Chemistry
Main topic
Main topic
My Poster Element "Silicon"
safety rules
10 Main safety rules
Follow the instructions!
Know the Location of Safety Equipment
Leave Experiments at the Lab
Dispose of Lab Waste Properly
Don't Experiment on Yourself
Don't Play Mad Scientist in the Laboratory
Know What to Do With Lab Accidents
Dress for the Lab
Don't Taste or Sniff Chemicals
Don't Eat or Drink in the Laboratory
Structure of the atom
Atoms consist of three basic particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons. The nucleus (center) of the atom contains the protons (positively charged) and the neutrons (no charge). The outermost regions of the atom are called electron shells and contain the electrons (negatively charged).
Physical and Chemical properties
Physical
A physical property is any property that is measurable, whose value describes a state of a physical system. The changes in the physical properties of a system can be used to describe its changes between momentary states
examples
Subtopic
Subtopic
Chemical
A chemical property is any of a material's properties that becomes evident during, or after, a chemical reaction; that is, any quality that can be established only by changing a substance's chemical identity.
examples
silicon
what is Silicon?
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, and lead are below it
Silicon atoms model
Bohr Diagram of Silicon
Physical and Chemical changes
Physical
Physical changes are changes affecting the form of a chemical substance, but not its chemical composition. Physical changes are used to separate mixtures into their component compounds, but can not usually be used to separate compounds into chemical elements or simpler compounds.
examples
Chemical
Chemical changes occur when a substance combines with another to form a new substance, called chemical synthesis or, alternatively, chemical decomposition into two or more different substances. These processes are called chemical reactions and, in general, are not reversible except by further chemical reactions.
examples
Bohr Diagram
Bohr diagrams show electrons orbiting the nucleus of an atom somewhat like planets orbit around the sun.
Subtopic
Counting Atoms
there are two types of words that helps to count atoms
Subscript
coefficient

WHMIS
there are 10 WHMIS symbols

Flammable Material
Subtosubstance capable for catching fire, products with this label can easily ignite and burn rapidly. A fire requires a fuel source, and oxygen.pic

Gas cylinder
Gas cylinder: Gases under pressure.

Oxidizing
products causing/ contribution to the combustion of other materials. Oxidizers gives off oxygen and therefore greatly increase the rise of fire or fire on explosion. Oxidizing substance can create a more intense fire.

Environment:
negative impacts on the aquatic environment. Aquatic environment include both short term and long term

Biohazzard
harmful micro-organism includes bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites.

Health Hazzard/Danger to health
products that cause chronic health effects.

Corrosion
Materials such as caustiest or acids, causing burns to skin or eyes.
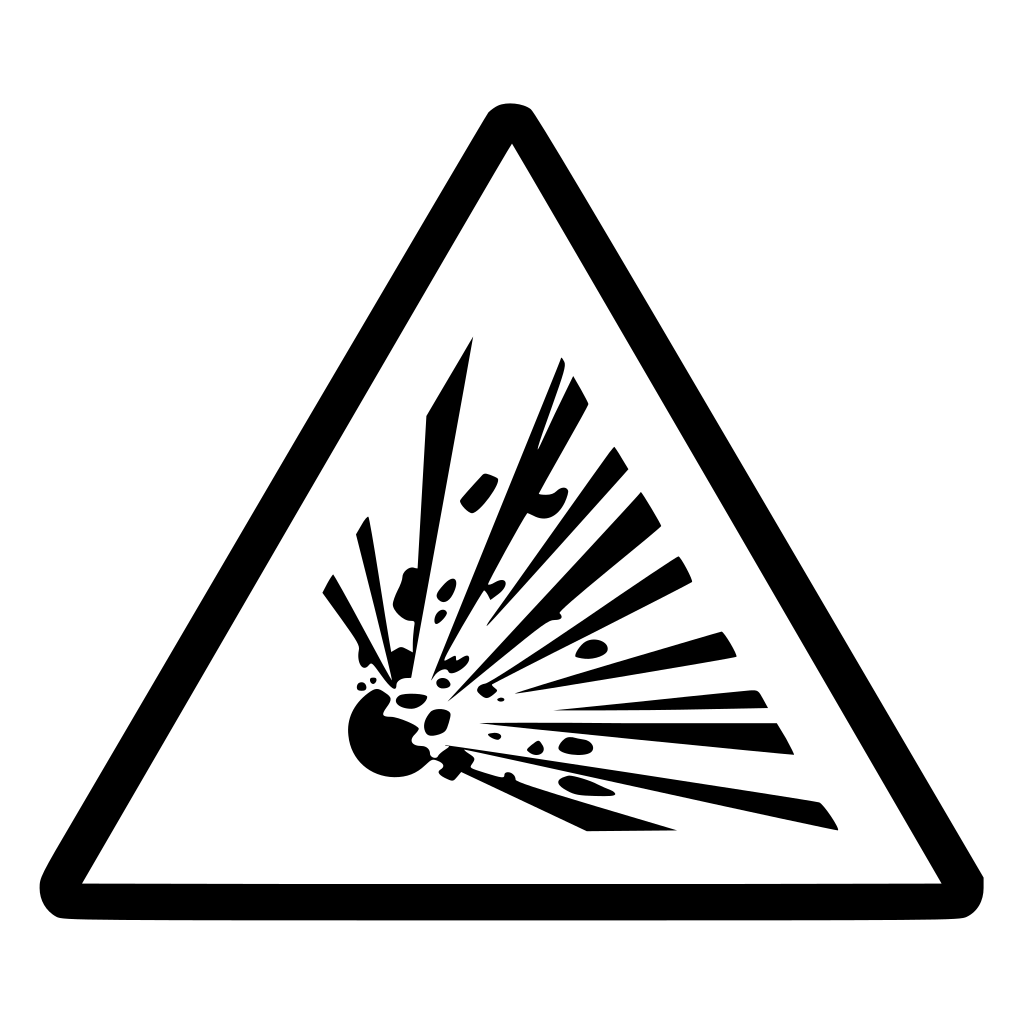

Exploding Bomb:
products that can become explosive if not handled in proper condition.

Exclamation Mark:
Eyes and skin irritation
Skull and crossbones:
products that dawn this label are fatal, toxic, or harmful if inhaled.

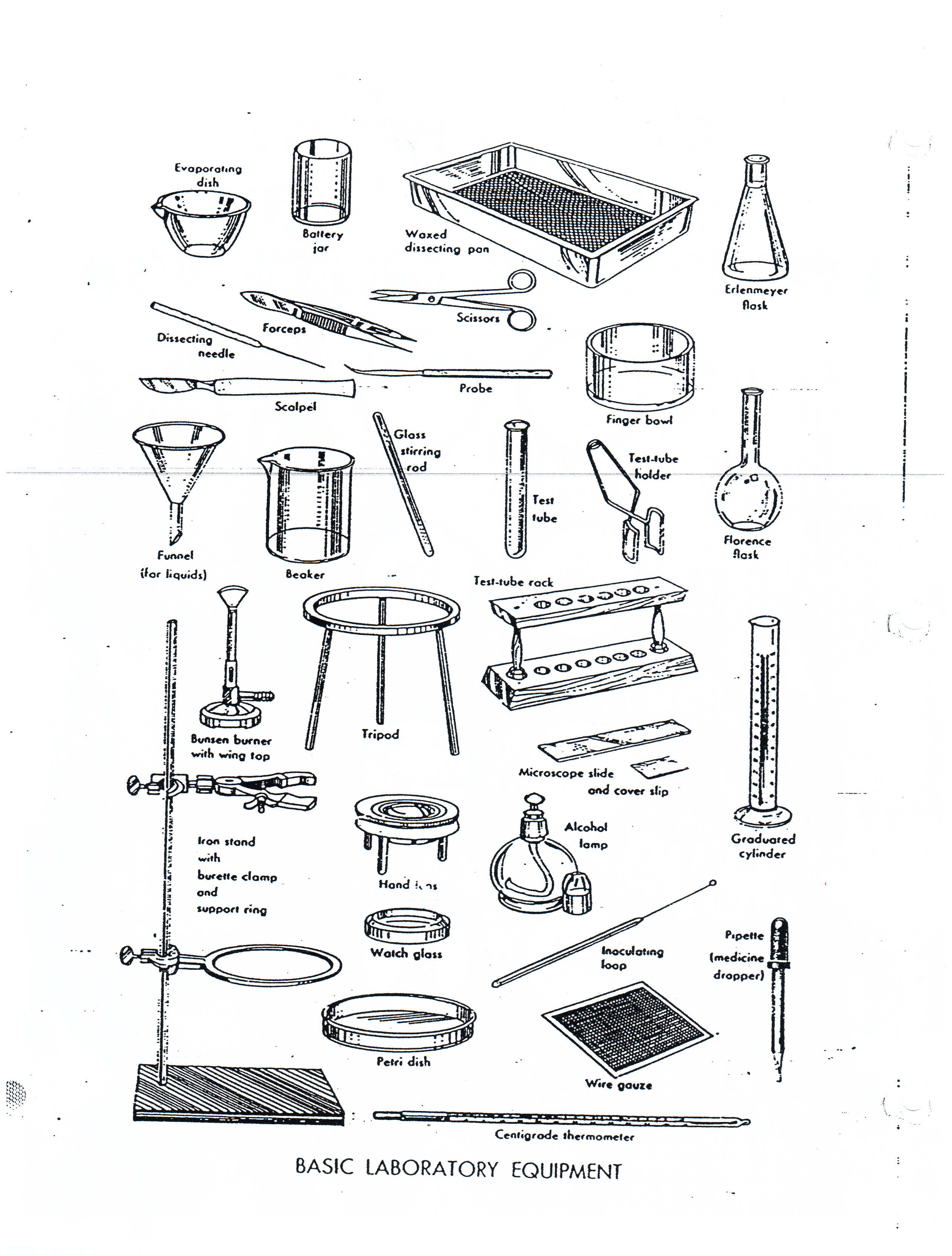
Lab equipment and uses

Erlenmeyer Flask
watch glass

Forceps

Ring Clamp

Apron

Bunsen burner

Mortar Pestle

Beaker Tongs

Metric ruler

Graduated Cylinder

Test Tube

Scoopula

Test Tube holder

Pipette

Test Tube rack

Beaker

Clay Triangle

Funnel

Glass stirring rod

Thermometer
Classification of matter
Matter
Pure Substances: made up of only one type of particle.
Mixtures: made up of two or more different types of particles.
Elements: made up of only one type of atom. Ex, Hydrogen.
Compounds: made up of two or more different atoms bonded together. Ex, Salt (NaCl).
Heterogeneous Mixtures: more than one part of the mixtures is visible. Ex, Pizza.
Homogeneous Mixtures Solution: only one part of the mixture is visible (look like one part online). Ex, Milk.
Subtopic

the Periodic table
What is periodic table?
A table of the chemical elements arranged in order of atomic number, usually in rows, so that elements with similar atomic structure appear in vertical columns.
There are 9 types of elements on periodic table
1. Alkali metals
2. Alkaline Metals
3. Transition metals
4. Non metals
5. Noble gases
6. Semi-metals
7. Halogens
8. Lanthanides
9. Actindes