Chemistry
Periodic Table
Matter
The Particle Theory
All materials are made up of solid, liquid or a gas. All materials are made up of very small particles held together by forces.
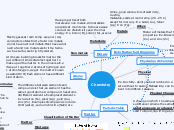
Classification of Matter
Matter
Pure Substances
Elements
Compounds
Mixtures
Heterogeneous
Homogeneous
Physical and Chemical Properties
Physical
E.x. Ductility- ability to be stretched in a wire without breaking. Malleability- can be bent into different shapes.
Physical Change
A change in which the composition of a substance remains the same. No new substances are produced. E.x.
solid to liquid, liquid to gas, liquid to solid.
Chemical
E.x. Combustibility- the ability to burn. Reactivity- undergo chemical reaction either by itself or with other materials and release energy.
Chemical Change
A new substance is created. The change affects the composition of matter. E.x. sugar cooked to make caramel. Heat changes the sugar molecules into different molecules which give caramel it's color and flavour.
Bohr Rutherford Diagrams
Electrons orbit the nucleus. Each orbit can hold a specific maximum number of electrons.
1st orbit: 2 electrons
2nd orbit: 8 electrons
3rd orbit: 8 electrons
4th orbit: up to 18 electrons
Atomic number= number of protons in an atom in the element. E.x. Krypton's atomic number is 36, therefore the number of protons is 36. Atoms have an equal number of protons and electrons. If the number of protons is 36, then the number of electrons is 36. The number of neutrons = Mass number - Atomic mass.
Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus. Protons are positively charged. Neutrons have no charge. Electrons orbit the nucleus. They have a negative charge.
Bohr Rutherford Diagram of Beryllium
Metals
Metals
Shiny, good conductors of electricity, ductile,
malleable, solids at room temp. (20-25 C) except for mercury. E.x. Gold (Au), Silver (Ag) Iron (Fe)
Alloys
Mixture of metals that have specific
properties. E.x. Brass is an alloy of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn)
Non metals
Mostly gases at room temp. are poor conductors of electricity. Solid non metals do not have lustre of metals. Most have a dull lustre. Solid non metals are brittle. Some such as sulfur, are brightly colored.
Metalloids
Have properties of both
metals and non metals. All metalloids
are solids at room temp. Some are weak conductors of electricity and thermal energy. E.x. boron (B), silicon (Si), arsenic (As)
Atoms
Atoms are building blocks for matter. We put different kinds of atoms together to make up all the matter in the universe. E.x. if we put together 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen, we get the matter known as water.(H2O) Each element has a different kind of atom.
The difference between elements and compounds is that, an element has the same type of atoms. A compound has atoms of different elements. Examples of elements include iron (Fe), silver (Ag), gold (Au), zinc (Zn). Examples of compounds include H2O (water), sodium chloride (NaCl) etc.
Reading Chemical Formulas
A chemical formula tells you important
information about a pure substance. The symbols in the formula tell you the elements
in the substance. If there is only one symbol,
the substance is an element. If there is more than one symbol, the substance is a compound. The subscript is a small number written slightly below another character. It tells the reader how many atoms of each element are in each molecule of the substance.