common ancestor
eukaryotes
(multicellular, contain
nucleus and have cellular reproduction)
protista
3 types of protists

protzoans, (animal- like protists)
method of nutrition- ingest

algae, (plant-like portists)
method of nutrition- photosynthesize

mold, (fungus- like protists)
method of nutrition- absorb
organization of protists
green, golden, red, and brown unicellular algae large
phylums
PLANT- LIKE PROTISTS
PHYLUM EUGLENOPHYTA: eg. EuglenaTrachelomonasPhacus
PHYLUM BACILLARIOPHYTA: eg. Coscinodiscophyceae
PHYLUM DINOFLAGELLATA: eg. dinophyceae
PHYLUM RHODOPHYTA: eg. florideae
PHYLUM PHAEOPHYTA: eg. kelp
PHYLUM CHLOROPHYTA: eg. chlorophyceae
FUNGUS- LIKE PROTISTS
PHYLUM MYXOMYCOTA: eg. myxogastria
PHYLUM ACRASIOMYCOTA: eg. fuligo septica
PHYLUM OOMYCOTA: eg. Peronosporales
ANIMAL- LIKE PROTISTS
PHYLUM SARCODINA: eg.amoeba proteus
PHYLUM SPOROZOA: eg. plasmodium
prokaryotes
(unicellular, lack
organelles and have binary fission
archaebacteria
types of organisms
lives in extreme environments

eg- Picrophilus torridus
lives in acidic conditions

eg-hay Bacillus (acidophile)
lives in moderate environments

eg-Listeria monocytogenes (mesoophile)
heat tolerant bacteria
eg-Thermus thermophiles (thermophile)
lives in +20 percent salt water

eg- halococcus (halophile)
Eubacteria (small, lacking nuclei)
shapes of eubacteria
spirillum= spiral shaped
eg- spirillum volutans
bacillus= rod shaped
eg-proteobacteria
coccus=spherical shaped
Staphylococci
nutrition method
photosynthesize
absorb
types of organisms
bacteria

Blue-green algae
spirochetes
Reproduction
asexual
binary fission
phylum ZOOMASTIGINA: eg. Giardia
plantae- multicellular form; do not have their own means of locomotion
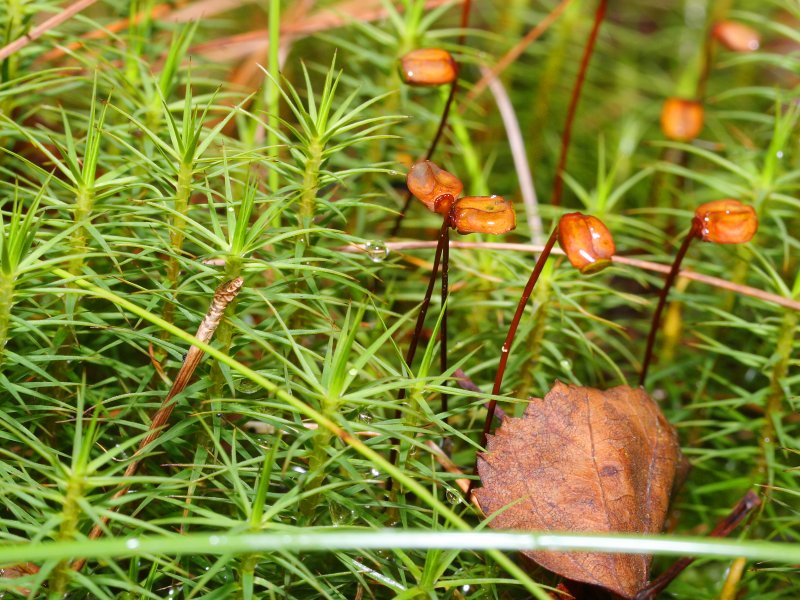

Bryophytes eg-Polytrichum commune
3 groups- Mosses, hornworts and liveworts
two adaptations- waxy cuticle and gametangia, waxy cuticle protects tissue from drying out and gametangia protects drying out of gametes.
live in rainy or humid environments for water
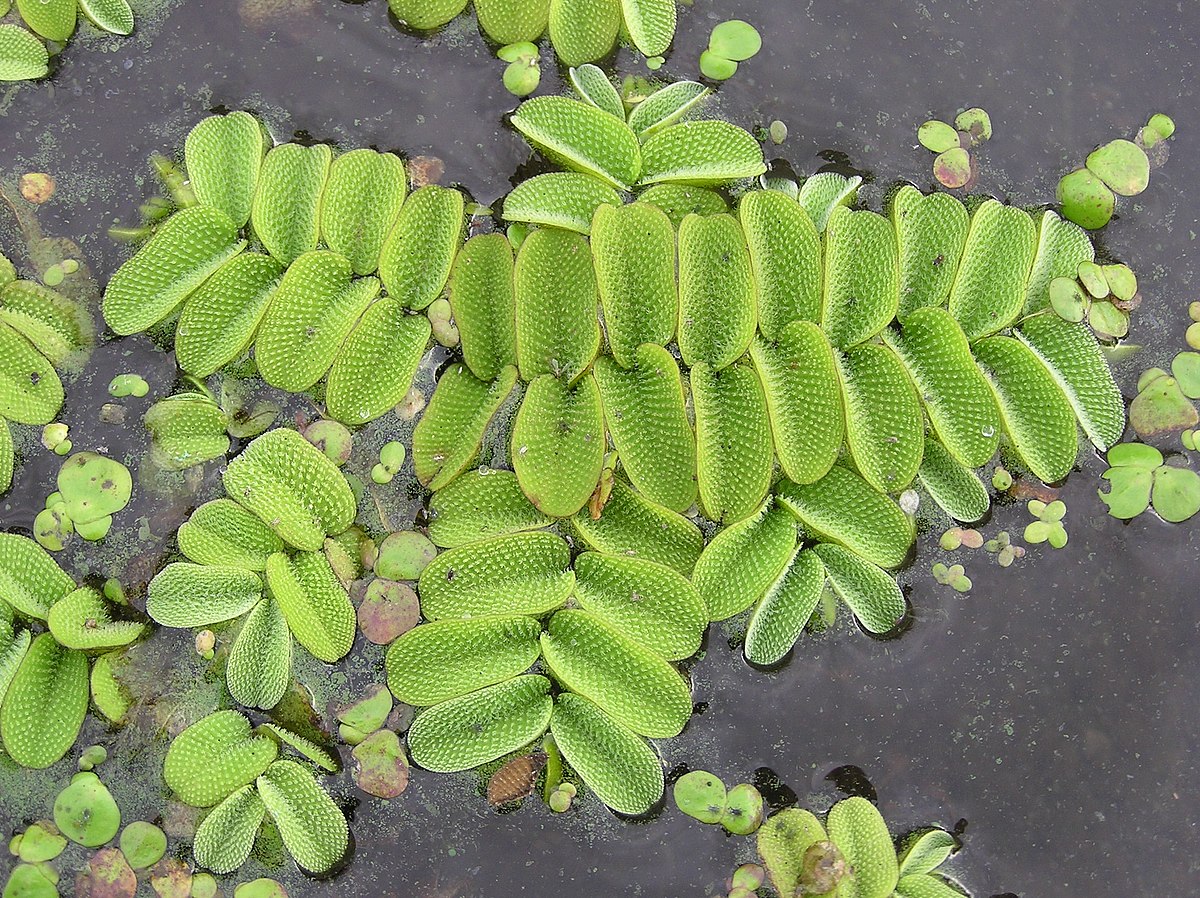

Pteridophytes eg- Salvinia natans
vessels collect water from moist soil and distribute it to the cells.
better adaptation in surviving on land than bryophytes

Gymnosperms eg-red pine
(xylem and phloem, which conduct water and nutrients up the body of the tree)
(system of pipes that sends water from the ground to leaves which conducts photosynthesis making it more adapted.)
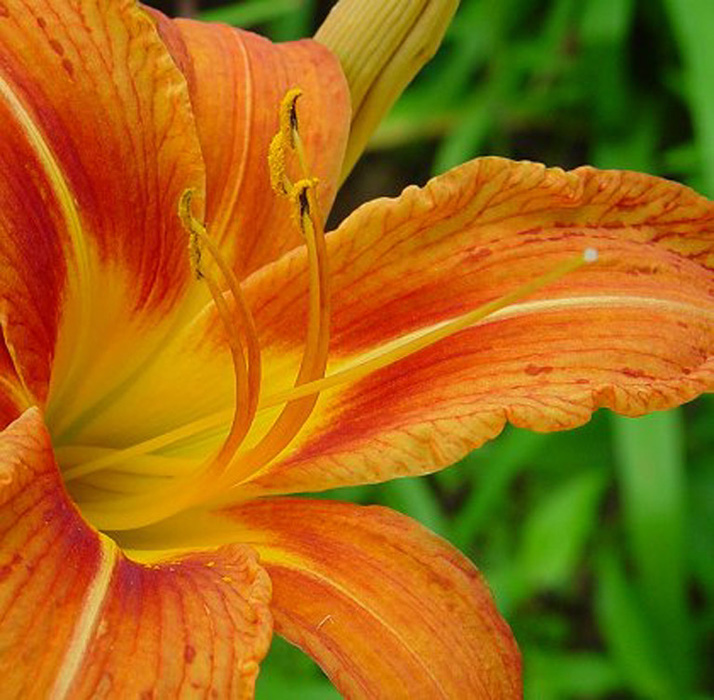

Angiosperms
flower attracts insects, birds. closed carpels to prevent desiccation ( seed drying). expanded leaves for maximum efficiency in photosynthesis
Animalia (multicellular, heterotrophs no cell wall)
9 Major Phyla
Phylum Porifera
(no locomotion, lives in colonies and has radical symmetry)

sponges
Phylum Cnideria
(like sac with tentacles, 2 tissue
layers and radical symmetry)
jellyfish
Phylum Platyhelminthes
(has organs, head, tail and bilateral symmetry

flatworm
Phylum Nematoda
(Tube like structure, digestive tube)

roundowrms
Phylum Mollusca
(soft body and some with shell)

snail
Phylum Annelids
(has a circulatory and digestive system, body divided in parts)

worms
Phylum Echinodermata
(found in water, water vascular
system and rough covering)

starfish
Phylum Athropoda
(has an exoskeletal system, thorax and abdomen)
supphyla, classes
Chelicerata

scorpion
Crustacea

lobster
Hexapoda

dragonfly
Myriapoda

centipede
spider
Phylum Chordata
(sexual reproduction,
complexity in systems and internal skeleton)
Subphyla
cephalochordate
(marina animals)

lanceletes
Urochordata
(notochord)

tunicates
vertebrata
(have backbone)
Classes
lion
Fungi
(Multi cellular, heterotrophs
and have cell wall)
Phylum basidiomycota
(asexual or sexual reproduction)

agaricus
Phylum Ascomycota
(sac-like structure)

morchella esculenta
Phylum Zygomocota
(animal material, in soil and on plants)

bread mold
Phylum Chytridiomycota
(large pores produce
flagellated spores)

allomyces
PHYLUM CILIOPHORO: eg. suctoria
3 Major orders
Order Artiodactyla
(even toes)

hippopotamus
Order Carnivora
(meat eaters)

cheetah
Order Cetacea
(live in water)

Dolphin
Placental Mammals
(most animals belong here)

most animals
Monotremes
(lay eggs)

echidnas
Marsupials
(has pouches to c
arry babies)

kangaroo