Earth in Balance
Climate Change
The change in global or
regional climate patterns
Due largely to increased levels
of atmospheric carbon dioxide
produced by use of fossil fuels
Greenhouse gas amounts
increase
Average temperature
increases
Earth is less sustainable
Increases in
- Carbon dioxide
- Methane
Causes extreme weather
More frequent and intense
storms, flooding, droughts,
heat waves, and snowfall
Increases extinctions
Environments become less
hospitable for certain plants
and animals
Leads to relocation for
survival
Some species are unable to
relocate
Leads to extinction
Leads to adaptations
Some species are unable to
adapt at the same speed at
which the climate is changing
Leads to extinction
Melts ices
(specifically at the poles)
Arctic ice is melting so
quickly that within a few
years the North Pole will
only be ice covered seasonally
Polar ice helps to reflect
sunlight and deflect heat
When it melts more heat
will stay in the atmosphere
Melting will lead to an
extreme rise in sea levels
Oceans are warmed
Water expands and
sea levels rise
Warmer waters kill coral reefs and krill
Both are essential to
supporting the sea
food web
Deforestation
Is the permanent removal of
trees to make room for something
besides forest
Forested areas are cleared to make
space for agriculture or grazing, using
the timber for fuel, construction,
or manufacturing
Leads to a loss of biodiversity
- Trees
- Plants
- Animals
- Microbes
Can affect production of
water vapour in tropical regions
which causes reduced rainfall
Accounts for almost 20%
of greenhouse gas emissions.
Vegetation that remove
carbon monoxide from
the air are removed.
Temperatures are rising due
to less forest canopy shading
the ground and cooling the
land beneath
Forests are a resource for many
communities around the world
Loss of forests mean
they can no longer rely on
the spaces for firewood,
timber, charcoal, etc.
Reduced amount of oxygen and increased
amounts of carbon dioxide contribute to
both global warming and the issue of air
pollution
Air Pollution
Made up of a mix of solid
particles and gases in the air
- Car emissions
- Chemicals from factories
- Dust
- Pollen
- Mold spores
- Smog
- Smoke
- Soot
- Methane
Some pollutants
are poisonous
Inhaling increases chances
of health problems
People with heart or lung disease,
elder people, and children are the most at risk
Ozone holes allow more
UV radiation to hit the Earth,
leading to higher temperatures.
Ozone-depleting Chemicals
- CFCs
- HCFCs
- HBFCs
- halons
- methyl bromide
-carbon tetrachloride
- methyl chloroform
Leads to acid rain
Contains high levels of
nitric and sulphuric acids
Makes waters
more acidic
Makes waters toxic to plants,
crayfish, clams, fish, and other
aquatic animals
Airborne particles can effect amounts
of nutrients in soil and waterways,
harm forests and crops, and damage
cultural icons (monuments, statues,
landmarks)
Haze
Happens when sunlight encounters
tiny pollution particles in the air
The pollutants are directly
emitted to the atmosphere
Obscures clarity, colour,
texture, and form of what we see
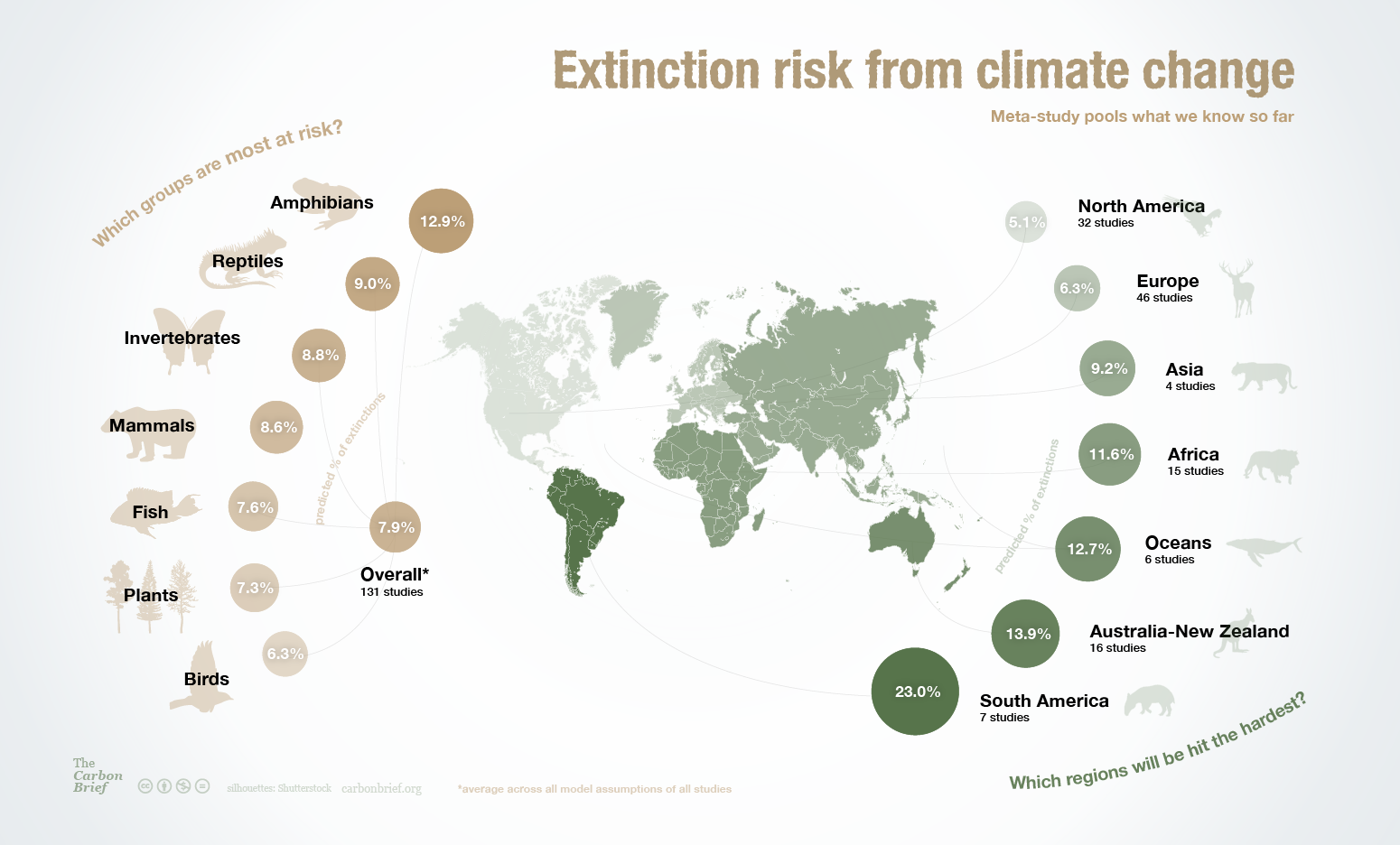
Extinction risks

Extreme Weather + Climate Change
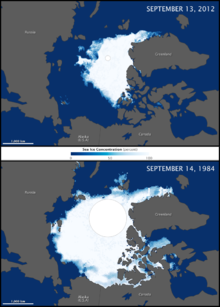
Arctic sea ice (2012 vs 1984)

Contributors to the Greenhouse Effect

Threats from loss of biodiversity

Water vapour production
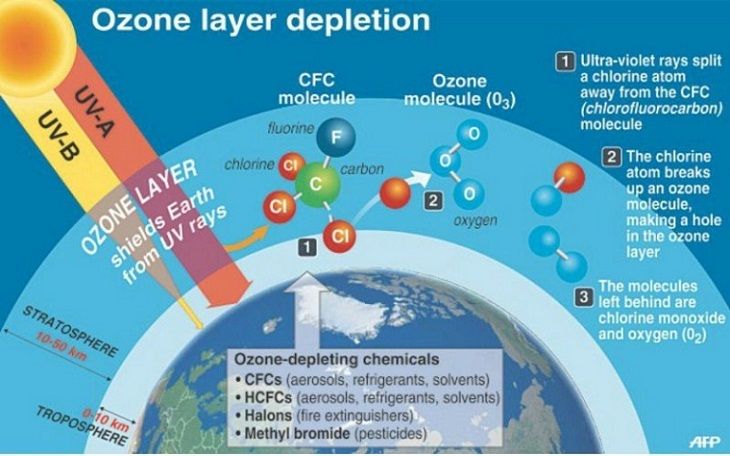
Ozone layer depletion

Air pollution in Hong Kong