Body Systems
The Immune System
Thymus
Bone marrow
Secondary lymphatic tissues
Spleen
Lymph vessels
Lymph nodes
Adenoids
Skin
Liver
Technology Used to Benefit
Antibiotics
Antibiotics (or aka antibacterials) are very powerful medicines that aid the immune system in destroying infectious bacteria when they enter the body, although can't fight against viruses. They're used when there's an extreme amount of bacteria and the immune system becomes"overwhelmed", in which antibiotics are administered. There are many different types, but they mainly work in 2 ways: bactericidal or bacteriostatic antibody.
Bactericidal antibodies are ones that actively kill and destroy bacteria that's invading the body.
Bacteriostatic antibodies help keep the invasive bacteria from multiplying
Plasmapheresis
Plasmapheresis is a procedure that's done that filters the blood and specifically removes harmful antibodies from certain organs. It's a extremely helpful process as if a patient was receiving a kidney transplant but the body rejected it due to incompatible blood type, the antibodies produced by the immune system could possibly attack the foreign organ. However, if this process is used before the surgery, the antibodies from the recipient are removed, making it impossible for them to attack the foreign organ. This procedure can also be used to treat specific illnesses involving antibodies attacking their own organs, examples being Gullian Barre Syndrome, Wegner's granulomatosis, Goodpasture syndrome, and etc.
Malfunctions
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Antibodies produced by the immune system attack the thyroid gland, slowly destroying the cells that produce thyroid hormone. Low levels of thyroid hormone develop (hypothyroidism), usually over months to years. Symptoms include fatigue, constipation, weight gain, depression, dry skin, and sensitivity to cold. Taking a daily oral synthetic thyroid hormone pill restores normal body functions.
Gullian Barre Syndrome
The immune system attacks the nerves controlling muscles in the legs and sometimes the arms and upper body. Weakness results, which can sometimes be severe. Filtering the blood with a procedure called plasmapheresis is the main treatment for Guillain-Barre syndrome.

Diagram of the immune system
The immune systems purpose is to help defend and destroy our body against foreign bacteria, microbes, or chemicals and remember them. The reason they remember that information is that so in the future, if that specific type of bacteria enters the body again the immune system will know exactly what to produce to fight it.
The Excretory System
Kidneys
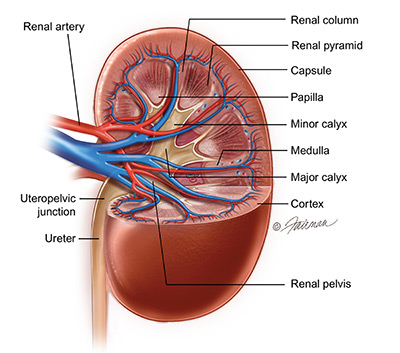
Diagram of the kidneys
Urinary bladder
Liver
Large intestine
Diseases
Kidney stones
Kidney stones form when urine become concentrated enough where certain chemicals become a solid mass (the stone) and can be found anywhere in the urinary system. Their size can vary from either small enough to flow freely through the urinary system to large enough where they cannot. Kidney stones can cause pain in the back and sides and this pain can range from very little to extreme pain.
Urinary tract infections
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) happen when a bacterial infection affects any part of the urinary tract and UTIs are more common in women (although they do happen to men too). Most infections aren't too serious, but certain infections can lead to serious issues. Long term kidney infections can permanently damage the kidneys, cause high blood pressure, and etc. Symptoms and signs for UTIs are when there's a burning feeling when you urinate, have a very frequent need to urinate even when you don't have a lot of urine, pain in your back or side below the ribs, cloudy, dark, bloody, or foul-smelling urine, fever or chills, and etc.
Technology used to benefit
Kidney dialysis
Kidney dialysis is a procedure that allows the body to filter waste out from blood using a machine. This process is used when a person develops end stage kidney failure (a point where their kidneys almost don't work anymore). How it works is that a machine filters waste, salt, and excess water using a artificial kidney and after the entire process is done, the blood is transferred back to the patient. This also helps control blood pressure, regulate certain chemicals in the body, and can be done in a hospital, a place with a dialysis machine, or in the patients home.
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy
(ESWL)
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) is a treatment used for kidney stones that are too large to be passed in urine. The method requires a ultrasound device to first detect where the stone is in the body. Ultrasound shock waves are then fired at the stone in order to separate it into smaller pieces so it can be released through urine. Painkillers are usually administered to the patient before the procedure as ESWL can be uncomfortable.
The excretory system serves to balance and remove waste buildup inside the body through the organs it contains. Liquid waste (urine) is disposed of via bladder while solid waste (feces) is removed by the large intestine.
The Respiratory System
Lungs
Larynx
Pharynx
Mouth
Nose
Bronchi
Trachea
Bronchioles
Alveoli
Diaphragm
Malfunction
Lung Cancer
With the ability to develop in any part of the lungs, this cancer is difficult to detect. Most often, the cancer develops in the main part of the lungs near the air sacs. DNA mutations in the lungs cause irregular cells to multiply and create an uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells, or a tumor. These tumors interfere with the regular functions of the lungs.
Bronchiectasis
Chronic bronchitis is a form of COPD emphasized by a chronic cough. Usually people cough up sputum (mucus from the lungs), especially in the morning. Dr. Meyer says this happens because mucus glands in the airways increase output, and patients have to cough that extra secretion out. Since chronic bronchitis is a form of COPD, it’s treated the same way. People can also develop acute bronchitis, which is not a long-term disease but rather an infectious problem. It develops from a viral or bacterial infection and can be treated with antibiotics. Symptoms associated with acute bronchitis will subside once the infection has resolved.
Asthma
Asthma is defined as a common, chronic respiratory condition that causes difficulty breathing due to inflammation of the airways. Asthma symptoms include dry cough, wheezing, chest tightness and shortness of breath. Dr. Meyer says there is a major connection between environmental allergies and asthma. Allergic reactions, infections and pollution can all trigger an asthma attack.
Technology Used to Benefit
Salbutamol
Salbutamol is a type of drug that helps relieve the symptoms of asthma and COPD like coughing, wheezing, feeling breathless, and etc. The medication comes in both inhaler form (usually blue), or it can come in tablets, capsules, or syrup for people that struggle using an inhaler. It can also be administered by a nebuliser, which is a machine that helps you breathe your medicine using a mask or mouthpiece and is used only if the asthma / COPD condition is severe. The regular way on how to use salbutamol inhalers is to have 1 or 2 puffs when it's needed, but up to a limit of 4 puffs in a single day.
Iron lung
An iron lung (or a negative pressure ventilator) was a machine that was used during the Polio outbreak around the world and functioned by creating a vacuum in the container which allowed the person inside to breathe. How it worked was that bellows attached to the side of the box would suck the air out of the box first and the loss of air pressure forced the patients lungs to expand, taking in air. The bellows would then allow air back inside the box and this action would cause the patients lungs to deflate, exhaling the air inside. This device saved thousands of people from dying due to Polio, but is not in use today as in 1950, a vaccine for Polio was created which caused the infected rates of the disease to drop rapidly.
Oxygen therapy
Oxygen therapy is a type of treatment that increases the amount of oxygen your lungs take in and deliver to your blood and is prescribed to patients that have certain condition where their blood oxygen levels are lower then the norm. Oxygen therapy can be given through a tube resting in the nose, a face mask, or a tube inserted in the patients trachea / windpipe. The oxygen can be stored as a gas or liquid in special tanks that can be delivered to the person home, but only contain a certain amount so they'll require refills. Although, another machine called a oxygen concentrator can be used and it functions by extracting oxygen from the air for immediate use.
Another type of oxygen therapy is called hyperbaric oxygen therapy which involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressured room / tube. How it works is that in a special chamber, the air pressure is increased to 3-4 times higher then regular air, which makes your lungs gather more oxygen by breathing. This procedure helps treat decompression sickness (a danger in scuba diving), infections, air bubbles in blood vessels, and wounds that can't heal due to certain conditions.
The Urinary System
2 Kidneys
2 Ureters
Bladder
Urethra
2 Sphincter Muscles
Bladder's Nerves
Technology Used to Benefit
Keflex (cephalexin)
Keflex (cephalexin) is an antibiotic that can help treat urinary tract infections and works by preventing bacteria from forming properly. In specifics, it works by stopping or slowing the growth of bacteria by making sure the cells can't create a cell-wall that surrounds them. This makes the bacterial cell vulnerable as the cell-wall helps protect the bacteria from the outside environment, keeps the contents together, and is vital in the cells survival.
Anticholinergics
Anticholinergics are a type of drug that helps treat urinary incontinence and works by blocking signals from acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter / chemical messenger that's in charge of transferring specific signals from cells to affect how the body works. How it works is that the drug blocks acetylcholine by binding their receptors on nerve cells, which inhibit certain actions called parasympathetic nerve impulses.
These impulses are responsible for muscle movements that you can't control in the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, and other areas of the body. Because this drug helps block those or decrease those specific muscle movements, it can help with an over-active bladder / incontinence, COPD, gastrointestinal disorders, asthma, dizziness, and etc.
Malfunction
Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is diagnosed in about 75,000 Americans each year and is more frequent in men and the elderly according. It is predicted that 81,190 new cases of bladder cancer (about 62,380 in men and 18,810 in women) and bout 17,240 deaths from bladder cancer (about 12,520 in men and 4,720 in women) will occur in 2018. The symptoms, including back or pelvic pain, difficulty urinating and urgent/and or frequent urination, mimic other diseases or disorders of the urinary system.
Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract; they can affect the urethra, bladder or even the kidneys. While UTIs are more common in women, they can occur in men In the United States, about 8.1 million people have a urinary tract infection each year.
The urinary system removes a type of waste called urea from your blood. Urea is produced when foods containing protein, such as meat, poultry, and certain vegetables, are broken down in the body. Urea is carried in the bloodstream to the kidneys. Then it goes through the rest of the organs in this system and exits through the urethra as urine
Nervous System
Neurnos
Axons
Dendrites
Brain
Spinal Cord
Nerves
Synapse
Technology Used to Benefit
Electroencephalography (EEG)
Electroencephalography (or EEG) is a test that's preformed to observe brain waves (electrical signals produce by nerve cells) in the brain. How the process generally works is by attaching small, flat metal disks called electrodes on your head that are connected to a recording machine via wires. The machine then converts the waves into patterns, which look like wavy lines, that can be transferred to a monitor or drawn. An EEG test can be helpful because it can identify the origin and type of seizures if you have them by uncovering where abnormal activities occur in the brain, causing the seizure. EEG's help to see weird brain waves caused by a head injury, stroke, or brain tumor and can help to see if the patient has dizziness, dementia, headaches, or sleeping problems. The process is also used to identify if someone is brain dead.
Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV) /
Nerve Conduction Study (NCS) test
A nerve conduction velocity (NCV) test is a test done to see how fast electrical signals travel through a nerve. The test is done by placing patches called surface electrodes onto different sections of the body in pairs. One of these surface electrodes produces a very gentle electric impulse, the second electrode records it, and then another electrode records the electrical activity from the other 2. The reason this test is done is to see what nerve damage / destruction is caused by and used to diagnose certain illnesses. Some of these illnesses include Guillain-Barré syndrome, Brachial plexopathy, Myopathy, Tarsal tunnel syndrome, and etc. NCVs are also used in tandem with Electromyography (EMGs) tests in order to see if there's a problem with the nerve specifically, or if the problem lies in the muscles not responding correctly to nerve signals.
Malfunction
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a chronic disorder, the hallmark of which is recurrent, unprovoked seizures. A person is diagnosed with epilepsy if they have two unprovoked seizures (or one unprovoked seizure with the likelihood of more) that were not caused by some known and reversible medical condition like alcohol withdrawal or extremely low blood sugar.
Alzheimer's
Alzheimer’s disease is an irreversible, progressive brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills and, eventually, the ability to carry out the simplest tasks. It is the most common cause of dementia in older adults. While dementia is more common as people grow older, it is not a normal part of aging.
The nervous system transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body, including internal organs. In this way, the nervous system’s activity controls the ability to move, breathe, see, think, and more. This system is split into 2 different parts. The central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS contains the spinal cord and the brain. The PNS contains mainly nerves that connect to every part of the body.
The Integumentary System
Skin
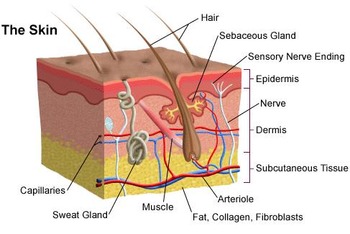
Diagram of skin
Sweat glands
Somatosensory receptors / nociceptors
Hair
Nails
Malfunctions
Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is an abnormal growth of skin cells, and the most common type is basal cell carcinoma. More than 4 million cases of basal cell carcinoma are diagnosed in the United States each year, according to the Skin Cancer Foundation. This type of cancer is skin colored, pink or has a slight pearly white color to it, and usually appears on sun-exposed areas of the face, ears or neck, according to the Mayo Clinic. It rarely spreads to other parts of the body, but it can be very problematic if it's not treated.
Eczema
Eczema looks like patches of red, itchy, bumpy skin, and the most common type is known as atopic dermatitis. The condition can occur anywhere on the skin. Sometimes, it flares up on its own, and at other times, it is caused by a specific trigger, such as a skin irritant like poison ivy, or exposure to an allergen.
Technology Used to Benefit
Acne cream / gel
Acne cream helps remove acne, which is when hair follicles become plugged with oil and dead skin cells, from the body. There are several different brands of acne cream or gel, 3 of them are Azelaic acid, Topical retinoids, and Topical antibodies. Azelaic acid functions by lowering the amount of Propionibacteria acnes (bacteria that causes the breakouts), regulating the shedding of dead skin, and decreases inflammation. Topical retinoids are a type of medication that comes from man-made vitamin A. They work by exfoliating the skin and unclogging pores extremely fast and helps prevent comedones. Topical antibodies help reduce acne by halting the growth of acne-causing bacteria, propioni acnes, lowering inflammation, and possibly unclog pores.
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid is used to help treat certain skin conditions like warts or acne. How it does this is that when applied, salicylic acid helps exfoliate skin and remove blackheads. It does this by loosening and separating desmosomes (connections between cells in the outer layer of skin), which encourages exfoliation of the skin and for pores to unclog. Salicylic acid is lipophillic which means it can go through oil skin to clean pores better and it's also anti-inflammatory.
The integumentary systems main function is to serve as the outer covering of the body, protecting it from infection, desiccation, abrasion, chemical damage, radiation, and etc. Organs in this system either serve to protect the body from infection, control certain factors in the body, or warn the body if something is dangerous.
The Endocrine System
Thyroid gland
Pituitary gland
Parathyroid gland(s)
Adrenal gland
Pancreas
Reproductive organs
Hypothalamus
Pineal body

Diagram of endocrine system
Technology Used to Benefit
Diabetic insulin
Diabetes insulin is used when a patient either has type 1 or 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is when beta cells, cells that produce insulin, in the pancreas have been damaged and can no longer make insulin. Type 2 diabetes is when the body can make insulin, but doesn't react to it properly. Both of these conditions require insulin shots in order to use glucose gained from food or other means.
Insulin for diabetes can come from animal fat or it can be genetically engineered from bacteria and works by allowing the body to convert the glucose from food into energy. Insulin can only be administered in shots below the fat of the body as if it was taken as a pill, it would be broken down during digestion. There several types of insulin, such as rapid-acting insulin, regular / short-acting insulin, intermediate-acting insulin, long-acting insulin, and ultra long-acting insulin.
Synthroid
(levothyroxine sodium tablets)
Synthroid (levothyroxine sodium tablets) is a man-made drug that helps treat the disease hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism is when your thyroid can either no longer produce or doesn't produce enough thyroid hormones and can lead to the body being more sensitive to the cold, gain weight, and be more fatigued then usual. Synthroid helps treat this condition by acting as "substitutes" for the thyroid hormones the body missing due to the condition. The main component in Synthroid is levothyroxine sodium, which is a man-made hormone that's identical to the hormones the thyroid produces, thyroxine.
Malfunctions
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer occurs in the cells of the thyroid — a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of your neck, just below your Adam's apple. Your thyroid produces hormones that regulate your heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature and weight.
Type 1 and 2 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is also called insulin-dependent diabetes. It used to be called juvenile-onset diabetes, because it often begins in childhood.Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition. It's caused by the body attacking its own pancreas with antibodies. In people with type 1 diabetes, the damaged pancreas doesn't make insulin. This type of diabetes may be caused by a genetic predisposition. It could also be the result of faulty beta cells in the pancreas that normally produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes is often a milder form of diabetes than type 1. Nevertheless, type 2 diabetes can still cause major health complications, particularly in the smallest blood vessels in the body that nourish the kidneys, nerves, and eyes. It also increases your risk of heart disease and stroke.
The main function of the endocrine system is to produce and release hormones into the bloodstream and these hormones help regulate metabolism, growth, tissue function, sexual function, reproduction, sleep, mood, and etc. The endocrine system also controls how much of the hormones get released to a part of the body as well.
The Reproductive System
Male System
The Penis
The Scrotum
The Testicles
The Epididymis
The Vas Deferens
The Urethra
Diagram of a Penis
Seminal Vesicles
Prostate
Unlike the female reproductive system, most of the male reproductive system is located outside of the body. These external structures include the penis, scrotum, and testicles. Penis: This is the male organ used in sexual intercourse.
Female System
The Vagina
The Cervix
The Uterus
The Fallopian Tube
The Ovaries
The Clitoris
The Bartholin’s glands
The Labia minora(Small Lips)
The Labia Majora(Large Lips)
A female's internal reproductive organs are the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. The vagina is a muscular, hollow tube that extends from the vaginal opening to the uterus. The vagina is about 3 to 5 inches long in a grown woman.
Malfunction
STD and STI
Having an STI means that an individual has an infection, but that it has not yet developed into a disease. Take HPV (human papillomavirus) for instance: Typically a woman with HPV does not have any symptoms, but she carries the virus. She has an STI; but if she develops cervical cancer from HPV, she now has an STD since cancer is a disease. The same is true for individuals who have chlamydia or gonorrhea infections that develop into pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the ovaries. The ovaries — each about the size of an almond — produce eggs (ova) as well as the hormones estrogen, progesterone and testosterone. If you think you’ve been checked for ovarian cancer, think again. There is no reliable screening test for this disease and no vaccine to prevent it. Yet ovarian cancer is the most fatal women’s cancer in Canada. One in two women diagnosed do not live to see another five years. While there is no vaccine to prevent ovarian cancer but there are ways to reduce the risk.
Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer starts in the cells of the testicle. A cancerous (malignant) tumor is a group of cancer cells that can grow into nearby tissue and destroy it. The tumor can also spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body. Cells in a testicle sometimes change and no longer grow or behave normally. These changes may lead to non-cancerous (benign) conditions such as epididymitis, orchitis and hydrocele. But in some cases, changes to testicle cells can cause cancer. Most often, testicular cancer starts in germ cells. These cells make sperm. These types of tumors are called germ cell tumors. The 2 main types of germ cell tumors that develop in the testicles are seminomas and non-seminomas.
Technology Used to Benefit
Viagra
Viagra (sildenafil citrate) is a prescription drug that's used to help treat erectile dysfunction (ED) and pulmonary arterial hypertension. How it works is that it relaxes blood vessel muscles in certain areas of the body, which allows blood to flow easier throughout the body. This type of drug has been widely used to help men treat erectile dysfunction, an illness that causes there to not be enough blood to flow to the penis to get an erection.
In Vitro Fertilization
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a widely known type of assisted reproductive technology (ART) and is used to help sperm fertilize a egg and then implant said egg into the female patients uterus. How it works is that the female first takes medicine that rapidly matures several of their eggs and makes them prepared for fertilization. The mature eggs are then extracted out of the ovaries and fertilized in a lab. Finally, the fertilized embryo(s) are then re-implanted into the patient, inside their uterus. IVF is important because it's a treatment method for infertility or genetic issues in women that don't allow or make it difficult for them to produce eggs / get pregnant. This method can also be used if the patient has certain conditions, examples being Fallopian tube damage / blockage, ovulation disorders, uterine fibroids, impaired sperm production / function, and etc.
The purpose of the organs of the male reproductive system is to perform the following functions: To produce, maintain, and transport sperm (the male reproductive cells) and protective fluid (semen) To discharge sperm within the female reproductive tract during sex. The female reproductive system is designed to carry out several functions. It produces the female egg cells necessary for reproduction, called the ova or oocytes. The system is designed to transport the ova to the site of fertilization.
The Skeletal System
Bones
Ligaments
Tendons
Joints
Cartilage
Technology Used to Benefit
Casts / Splints
Casts and splints are devices that help support and protect fractured / injured bone and soft tissue. Both of them help immobilize the injured part of the body to allow the broken bone to stay in place and fully regenerate. Where casts and splints differ is that casts provide more support and protection for a injured limb / body part and are made out of plaster or fiberglass, which can be molded into the broken limbs shape easily.
Splints (or half-casts) on the other hand provide less support / protection, but are easier to use and faster to apply. They can also be tightened or loosened easily if the swelling in the place it's on either grows or shrinks. There are many different types of splints like leg, arm, finger, and etc and velcro straps are included to make it easier to take them on or off.
Internal fixations
Internal fixations is a method of treating a fractured or broken bone and involves metal plates, screws, nails, wires, and etc being inserted on or into the bone. The metal that's used for internal fixations are usually stainless steel or titanium as those metals are extremely durable and sturdy. How they work is that first, the broken bone is realigned to its normal position (fragments placed where they originally were; not healed, but "normal"), then either plates, screws, nails, wires, or etc are affixed to the bone depending on the type of injury.
Plates are used as "splints" that hold the broken bone together along with nails and can be left even after the healing is done.
Rods and nails are used for fractured long bones. The rod is inserted through the hollow center of the bone and screws are placed at the each end of the rod, keeping it in place whilst preventing the fracture from shortening / rotating.
Wires and pins are used to treat fractures in small bones that're too tiny to be used with screws. This method is often used together with the other ways of internal fixation, but it can be used alone as well.
Malfunction
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a sideways curvature of the spine that occurs most often during the growth spurt just before puberty. While scoliosis can be caused by conditions such as cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy, the cause of most scoliosis is unknown. Most cases of scoliosis are mild, but some children develop spine deformities that continue to get more severe as they grow
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by a decrease in the density of bone, decreasing its strength and resulting in fragile bones. Osteoporosis literally leads to abnormally porous bone that is compressible, like a sponge. This disorder of the skeleton weakens the bone and results in frequent fractures (breaks) in the bones. Osteopenia, by definition, is a condition of bone that is slightly less dense than normal bone but not to the degree of bone in osteoporosis. Normal bone is composed of protein, collagen, and calcium, all of which give bone its strength. Bones that are affected by osteoporosis can break (fracture) with relatively minor injury that normally would not cause a bone to fracture.

Skeletal system
The function of the skeletal system is to provide support to the body, protect the organs inside, and produce red blood cells or other types of cells. Humans have endoskeletons, which means that their skeletons are located underneath the skin and muscle and when humans reach adulthood, they have a total of 206 bones in their body.
The human skeleton can be separated into 2 categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton creates the central axis of the body that is made up of the skull, spine, and rib-cage which protects the brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs, esophagus, and other vital sensory organs. Appendicular skeleton are the limb bones and the bones of the shoulder and pelvis.
The Muscular System
Technology Used to Benefit
Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a process that's done to assess the condition of muscles and the nerve cells (motor neurons) that allow them to work. This process is also used to see and test if a person has any abnormalities in the muscles. How it works is that it uses small machines called electrodes that intercept and translates signals sent from motor neurons (signals cause muscles to contract and move) into graphs, sounds, or numbers. Why this procedure is done is that it if a person is showing certain symptoms related to a muscular illness, they can use this method to help diagnose the patient and see what is actually wrong with their body.
Microthreads
Microthreads are extremely tiny threads coated with human muscle cells that are implanted into something to help repair serious muscle injuries. So far, this technique has been tested out on mice with muscle wounds and helped the wound heal drastically. The microthreads are made out of the same material that the body uses to heal injuries and when it's applied, act as a medium for healthy tissue to grow. This is incredibly helpful as extreme muscle injuries don't tend to heal completely as scar tissue can restrict the process. Although, when using microthreads, it was observed that it helps start the original healing process in the organism and sends signals to other cells to move to the wounded area and heal.
Malfunctions
Fibromyalgia
A condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain that researchers believe is caused by amplified pain sensations as perceived by the brain. Women more commonly present with fibromyalgia and typically do not have a single triggering event, but sometimes the condition may begin after physical trauma, surgery, infection, or significant psychological stress. There is no cure for fibromyalgia. Symptoms may be managed using a variety of medications, exercise, and relaxation techniques.
Rhabdomyolysis
This is a condition characterized by the rapid breakdown of damaged skeletal muscle. Injury to the muscle may be indirect or indirect, which then causes dead muscle fibers and constituents to be released into the bloodstream. The problem with this is that these can then cause serious complications with the kidneys, leading to kidney failure. Urine samples are often tea-colored or a dark inconsistency as a result.

Diagram of the muscular system
The function of the muscular system serves to help the body move around and perform tasks, aids the heart in beating, and making up the walls for hollow organs. How muscles move is that signals are transferred from the nervous system to the muscle cells which produce electrical changes. During this, calcium is secreted into the cells and this results in a small muscle twitch.
Diagram of a Vagina
Diagram of the Urinary Tract
Diagram of the Digestive system
The Digestive System
Small Intestine
Esophagus
Salivary glands
Pharynx
colon
Rectum
Liver
Gallbladder
Pancreas
Stomach
Mouth
Technology Used to Benefit
Colonoscopy
A colonoscopy is a process where the large intestine (colon) and rectum are examined to see if there are any abnormalities or symptoms in them. How it's done is that a very long, flexible tube called a colonscope is inserted in the rectum and makes its way through the large intestine. A small video camera is at the end of the tube, allowing the doctor to see inside the colon and sometimes during the procedure, polyps or abnormal tissues can be removed through the scope. A biopsy (tissue sample) can also be taken to analyse it. The reason this process is done is that it helps to see if there are any signs or symptoms of intestinal problems and to diagnose them, screen in case the patient is at risk of colon cancer, and to look for and possibly remove more polyps.
Flagyl (metronidazole)
Flagyl (metronidazole) is a prescription antibiotic that's used to fight several parasitic infections, one of them being dysentery. It works by killing any bacteria or parasites in the body that are causing infection and is sometimes taken in tandem ciprofloxacin, another type of antibody. The medication comes in tablet form and is taken orally with water, but in order for it to be effective, there must be a constant amount of drug inside the bloodstream. Flagyl is a very versatile drug and can be taken to treat many infectious diseases, examples being Giardia infections, amebic liver abscess, amebic dysentery, bacterial vaginosis, and etc.
Malfunctions
Dysentery
Dysentery, infectious disease characterized by inflammation of the intestine, abdominal pain, and diarrhea with stools that often contain blood. Dysentery is a significant cause of illness and death in young children, particularly those who live in less-developed countries. There are two major types: bacillary dysentery and amebic dysentery, caused respectively by bacteria and by amoebas.
Celiac
Celiac disease, is an inherited autoimmune digestive disorder in which affected individuals cannot tolerate gluten, a protein constituent of wheat, barley, malt, and rye flours. General symptoms of the disease include the passage of foul pale-coloured stools (steatorrhea), progressive malnutrition, diarrhea, decreased appetite and weight loss, multiple vitamin deficiencies, stunting of growth, abdominal pain, skin rash, and defects in tooth enamel. Advanced disease may be characterized by anemia, osteoporosis, vision disturbances, or amenorrhea (absence of menstruation in women).
The muscles of the small intestine mix food with digestive juices from the pancreas, liver, and intestine, and push the mixture forward for further digestion. The walls of the small intestine absorb water and the digested nutrients into your bloodstream. Each part of your digestive system helps to move food and liquid through your GI tract, break food and liquid into smaller parts, or both. Once foods are broken into small enough parts, your body can absorb and move the nutrients to where they are needed. Your large intestine absorbs water, and the waste products of digestion become stool. Nerves and hormones help control the digestive process.
Diagram of the Circulatory System
Circulatory System
Arteries
Veins
Blood
Heart
Lungs
Technology Used to Benefit
Ventricular assist device (VAD)
A ventricular assist device (VAD) is a mechanical pump meant for the heart and aids in pumping blood from the lower chambers in the heart (ventricles) to the rest of the body. The overall device is made up of a pump that's connected to either the left, right or both ventricles in the heart, an outside controller (e.g computer) that monitors the pump, a cable that connects pump to controller, and a power source. Although, in order to actually have a VAD, open-heart surgery is needed to complete the procedure, but if the patient has severe heart failure it could be life-saving. Reasons why someone would get a VAD could be that they're waiting for a heart transplant, aren't suited for a transplant, their heart's function could become normal again, etc.
Enhanced external counterpulsation
(EECP)
Enhanced external counter pulsation (EECP) is a non-invasive method for treating angina episodes and works by stimulating the openings / formation of collaterals (small branches of blood vessels) to make a bypass around narrowed or blocked arteries. How this process is done is by first attaching electrodes to the chest, which is connected to a electrocardiograph (ECG) that monitor heart rate and blood pressure. Inflatable cuffs are then wrapped around the patients calves, thighs, and buttocks and they continuously inflate and deflate depending on the heart rate. The inflation and deflation of the cuffs is synchronized to the heartbeat to better treat the patient. EECP helps increase the amount of blood returned to the heart as when it's inflated, it compresses the blood vessels in the lower limbs to allow more blood into the heart when it's relaxing. But, when the heart pumps again, they deflate which causes the resistance in the blood vessels to lower, allowing blood to be pumped easier.
Malfunction
Interstitial cystitis
Interstitial cystitis is a chronic bladder condition, primarily in women, that causes bladder pressure and pain and, sometimes, pelvic pain to varying degrees, according to the Mayo Clinic. It can cause bladder scarring, and can make the bladder less elastic. While the cause isn't known, many people with the condition also have a defect in their epithelium, the protective lining of the bladder.
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are clumps of calcium oxalate that can be found anywhere in the urinary tract. Kidney stones form when chemicals in the urine become concentrated enough to form a solid mass, according to the Cleveland Clinic. They can cause pain in the back and sides, as well as blood in the urine. Many kidney stones can be treated with minimally invasive therapy, such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy, which disintegrates the kidney stones with shock waves.
The circulatory system consists of three independent systems that work together: the heart (cardiovascular), lungs (pulmonary), and arteries, veins, coronary and portal vessels (systemic). The system is responsible for the flow of blood, nutrients, oxygen and other gases, and as well as hormones to and from cells. Combined with the cardiovascular system, the circulatory system helps to fight off disease, helps the body maintain a normal body temperature, and provides the right chemical balance to provide the body’s homeostasis, or state of balance among all its systems. There are different systems in the circulatory system and they are cardiovascular, pulmonary, and systemic.