Elementary Mathematics
Ratios and Proportions
Ratio: a:b a over b a to b
Proportion: statement about ratios involving more than one ratio
"=" means same as
ex. 3/4 is the same as 9/12
additive inverse: a+?=0
a+(-a)=0
Problem Solving
Understand the problem
Devise a plan
Look for a pattern
Examine a related problem
Examine a simpler case
Identify a subgoal
Make a table
Make a diagram
Write an equation
Carry out the plan
Look back/ Check the results
Use guess and check
Work backwards
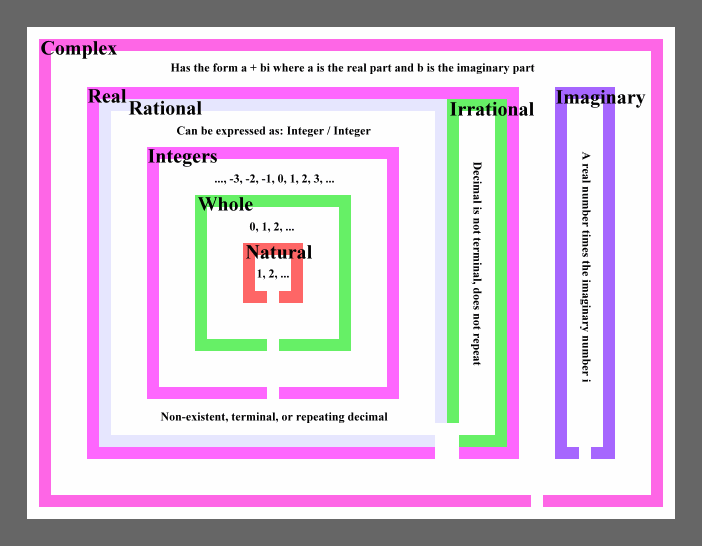
Number Systems
Algorithms
Standard Algorithm:
Standard column by column
ex.
10
+15
------
25
Denominate number:
writing out the places and only adding with same place (noun)
Expanded notation:
ex.
123
+ 10
--------
100+20+3
10+0
-------------
100+30+3= 133
Estimation
Front-end: ex. 1.50, 2.50, 3.75, 1.25
1+2+3+1= 7
adjust- .50+.50= 1 .75+.25= 1
so..... 7+1+1= 9
Clustering: ex. 500, 501, 499, 502, 498
1. estimate the "average" -about 500
2. multiply the "average" by the number of values
500x5=2500
Rounding: 14x6
about 15x5 which equals 75
Compatible numbers: 27+59+35+65+41+73
27+73=100
59+41=100
35+65=100
= 300
Special numbers: estimating with fractions
ex. 1/2+3/8=1?
no because 3/8 is close to 1/2 but less so it can not equal to one when added to another half
Decimals
10^3 10^2 10^1 10^0 . 10^-1 10^-2 10^-3
1000 100 10 1 . 1/10 1/100 1/1000
Repeating decimals to fractions:
x=.3333
10x=3.3333 -/These cross out
- x= .3333
---------------
9x= 3
--- ---
9 9
x=1/3
Chip Model
Negative in first number means "opposite of"
+
- = 0
(-3) - 2
- - -
++ (these cancel)
- - =(-5)
Bases
Prime Factorization, GCF, LCM

Fractions
Part-Whole Comparisons with Unitizing:
“3 parts out of 4 equal parts”
Measure:
“3 (1/4 units)”
Operator:
“3/4 of something”
Quotient:
“3 divided by 4”
Ratio:
“3 to 4”
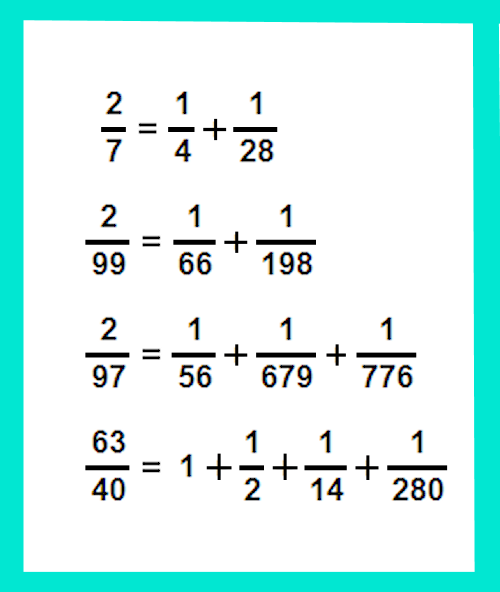
Egyptian Fractions
-Unit fractions meaning 1/n
- breaking larger fractions into smaller parts
Multiplying Fractions
Dividing Fractions
Number line method:
3/4 divided by 2/3
Step 1. Find common denominator
9/12 divided by 8/12
Step 2. Draw numberline for 12/12
0-----------12/12
Step 3. Specify 9/12 which is what you are dividing from
0--------9/12--12/12
Step 4. Make groups of 8 from the 9/12
0-------8/12 9/12--12/12
Step 5. You could fit one whole group and 1/8 of another so your answer is 1 and 1/8
Divisibility Rules
Divisibility rules help you to easily know if a number is divisible by another without having to do all of the long math like usual. Some rules are easy to follow, like 2 and 5, but other can get confusing.
Properties
Addition:
Commutative- the flip of the equation has the same answer
Associative- the numbers can be put into different groups with parenthesis and still equal the same no matter what
Identity- Anything +0 equals itself
Multiplication:
Closed- an integer multiplied by another integer equals an integer
Commutative- the flip of the equation has the same answer
Associative- the numbers can be put into different groups with parenthesis and still equal the same no matter what
Identity- Any number multiplied by one will equal itself
Subtraction:
Subtraction does not have commutative or associative properties. But it could have an identity property by subtracting 0 from the number and getting itself
Properties of Division
- Division does not have commutative or associative properties
- Division have an identity property. If you divide the number by one, it will equal itself
Sets
1-1 Correspondence:
There in one input for every one output
Sequences:
Sequences are just like sets in the way that they are a list of elements, but sequences have to be in order
ex: 1, 2, 3. 4
Venn Diagrams are a way to visually represent sets.

Clock/Modular Arithmetic
We are used to only a 12 hour clock, but when using a 24 hour cloch, it help to know how to use clock arithmetic.
Absolute Value
Means the distance away from zero
-| x | = 2 (none)
-| x | = negative (all integers except 0)
-| x | = positive (none)
-x + 1 = positive (x is less than one)
Sequences
Arithmetic:
Sequences of numbers with a common difference. (+,-)
explicit equation= a sub 1 + (n-1)d with d being the common difference
Geometric:
Has a common ratio. (multplication, division)
explicit equation= r to the (n-1) times a sub 1
