Problem: Cells still need to take in substances even if the concentration is higher inside the cell.
Intestine cells need to absorb nutrients to pass them to the bloodstream but the concentration of nutrients is already higher in the intestine cell.
This is where active transport comes into play.
Active transport: movement across a semipermeable membrane that REQUIRES energy.
We will discuss how cells create energy this afternoon!
Like facilitated diffusion, active transport involves proteins in the cell membrane.
Unlike facilitated diffusion, active transport uses energy.
Because in active transport substances are being transported from an area of low concentration to high concentration.
Energy for Our Cells
Many reactions in our cells require energy!
We know that we eat food for energy, but the chemical energy stored in macromolecules we consume isn’t in a form our cells can use.
Food molecules go through chemical reactions that create energy that cells use to create ATP
ATP or adenosine triphosphate is the molecule cells use for energy.
How Cells Use ATP
ATP is a nucleotide made of adenosine and three phosphate groups
ATP goes through a chemical reaction that releases a burst of energy used by the cell
This creates ADP, adenosine diphosphate, and a free phosphate group
Exocytosis
allows a vesicle inside the cell to bind with the cell membrane and to release the substance.
ANIMAL CELLS
multicellular
multiple cells working together to complete a organism
Parts of the cell
cytoplasm
cell membrane
nucleus
ribosomes
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
smooth ER
rough ER
golgi body
vacuoles
lysosomes
mitochondria
centriole
Diffrent types of animal cells
Liver cells
kidney cells
stem cells
blood cells
etc.
PLANT CELLS
Multicellular
multiple cells working together to complete a organism
Two main diffrences from animal cells
they have chloroplasts
They have cell walls
Chloroplasts
used to make their own food during photosynthesis
responsible for green color plants
contains enzymes and other chemicals used in photosynthesis
Cell wall
surrounds the cell membrane
strong and ridged
helps give the plant structure and shape
mostly made of cellulose (fibre)
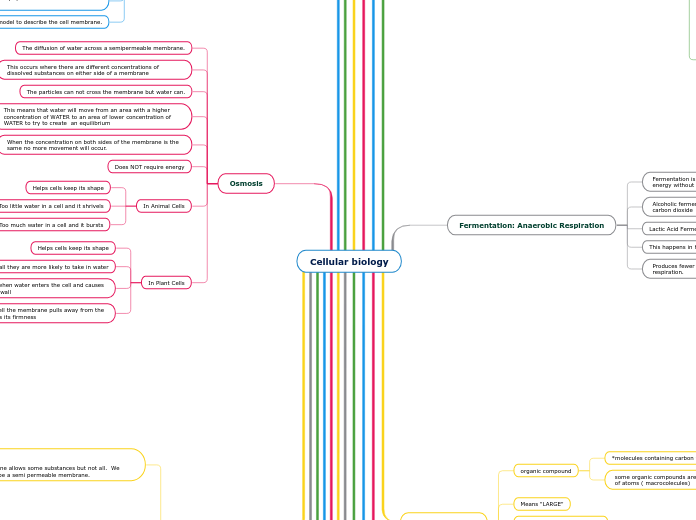
Fermentation is one process that organisms can produce energy without oxygen.
Alcoholic fermentation: Pyruvate is converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide
Lactic Acid Fermentation: Pyruvate forms lactic acid.
This happens in human muscle cells
Produces fewer ATP per glucose molecule compared to cellular respiration.
organic compound
*molecules containing carbon that make up life*
some organic compounds are made of hundreds or thousands of atoms ( macrocolecules)
Means "LARGE"
often has complex structures
polymers
Type of macromolecule
long chain like molecules made of smaller molecules linked together
the smaller molecules are called " monomers"
complex carbohydrates
Glycogen in humans (often in liver cells and muscle cells)
Storage polysaccharide: To store sugars
Polysaccharides: Polymers consisting of several hundred to several thousand monosaccharides linked together
Structural polysaccharides: Building material for structures that give organisms shape
three main types
Monosaccharides “single sugars”
The simplest carbohydrate used biologically
Used by cells for fast energy
Building block of more complicated carbohydrates
Clear and colourless as sugars
Examples;
Glucose (most common)
Fructose (in plants)
Galactose (in milk)
Disaccharides “two sugars”
Trisaccharides “many sugars”
Composed of C, H, and O atoms
Enzyme inhibitors control the amount of a product being made.
Like an on/off switch
Two types of inhibitors
Non-competitive Inhibitors
A molecule bonds to a different site that then changes the shape of the active site.
Competitive Inhibitors
A molecule other than the intended bonds to the active site.
Sometimes inhibitors have an negative effect
If a chemical bonds to stop a vital reaction is a hazard.
An example of this carbon monoxide
An competitive inhibitor
Cells need an way to help control the chemical reactions, that's where enzymes come in
An substance that controls the rate of an reaction is called an catalyst
Because enzymes are a part of most reactions in a body problems can occur if an enzyme is missing or depleted.
Humans who are lactose intolerant are missing the enzyme lactase
Without it the small intestine can't digest lactose
We can produce tablets by extracting lactate from other places and take in pill form
HOW IT WORKS
Enzymes bond to the reactant molecules, also called substates
The place where an substrate connects is called the active site
This puts the substrates in the best position for the reaction to occur
This also helps weaken existing bonds making it easier for product bonds to form
Once the reaction has occurred the enzyme is ready to work again
Factors affecting enzymes:
Because enzymes are proteins they can be damaged or denatured
Ph
Temperature
Cholesterol
Embedded in Phospholipid bilayer
Helps keep fluidity of membrane
Reduced fluidity at high temperatures
Increases fluidity at low temperatures
Proteins
Most are embedded in the Phospholipid bilayer
Some are attached outside or inside the Phospholipid bilayer
Some transport substances across the membrane
Some are enzymes
Some transmit signals from the other cells in the body
Carbohydrates
Attach to proteins or Phospholipids and protrude outside the cell
Allow other cells to recognize the cells belonging to the body
Not an intruder
Phospholipids
Provides overall structure
Arranged in two layers
Acts as an protective layer between the cell and the outside
Holds other components
Cell Membranes are like the security or bouncers of a cell. They control what gets in and out!
Made up of a phospholipid bilayer, but NOT ONLY phospholipids!
If it were only made of phospholipids not all the substances that needed to go or out of the cell would be able to
We use the fluid mosaic model to describe the cell membrane.
The diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane.
This occurs where there are different concentrations of dissolved substances on either side of a membrane
The particles can not cross the membrane but water can.
This means that water will move from an area with a higher concentration of WATER to an area of lower concentration of WATER to try to create an equilibrium
When the concentration on both sides of the membrane is the same no more movement will occur.
Does NOT require energy
In Animal Cells
Helps cells keep its shape
Too little water in a cell and it shrivels
Too much water in a cell and it bursts
In Plant Cells
Helps cells keep its shape
Because of the cell wall they are more likely to take in water
Helps keep the cell firm when water enters the cell and causes pressure against the cell wall
When water leaves the cell the membrane pulls away from the cell wall and the cell loses its firmness
Simple diffusion
The cell membrane allows some substances but not all. We consider this to be a semi permeable membrane.
Substances that can pass through;
Small molecules (water, oxygen, carbon dioxide)
Small lipids (fatty acids)
When these substances cross the cell membrane it's called simple diffusion.
Does NOT require energy
Facilitated diffusion
Some particles cannot pass through the cell membrane on their own
Some of these particles include:
Ios (charged particles)
Large molecules
This happens in two ways:
An protein can provide an channel to hydrophilic particles
An protein can bind to an protein, transport it across the membrane and release it inside the cell
Glucose is transported this way
Does NOT require energy
These particles still travel across the membrane using what we call facilitated diffusion
In facilitated diffusion particles are transported across the membrane by proteins
made of three long hydrocarbons called fatty acids bonded to glycerol, a three carbon molecule.
The structure of the fatty acids determine the properties of the triglyceride
Similar to triglycerides but they have two fatty acids
The phosphate head is hydrophilic
The fatty acid “tails” are hydrophobic
An example is Cholesterol, a key part of animal cell membranes
Commercially produced steroids are used to treat asthma.
Nucleic acids are a polymer made of monomers called nucleotides.
RNA (ribonucleic acid)
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
have the most jobs in a cell of any other biological molecule.
their jobs
Control what going in and out of a cell
Carry oxygen in blood
Help blood to clot
Build hair and fingernails Ect.
Macrobiology
things that can be seen by the naked eye
Microbiology
Things that can only be soon from a microscope
Prokaryotes
no nucleus
no (or few) organells
Unicellular
Examples: Bacteria
Eukaryotes
has nucleus
has organelles
unicellular AND multicellular
Examples: Animals, plants, fingi, protists (like algae)
Plants make their own food using photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts.
After reading glucose plant cells also go through cellular respiration.
If plants use oxygen in cellular respiration why do we say they release oxygen?
Plants still create more oxygen than they use!