Biology
animal systems
the hierarchy of structure in animals goes from most complex things at the top to most simple things at the bottom. In this case it'd be, organ system, organs, tissues, cells.
cellular differentiation is when cells become specialized to perform certain functions. stem cells are the beginning of this process when they are undifferentiated and then divide to form a specialized cell.
digestive system
its function is 1. it takes in food 2. digests food 3. excretes waste
the parts include the digestive track and accessory organs which includes the liver, pancreas, and gall bladder.

Circulatory system
its function is 1. transport substances around the body 2. move nutrients
its parts include the blood, heart, and blood vessels.

Respiratory system
its functions are 1. providing oxygen 2. removing carbon dioxide
its parts include, the lungs, nose, diaphragm, trachea, and bronchus.

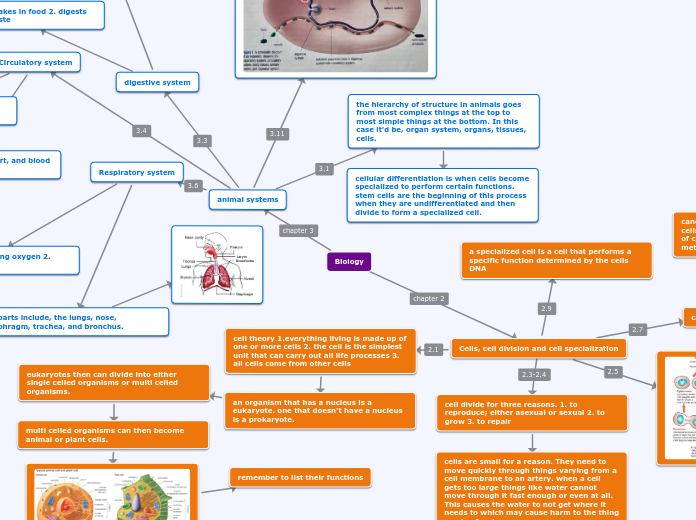
Cells, cell division and cell specialization
cell theory 1.everything living is made up of one or more cells 2. the cell is the simplest unit that can carry out all life processes 3. all cells come from other cells
an organism that has a nucleus is a eukaryote. one that doesn't have a nucleus is a prokaryote.
eukaryotes then can divide into either single celled organisms or multi celled organisms.
multi celled organisms can then become animal or plant cells.

remember to list their functions
cell divide for three reasons. 1. to reproduce; either asexual or sexual 2. to grow 3. to repair
cells are small for a reason. They need to move quickly through things varying from a cell membrane to an artery. when a cell gets too large things like water cannot move through it fast enough or even at all. This causes the water to not get where it needs to which may cause harm to the thing needy of water.
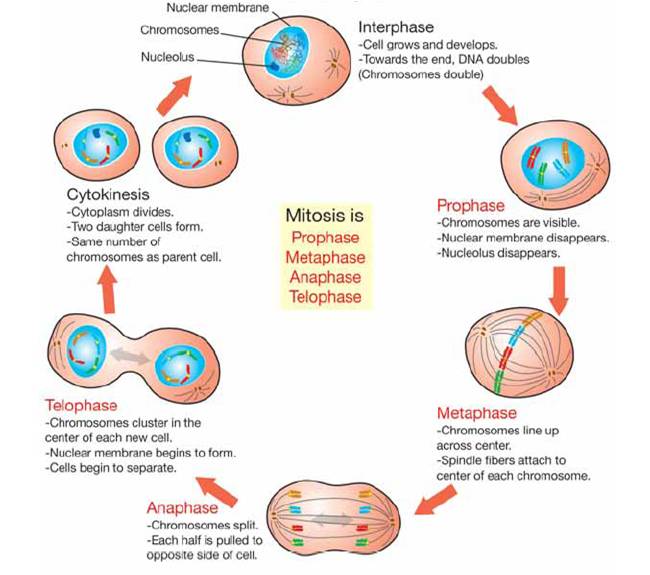
cancer
cancer in the mass growth of uncontrolled cells that form a tumour. Theres three types of cancer. 1. benign 1. malignant 3. metastasis
it can be caused by either a mutation or use of carcinogens.
to find out if someone has cancer they go to a cancer screening. there are many different tests for different parts of the body. these include pap test, endoscopy, x-ray, ultrasound, CT scanning and MRI.
treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and biophotonics.
a specialized cell is a cell that performs a specific function determined by the cells DNA
Chemistry
Chemicals and properties
A physical property is a description of a substance that does not involve forming a new substance. for example colour, texture, density, smell, solubility, taste, melting point, and physical state. A chemical property is a description of what a substance does as it changes into one or more substances. For example reaction of an acid with a base, flammability, bleaching ability, corrosion.
WHMIS means workplace hazardous materials information system and it provides Canadian workers with information on the safe use of hazardous project products. employers must provide this information; it can be conveyed by product labels or MSDS (as in material safety data sheets) and worker training.

A period is a row of elements in the periodic table. A group is a column of elements in the periodic table with similar properties.

Atomics radius (down, left) electron affinity (up, right)
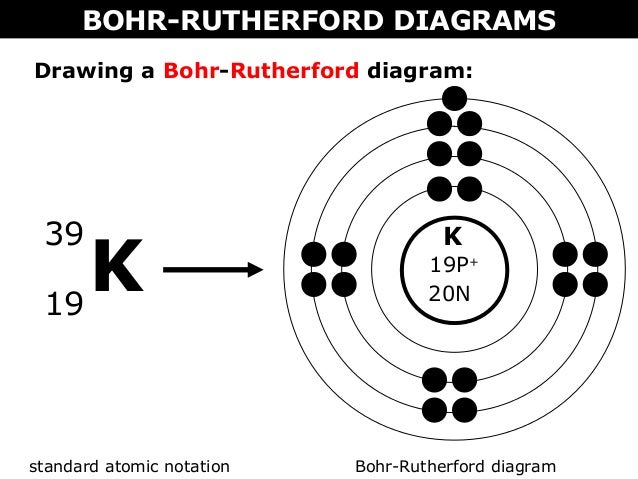
Ion is a charged particle that results when an atom gains or loses one or more electron.
a cation is a positively charged ion
an anion is a negatively charged ion

an ionic compound is a compound made up of one or more positive metal ions cations and one or more negative nonmetal ions.
to name an ionic compound it must have two parts. the first part is the metal ion and the second part is a non metal ion. the metal name stays the same, but you have to add "ide" to the end of the non metal ion. example, aluminium oxide.
A polyatomic ion is an ion made up of more than one atom that acts like a single particle.
to name it also has two parts: a metal and non-metal ion. Although this time the anion is named according to the polyatomic ion. example, iron (III) nitrate.
a molecular compound is a pure substance formed from two or more nonmetals.
molecular compound use prefixes for their naming. This means one atom is mono, two atoms is di- and so on. an example of this is carbon monoxide.
Chemicals and their reactions
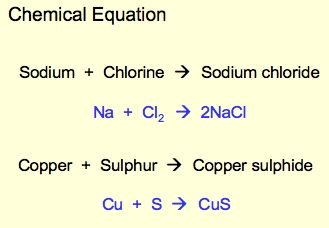
A chemical reaction is a process in which substances interact, causing the formation of new substances with new properties.
An arrow indicates the direction in which the chemical reaction is going the arrow is read as yields. Substances to the left of the arrow are called reactants. and substances to the right of the arrow are called products if several reactants are involved a plus sign is placed between them. If several products are formed a plus sign is placed between them. State symbols state of each substance for example s means solid.
The law of conservation of mass is, in any given chemical reaction the total mass of reactants equals the total mass of products.
example, H2 + Cl2 = HCl is incorrect because there is 2 H atoms and 2 Cl atoms but on the right side there is on of each. Although, if u make the equation H2 + Cl2 = 2 HCl, then it is balanced
There are five types of chemical reactions these include synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, and double displacement, and lastly combustion.
to balance equations you want to get an equal number of atoms on each side. example, Mg + 02 = MgO balanced is 2 Mg + O2 = 2 MgO because now there is 2 Mg and 2 O on each side of the "yields" sign. a greta method to use is the T method (shown below).

Corrosion is the breakdown of a metal resulting from reactions with chemicals in its environment only iron or metals with iron in it can rust.
Acids and Bases
A base is an equation solution that conducts electricity and always ends with a OH. example, NaOH, LiOH
An acid is an equation solution that conducts electricity, taste sour, and neutralizes bases. Acids always begin with H. example HCl, H2SO4.

Physics
The Production and Reflection of Light
A laser is a special type of light. it produces light waves at the exact same energy level, it a pure colour, its intense/focused and it doesn't spread out light normal light bulbs.
light can be produced a number of ways from different sources. These sources are called luminous, non luminous, incandescence, electric discharge, phosphorescence, fluorescence, chemiluminescence, bioluminescence, triboluminescence, and LED.
Light is what makes things visible. its an electromagnetic wave meaning it shows both electric and magnetic parts. it does not require a medium and it is the fastest thing in the universe.

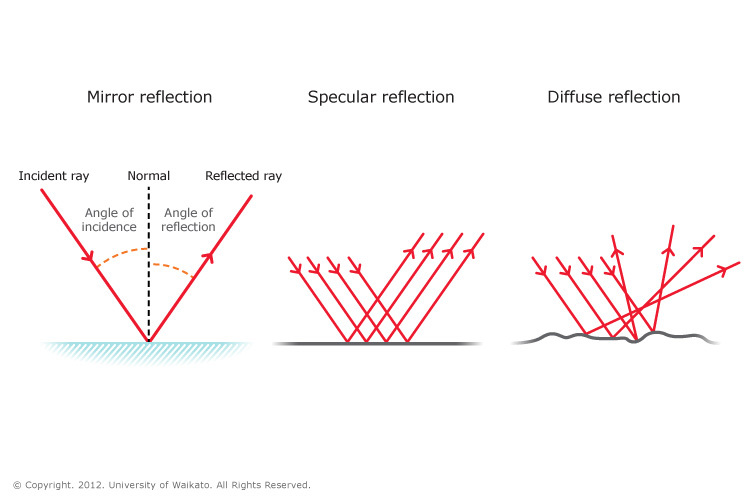
the laws of reflection are 1. the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection 2. the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane.
(How-to step by step) 1. the distance from the object to the mirror is exactly the same as the distance from the image to the mirror. in other words, the image appears to be located the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror. 2. the object dash image line is perpendicular to the mirror surface.
SALT stand for size, attitude, location, and type. We use salt characteristics to help find an image.
how-to step by step
how-to step by step
The Refraction Of light
to solve for index of refraction, just plug in the numbers into the equation n = c/v. this equations is also equal to n = sin angle or incidence/sin angle of the refracted ray. Use the GRASP method to help.
what is refraction? Refraction is the bending of light or change in direction of light when it travels from one medium into another. It caused by the changes of speed in these different mediums. the speed of light is 3.00 x 10(8) m/s and the speed of water is only 2.26 x 10(8) m/s which causes lights passing through to beng toward the normal.
two rules of refraction are 1. the incident ray refracted ray and the normal all lie in the same plane the incident ray and the refracted ray are on opposite sides of the line that separates the two media 2. light bends towards the normal when the speed of light in the second medium is less than the speed of the light in the first media and vice versa.
TIR or total internal reflection is the situation when the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle. TIR only occurs when these to things happen 1. light is travelling more slowly in the first medium than the second 2. the angle of incidence is large enough that no refraction occurs in the second medium. Instead the ray is reflected back. Fibre Optics uses TIR for phones computers and Tv's. Prisms also exhibit TIR for binoculars and periscopes.
refraction phenomena
apparent depth is a phenomena cause by refraction. an example of this could be a 'bent' pencil in water. another phenomena caused is mirages.
Lenses and optical devices
how does the eye work compared to a camera?

Lens equations


how does light behave through a lens?
how to locate the image