates, also contains the root and
and shoot systems of the plant.
Dermal tissue
Absorbs water, and is covered with
wax to waterproof the plant.
Plant Systems
Shoot system
Anchors the plant, absorbs water, stores food.
Root system
conducts photosynthesis and
reproduction.